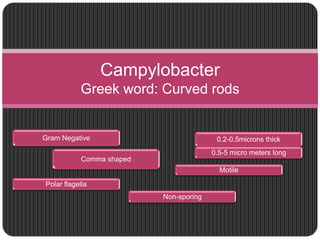
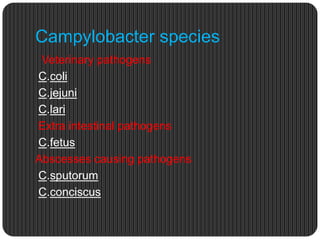
Campylobacter is a genus of gram-negative, microaerophilic, curved rods that are common causes of foodborne illness in humans. The most common pathogenic species that infect humans are Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Campylobacter jejuni is the leading cause of bacterial diarrhea in the developed world. Campylobacter species are commonly found in the intestinal tracts of animals and can be transmitted to humans through contaminated food, water, or direct contact with infected animals. Symptoms in humans typically include diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever within 1-7 days. Diagnosis involves isolating the bacteria from a stool sample and identifying it through microscopy and culture techniques.