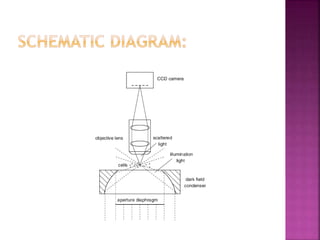
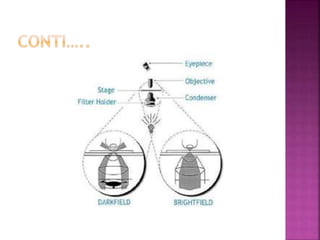
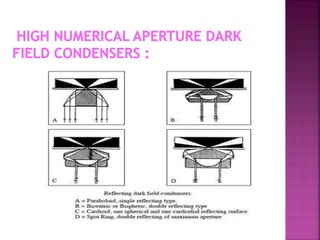
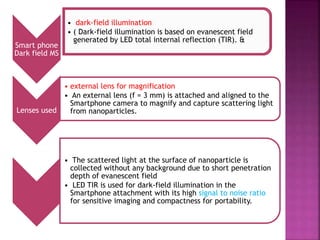
This document discusses dark field microscopy. It begins by defining dark field microscopy as a technique that produces bright objects against a dark background without using stains. This is achieved through a condenser that blocks light from entering the objective lens directly, allowing only light scattered from the specimen to pass through. Applications of dark field microscopy include viewing unstained samples like microorganisms, cells, and fibers. Advantages are its ability to examine transparent specimens, while disadvantages include sensitivity to dust or bubbles. Recent developments include using smartphone microscopy with LEDs for portable dark field imaging of nanoparticles.