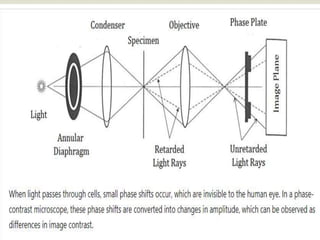
Phase-contrast microscopy is a technique that converts phase shifts in light passing through a transparent specimen to brightness changes in the image, allowing living cells that are otherwise invisible to be seen. It works by separating light rays that pass through a specimen unchanged from those that are diffracted, using an annular diaphragm and phase plate in the light path. Phase-contrast microscopy is widely used in biological research for observing living cells, microorganisms, and other transparent specimens without staining or fixing.