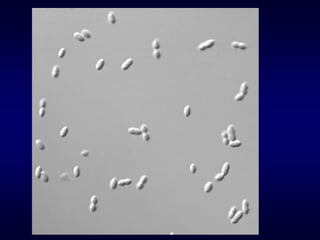
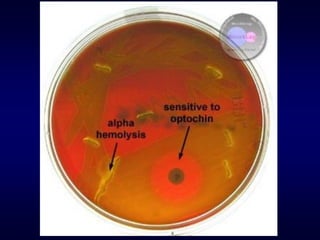
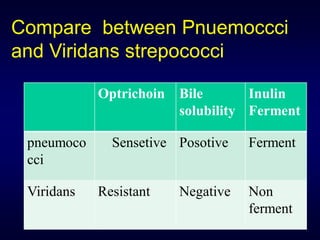
The document provides information about Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococci) and Streptococcus viridans. It describes the typical morphology, culture characteristics, pathogenicity and laboratory identification of these two types of bacteria. S. pneumoniae is a leading cause of community-acquired pneumonia and other infections. It is distinguished from S. viridans by being optochin-sensitive, bile soluble and able to ferment inulin.