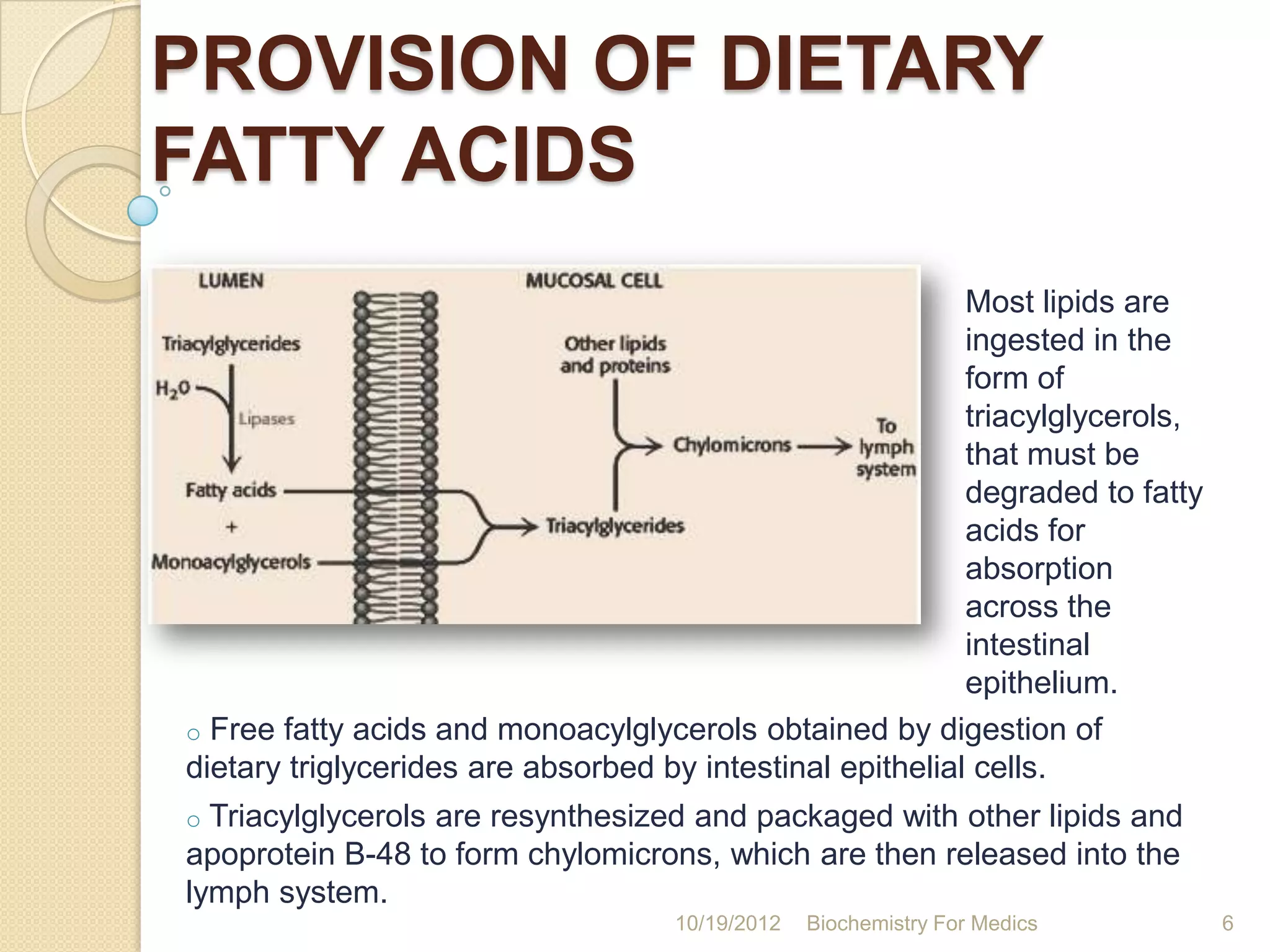
1) Fatty acids are oxidized through beta-oxidation in the mitochondria to generate acetyl-CoA units and energy in the form of ATP.
