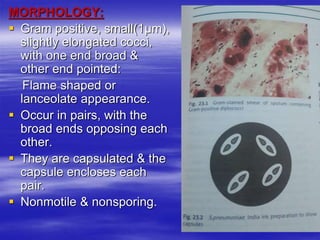
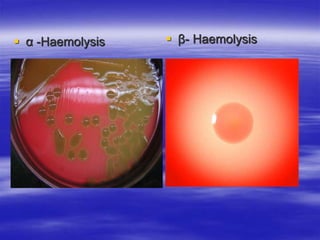
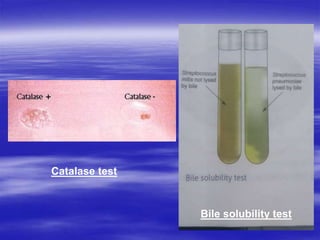
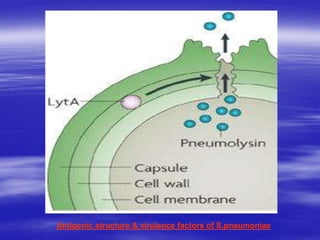
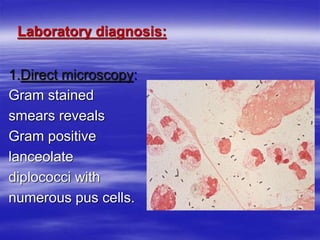
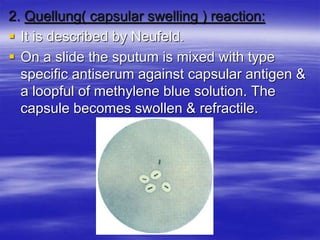
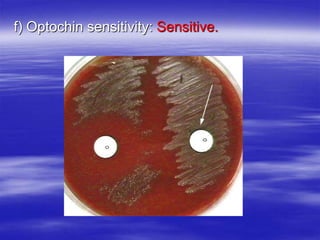
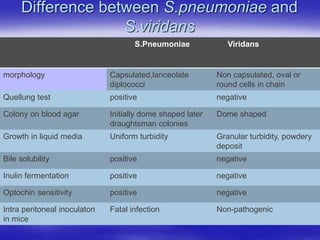
Streptococcus pneumoniae, commonly known as pneumococcus, is a gram-positive bacterium that is a major cause of pneumonia, meningitis, and sepsis. It was first observed in 1881 and its relationship to pneumonia was established in 1886. It is a lancet-shaped diplococcus that appears in pairs and is encapsulated. Pneumococcus can be identified through its morphology, culture characteristics, and reactions like optochin sensitivity and bile solubility. It is a human pathogen that can cause diseases like pneumonia, meningitis, and sepsis. Vaccines like PCV7 for children and PPV23 for adults help prevent pneumococcal infections.