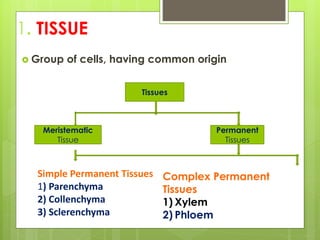
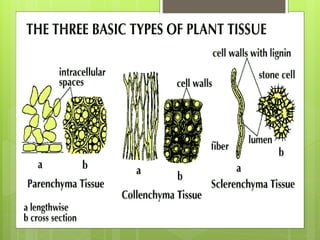
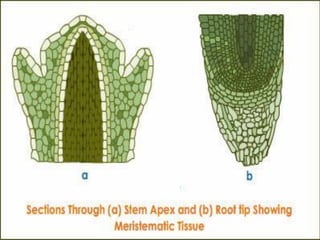
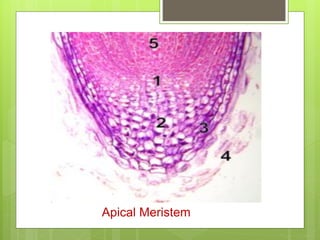
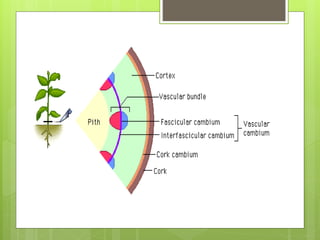
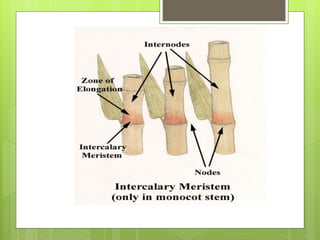
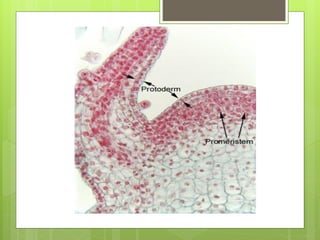
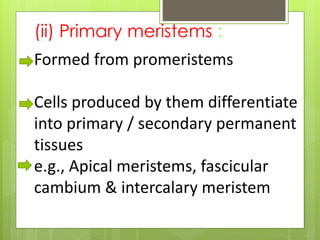
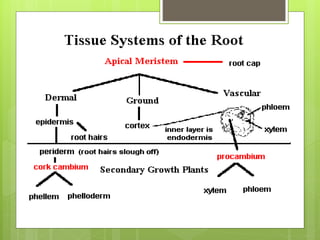
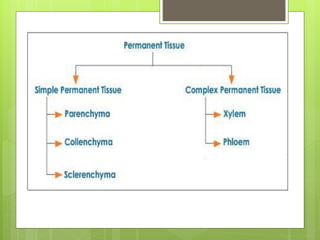
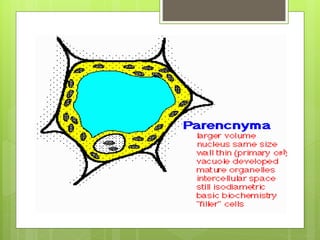
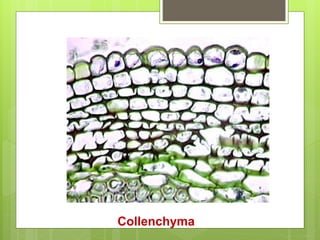
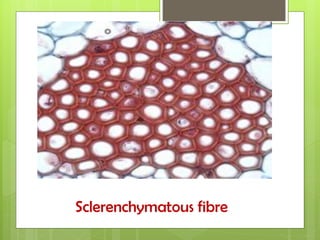
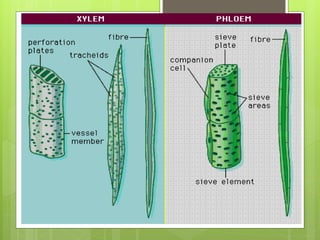
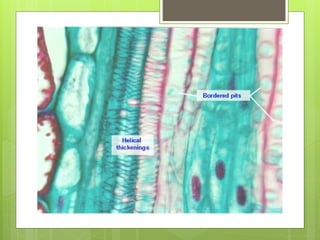
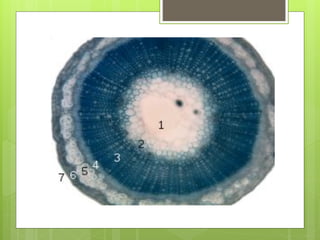
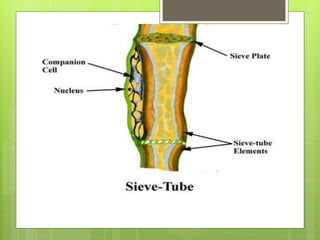
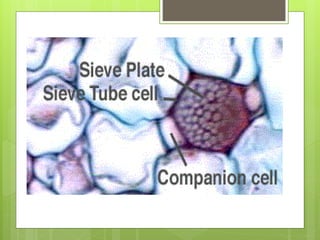
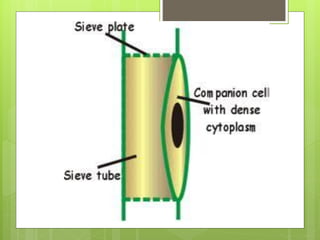
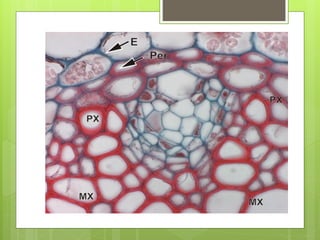
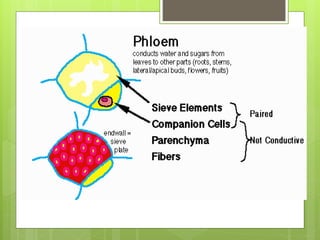
This document provides information about plant tissues, including meristematic and permanent tissues. It discusses the characteristics and classifications of meristematic tissue, including apical, lateral, and intercalary meristems. Simple permanent tissues are described as parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma. Complex permanent tissues include xylem, which transports water and minerals, and phloem, which transports organic substances. Xylem elements are described as vessels, tracheids, parenchyma, and fibers. Phloem elements include sieve tubes, sieve cells, companion cells, parenchyma, and fibers.