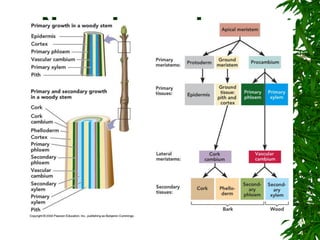
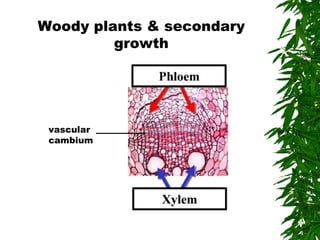
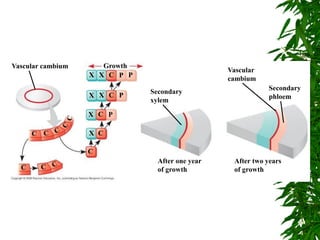
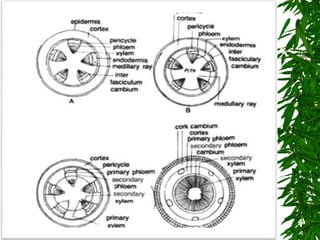
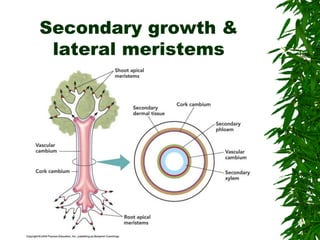
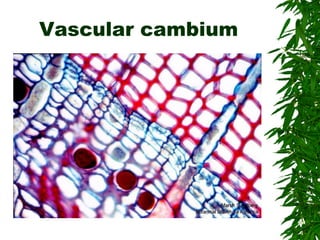
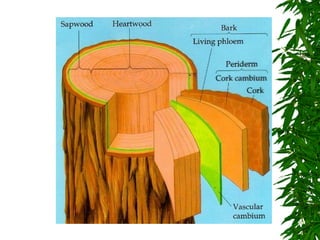
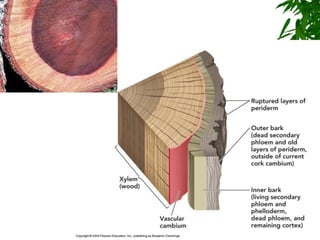
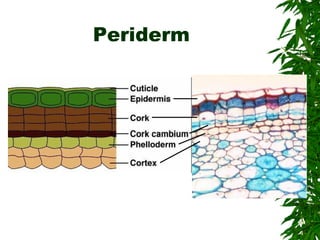
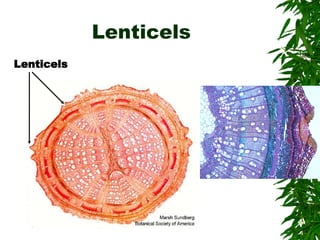
1. Secondary growth in dicot stems occurs through the activity of vascular cambium, which forms as strips between and around vascular bundles and joins to form a continuous cambium ring.
2. The cambium undergoes cell division, with cells on the outer side forming secondary phloem and cells on the inner side forming secondary xylem.
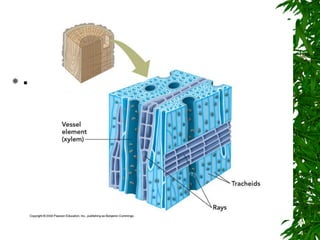
3. Secondary xylem consists of tracheids, vessels, fibers, and wood parenchyma that make up the vertical and radial systems, while secondary phloem consists of sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma, and phloem fibers.