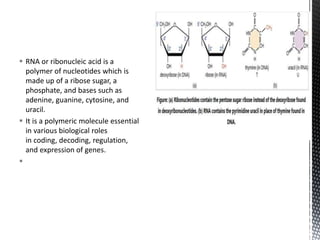
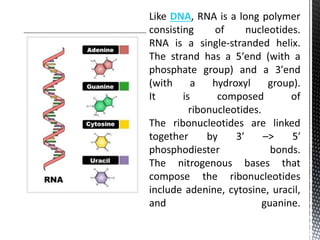
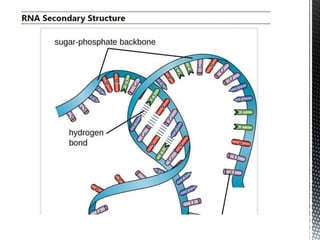
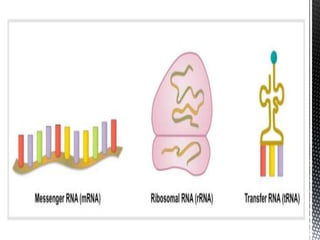
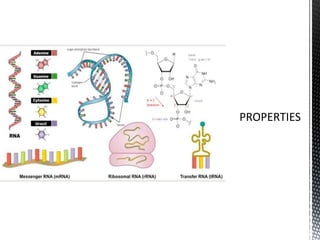
This document discusses the key differences between RNA and DNA. It notes that RNA contains ribose sugar rather than deoxyribose, contains uracil rather than thymine, and is typically single-stranded. It describes the three main types of RNA - rRNA, tRNA, and mRNA - and their functions in protein synthesis, with rRNA in ribosomes, tRNA transferring amino acids, and mRNA carrying DNA's genetic code to the cytoplasm. The document provides details on the structure and role of each RNA type.