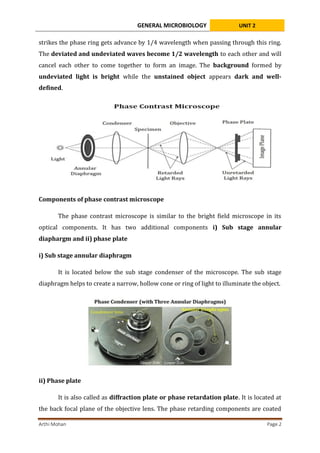
The phase contrast microscope allows viewing of unstained living cells by converting small phase changes in light passing through specimens into visible brightness differences. It uses an annular diaphragm to produce a hollow cone of illumination and a phase plate to shift the phase of undeviated light rays relative to deviated rays. This shifts the waves 1/2 wavelength out of phase, resulting in interference that produces image contrast between structures of different refractive indices in unstained specimens. The phase contrast microscope enabled important advances by allowing observation of live cellular processes without chemical staining or fixation.