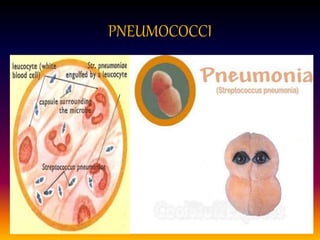
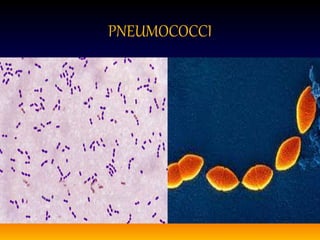
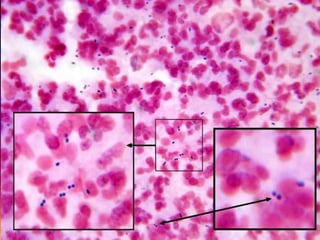
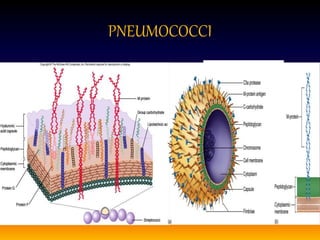
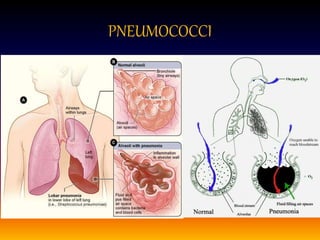
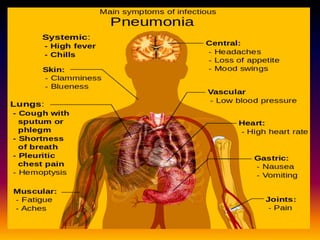
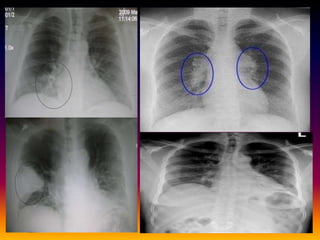
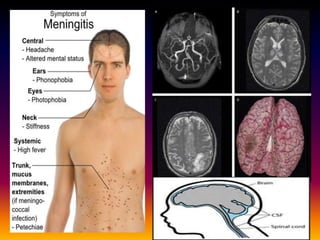
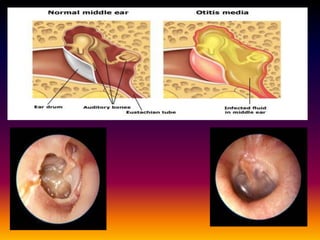
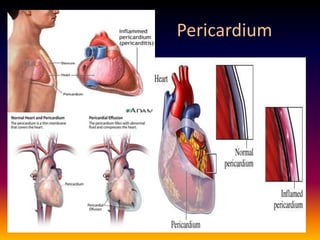
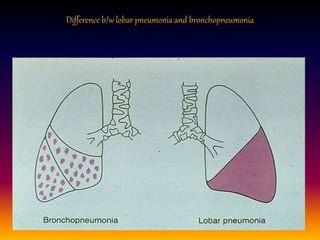
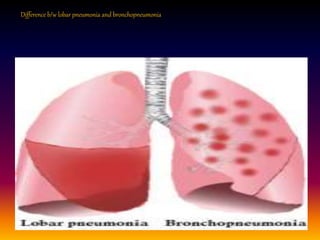
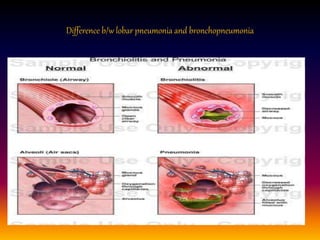
Streptococcus pneumoniae, also known as pneumococcus, is a gram-positive bacterium that can cause pneumonia as well as other infections. It is encapsulated and appears as diplococci or short chains under microscopy. It grows on blood agar and chocolate agar, producing alpha hemolysis. Pneumococcus has over 80 serotypes defined by its capsular polysaccharide. The capsule helps it evade phagocytosis and causes virulence. Pneumococcus commonly causes lobar pneumonia through alveolar exudation and consolidation of portions of the lung. It can also spread through the bloodstream and cause complications like meningitis. Treatment involves penicillin and other antibiotics. Vaccines provide type-specific protection against