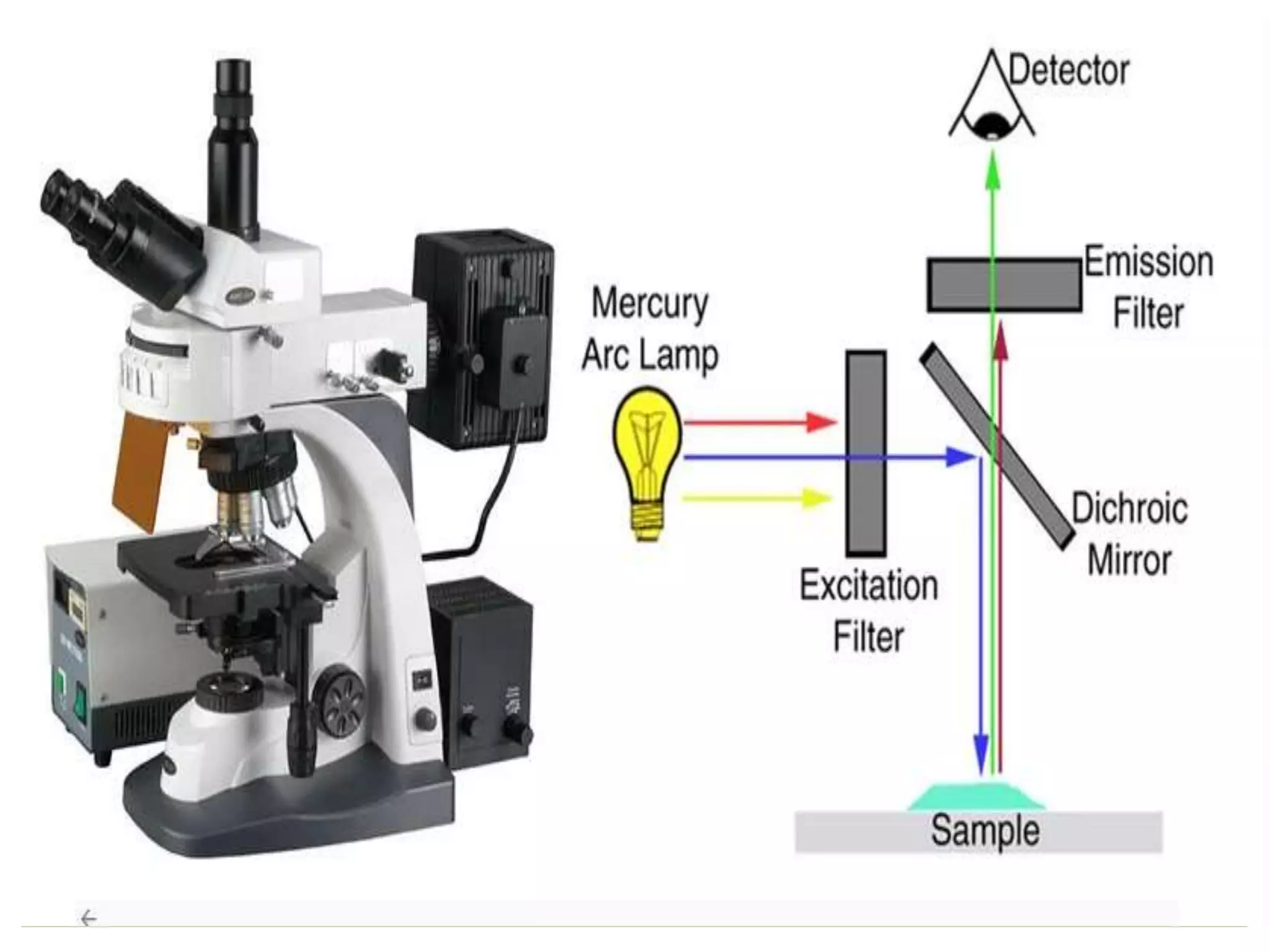
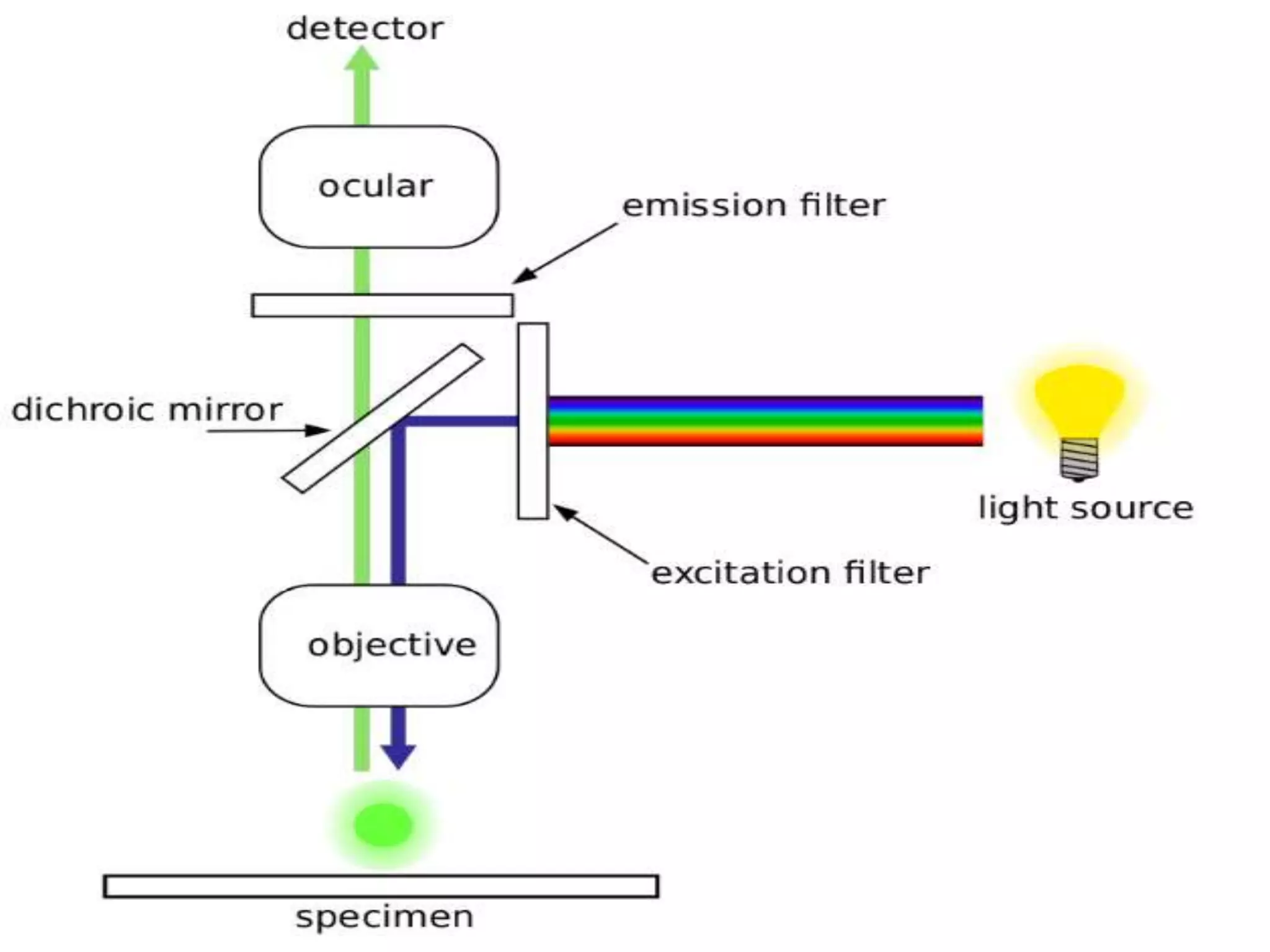
The document discusses fluorescence microscopy. It describes how fluorescence microscopy uses fluorescent dyes and fluorophores to stain cellular components and structures, which are then excited by light and emit light of a longer wavelength, allowing their visualization. The key parts of a fluorescence microscope are described, including the light source, excitation and emission filters, and dichroic mirror. Applications include identifying structures in fixed and live samples, and advantages are its ability to specifically label proteins and track multiple molecules simultaneously.