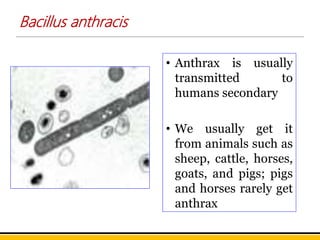
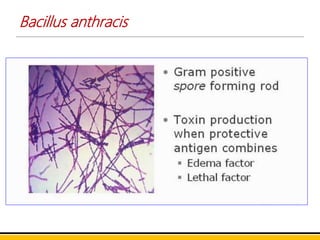
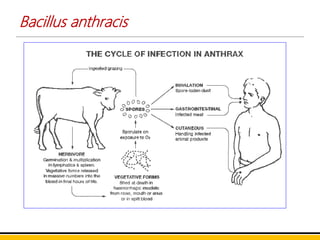
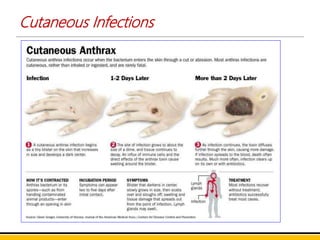
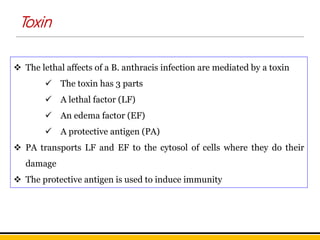
Bacillus anthracis is the bacterium that causes anthrax. It forms spores that allow it to survive in the environment for many years. Anthrax infection can occur through the skin, lungs, or gastrointestinal tract. Cutaneous anthrax is the most common form, resulting in a painless skin lesion. Inhalation anthrax from breathing spores can be fatal without treatment. Symptoms include breathing problems and shock. Gastrointestinal anthrax occurs from eating contaminated meat and causes nausea, vomiting and severe diarrhea. The bacterium produces a toxin that is the main cause of symptoms and death. Vaccines contain a toxoid to induce protective immunity and antibiotics are used to treat infections.