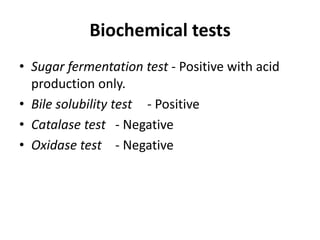
Pneumococcus, or Streptococcus pneumoniae, is a Gram-positive bacterium that can cause pneumonia. It appears in pairs under the microscope (diplococci) and each pair is enclosed in a polysaccharide capsule. It grows best at 37°C in an atmosphere containing carbon dioxide. On blood agar plates it forms alpha-hemolytic colonies. The capsule protects it from phagocytes and allows it to attach to cells in the nasopharynx before migrating to the lungs. This can cause lobar pneumonia in adults and bronchopneumonia in children. Diagnosis involves finding the bacteria in sputum or other samples through microscopy, culture, and serological tests. Treatment involves antibiotics like penicillin and