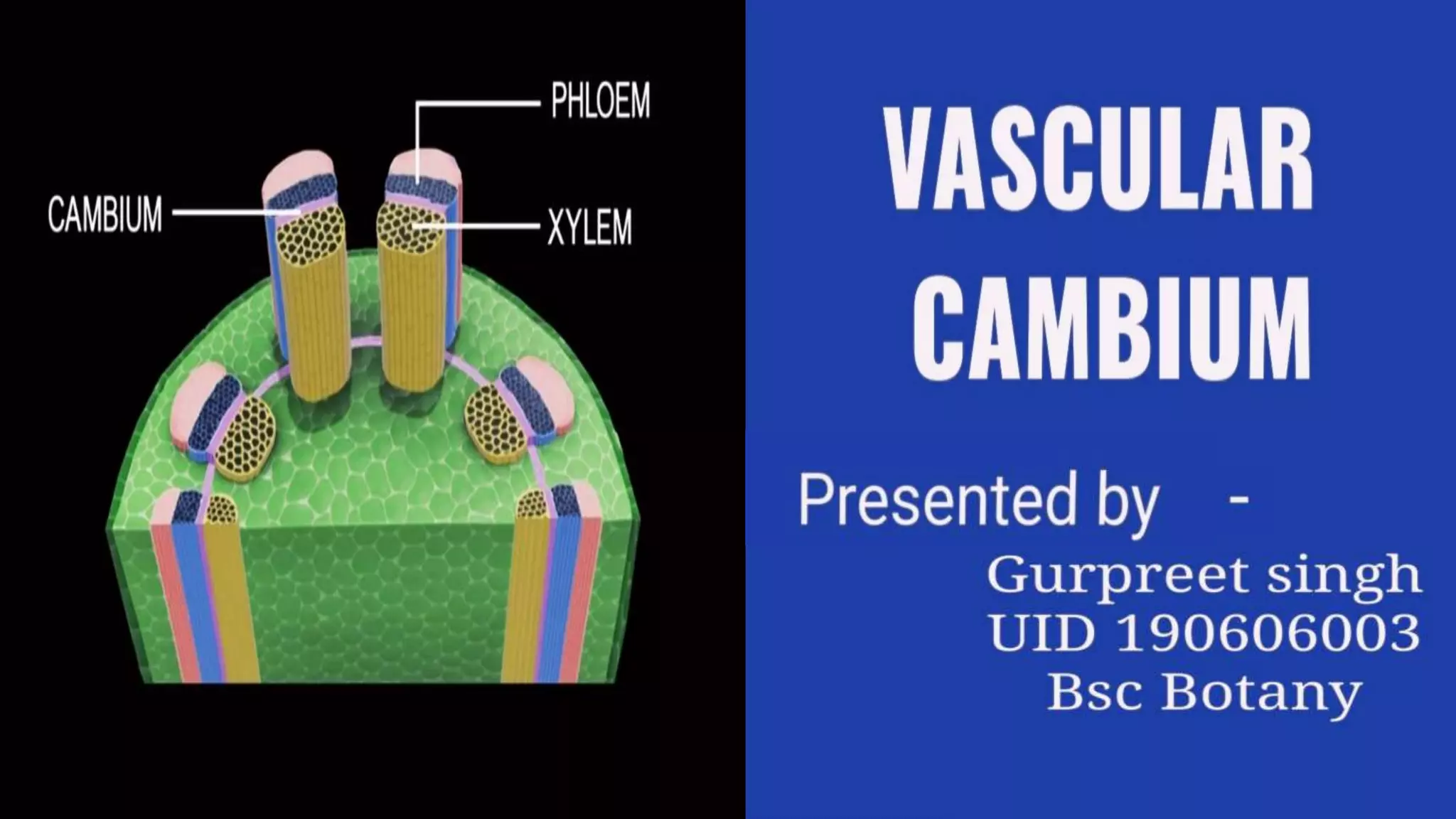
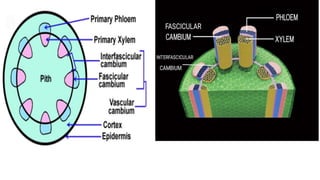
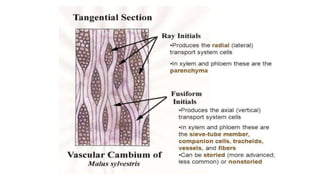
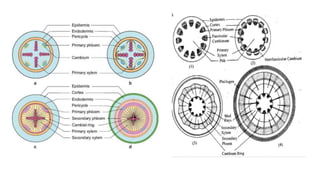
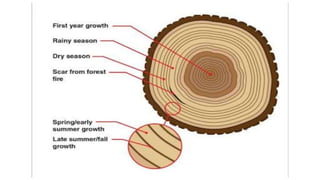
The vascular cambium is a lateral meristem that increases the diameter of stems and roots through secondary growth. It is composed of fusiform initials that divide to form vertical tissues and ray initials that form horizontal tissues. In dicots, intrafascicular cambium initially develops within vascular bundles and interfascicular cambium develops between bundles, eventually joining to form a complete cambial ring. The cambium divides to produce secondary xylem internally and secondary phloem externally. Its seasonal activity varies the structure of the tissues produced.