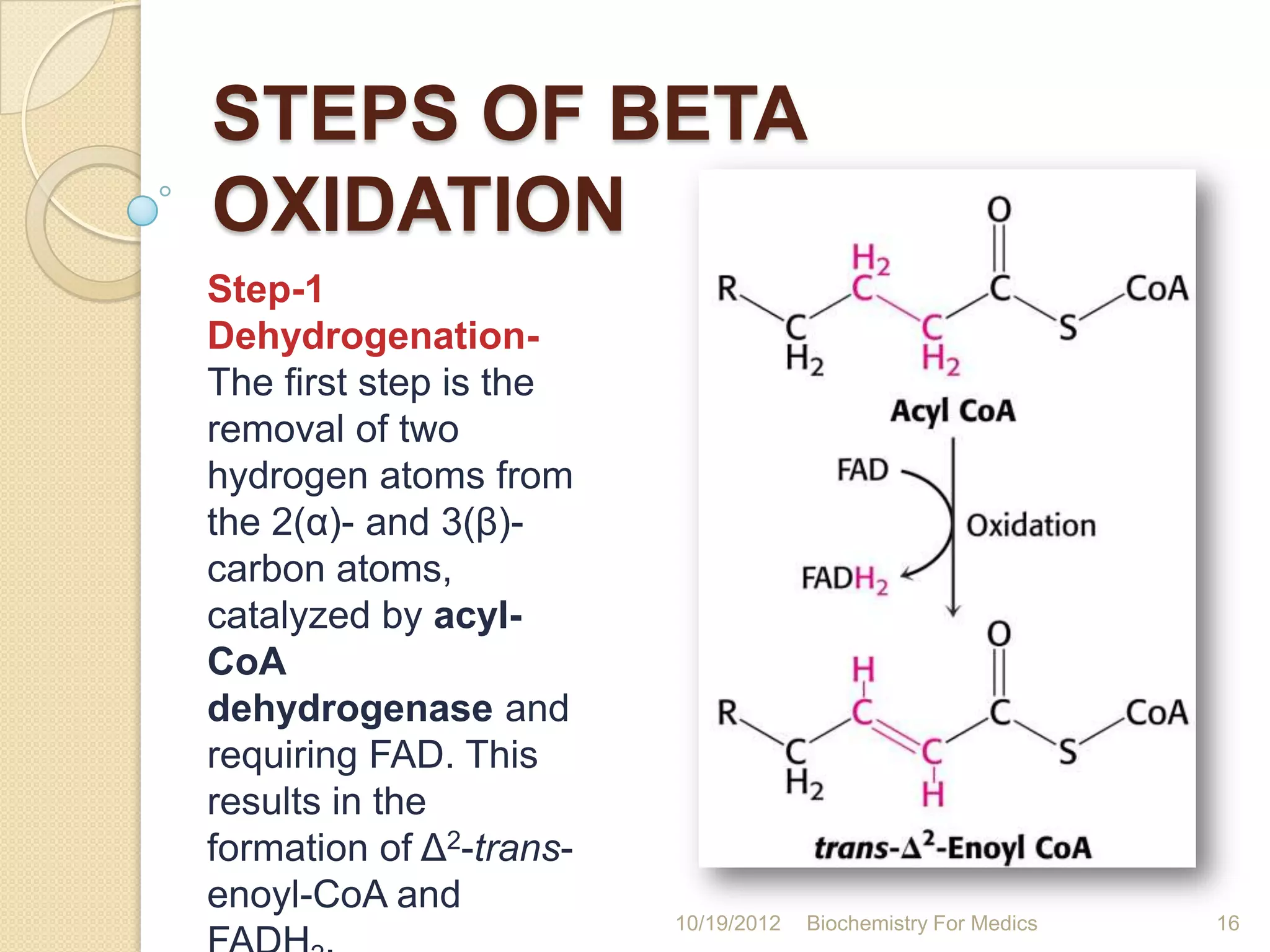
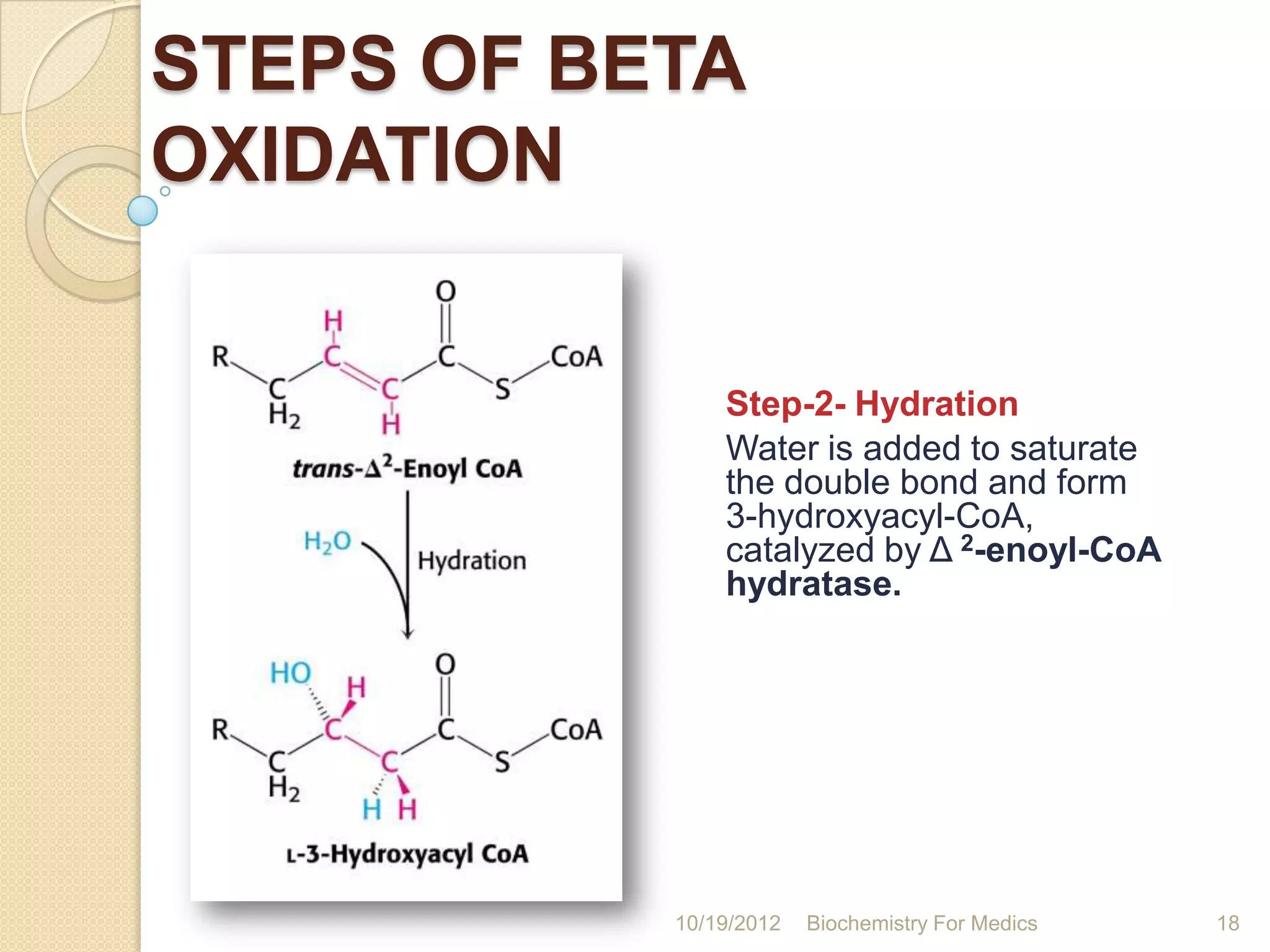
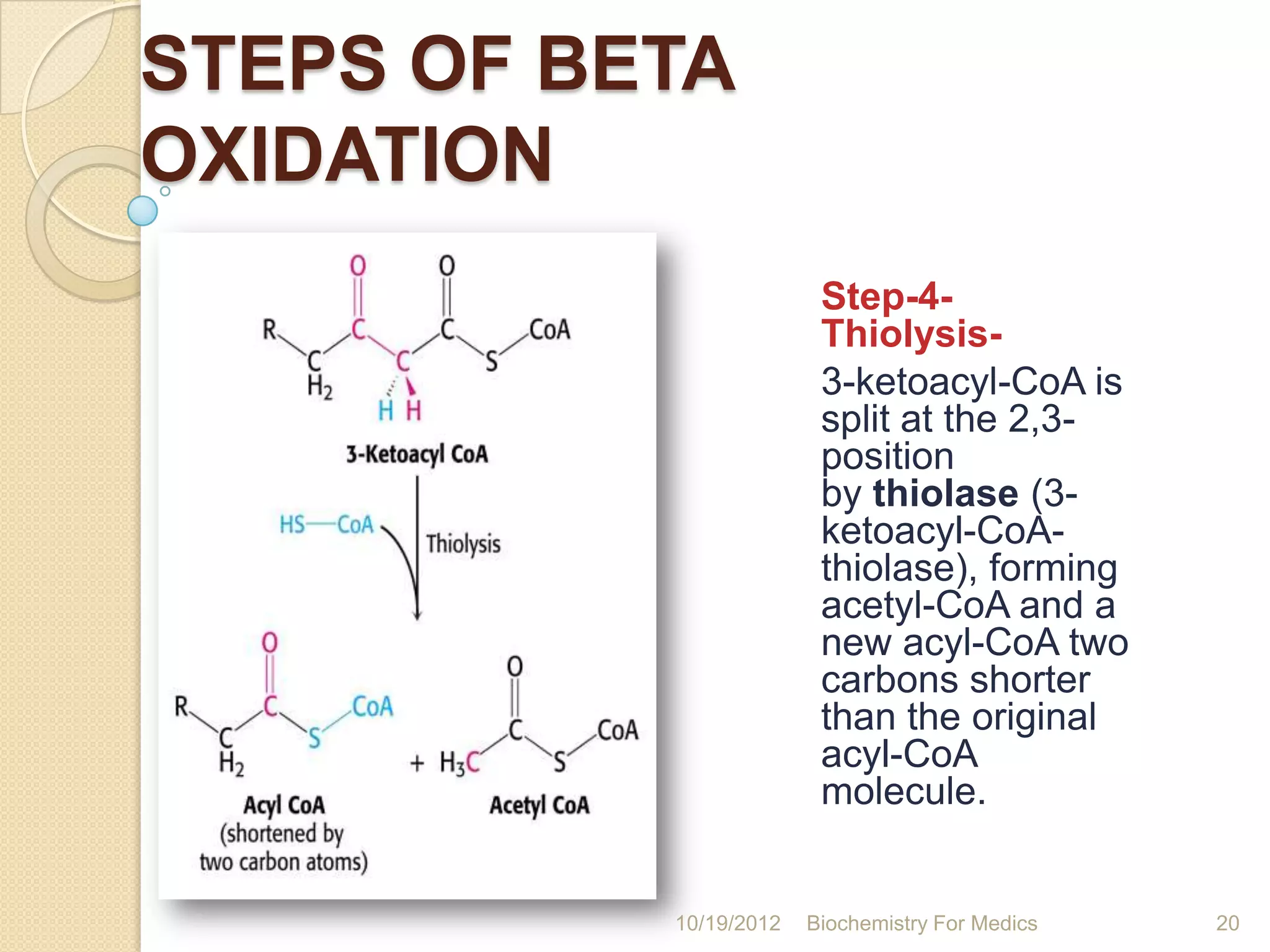
