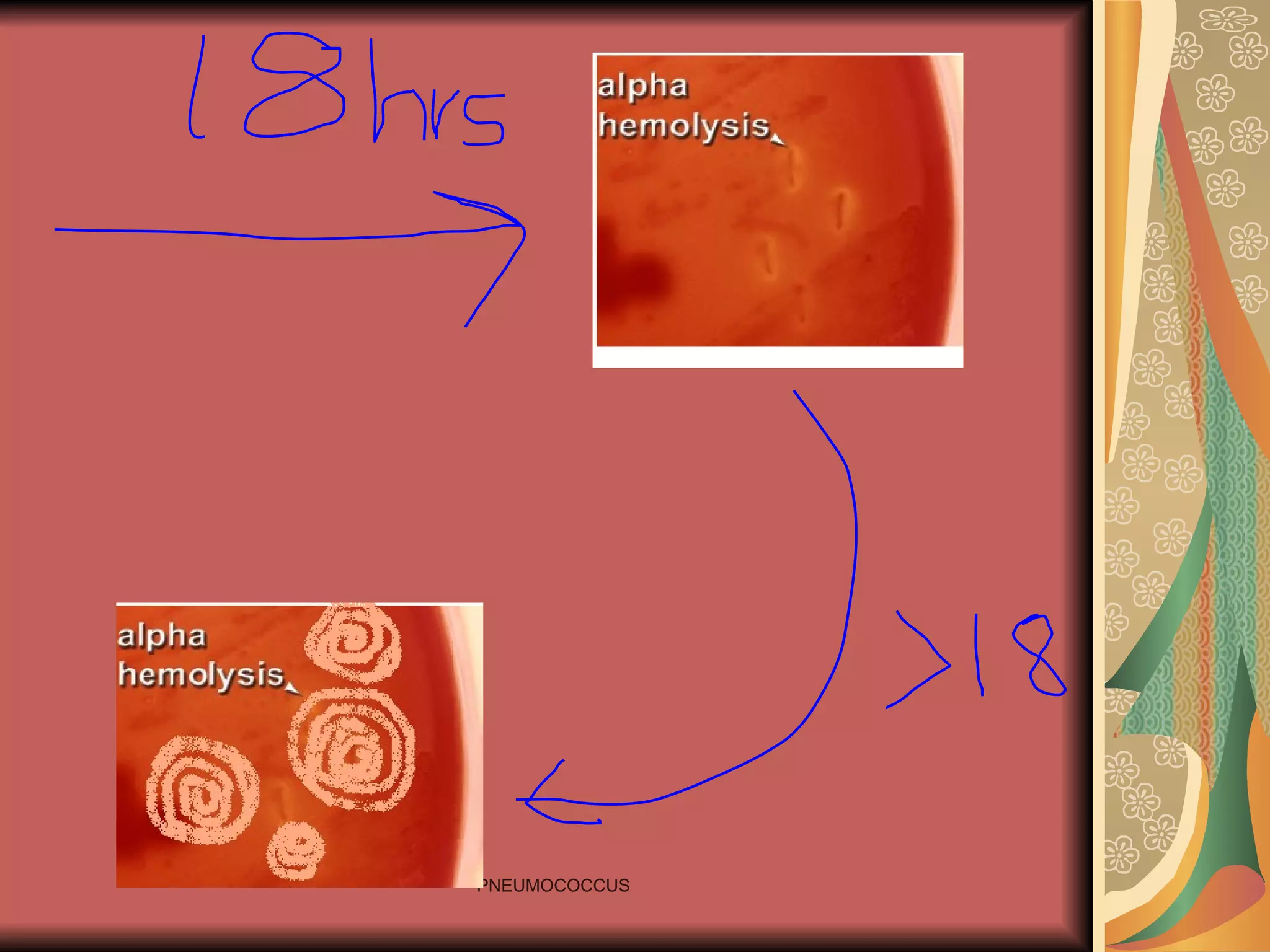
Pneumococcus, also known as Streptococcus pneumoniae, is a Gram-positive bacterium that is a major cause of pneumonia as well as other infections like otitis media, sinusitis, and meningitis. It forms lance-shaped diplococci and is encapsulated, with over 90 known capsular serotypes that determine its antigenic properties and virulence. The capsule allows it to evade phagocytosis by immune cells. Pneumococcal disease is generally acquired through inhalation from respiratory carriers and occurs when host defenses are compromised.