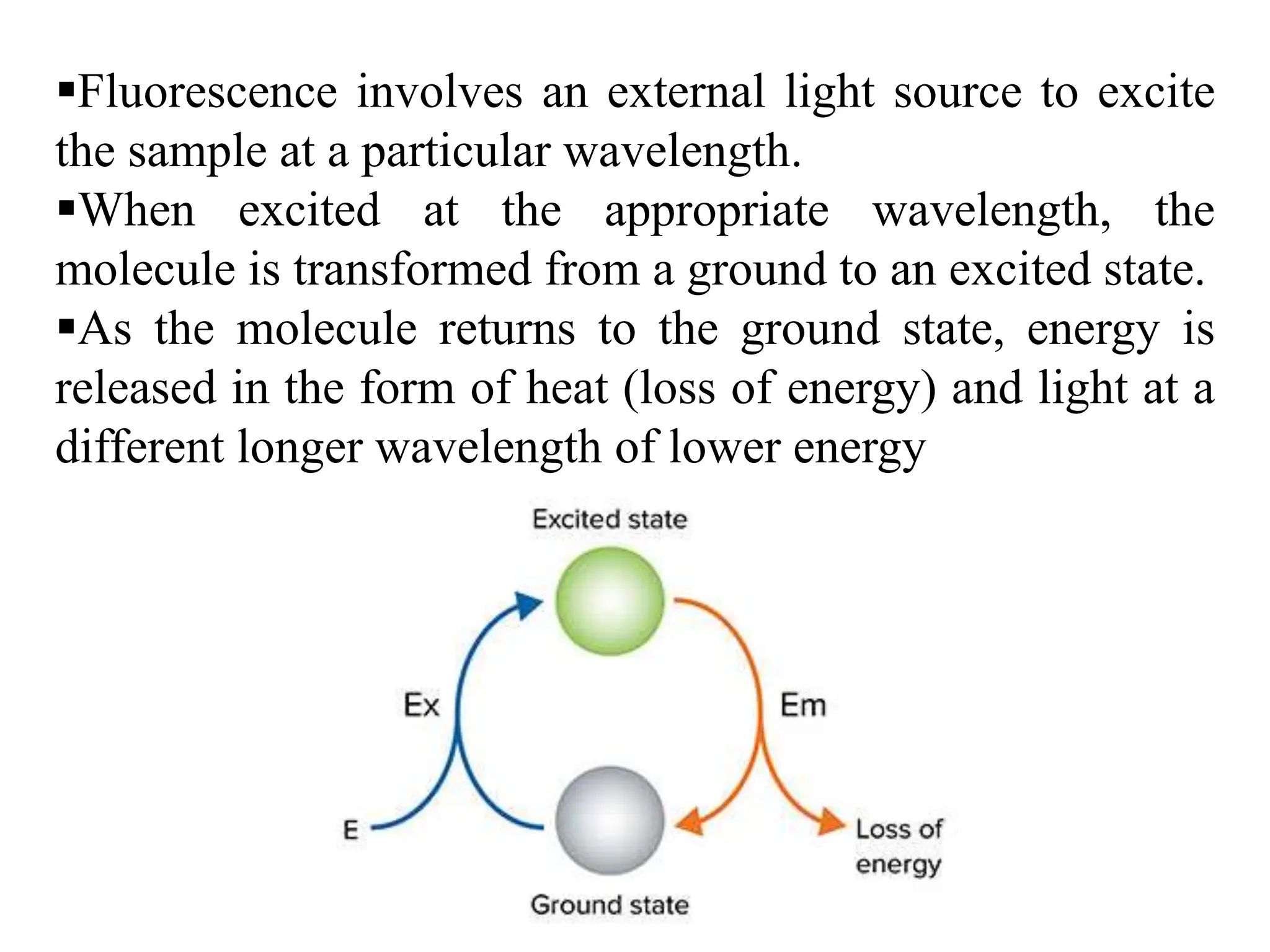
The document describes fluorescence and phase contrast microscopy. Fluorescence microscopy uses fluorescent dyes and an external light source to excite samples, causing them to emit light of a longer wavelength. This technique allows visualization of cellular components. A fluorescence microscope contains a light source, excitation and emission filters, and detector. Phase contrast microscopy converts phase shifts in light passing through transparent samples to brightness changes, making highly transparent objects more visible without staining. It works using a phase annulus and plate to shift light rays passing through samples.