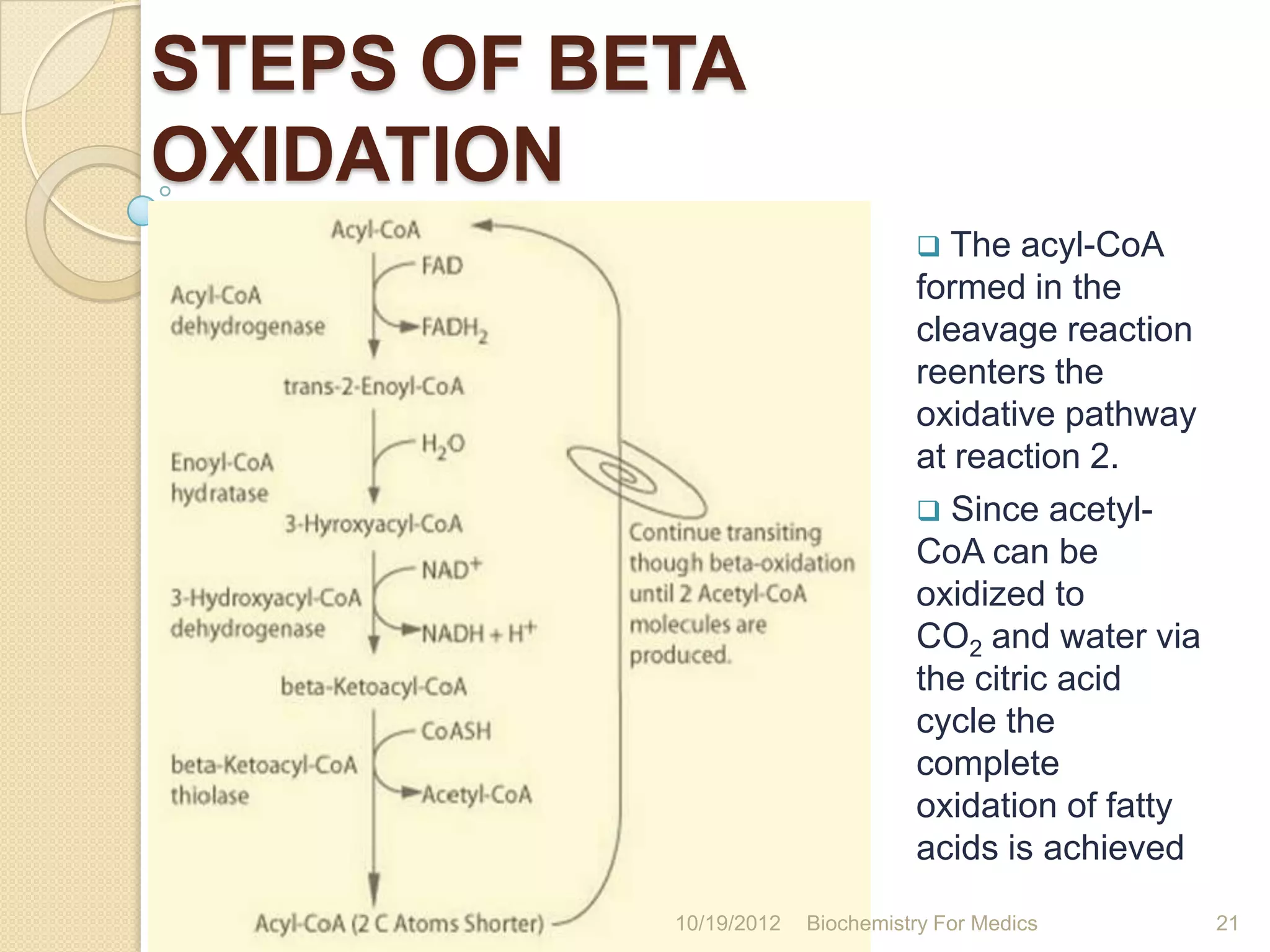
2) Beta-oxidation involves four steps - dehydrogenation, hydration, dehydrogenation, and thiolysis - that occur in a recurring cycle to shorten the fatty acid by two carbons each time.
3) Fatty acid oxidation provides the major source of energy during periods of fasting or low carbohydrate availability and yields substantial ATP through the electron transport chain.