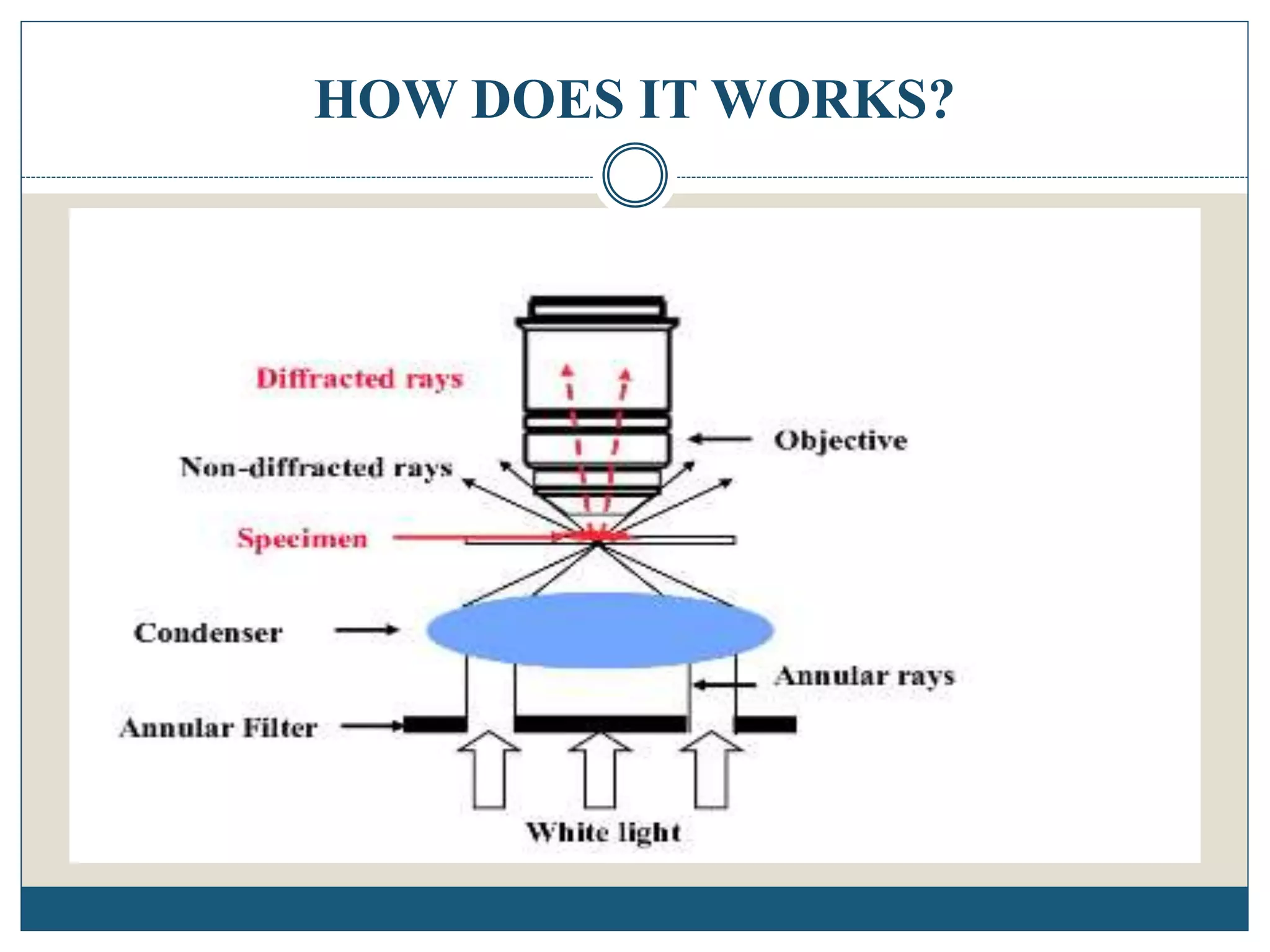
Dark-field microscopy is a technique used to illuminate unstained samples, causing them to appear brightly lit against a dark background, utilizing a special condenser that forms a hollow cone of light. It offers better resolution and contrast than bright-field microscopy without the need for staining, making it suitable for observing live bacteria and other small organisms. However, it has limitations such as the need for strong illumination, potential damage to samples, and challenges with sample density affecting image quality.