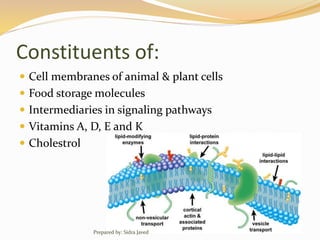
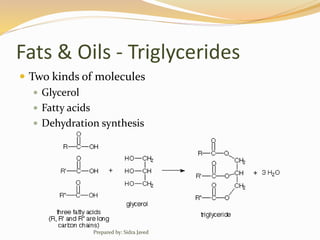
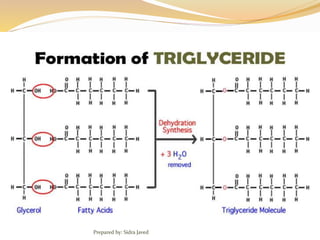
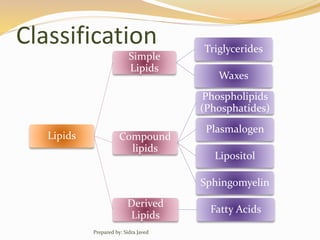
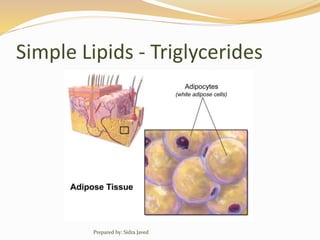
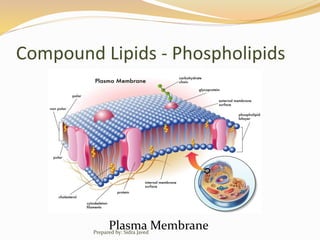
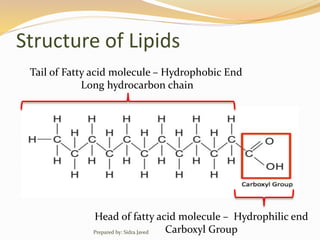
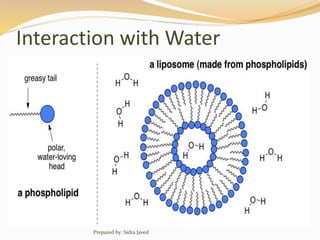
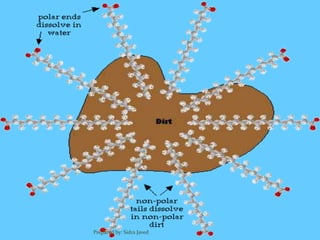
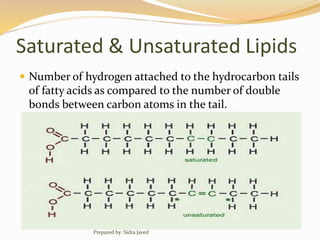
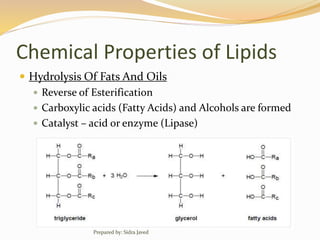
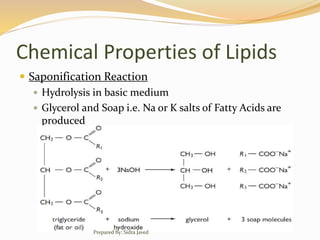
Lipids are naturally occurring organic compounds that are soluble in organic solvents but insoluble in water. They include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. Lipids are classified as simple lipids like triglycerides and waxes, or compound lipids like phospholipids. The main roles of lipids include serving as energy stores, components of cell membranes, and intermediaries in signaling pathways. Essential lipids like omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids must be obtained through diet as the body cannot produce them. Lipids are important for many biological functions including energy storage, cell membrane structure, hormone synthesis, and brain and vision health.