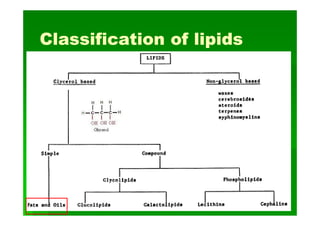
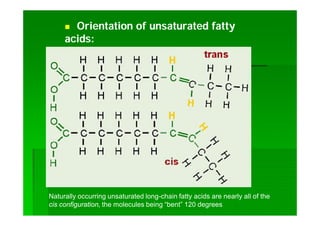
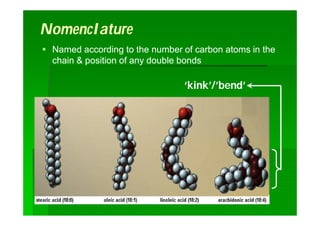
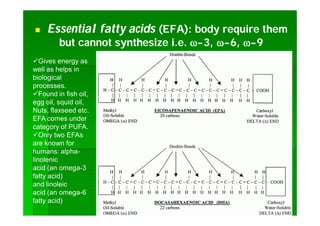
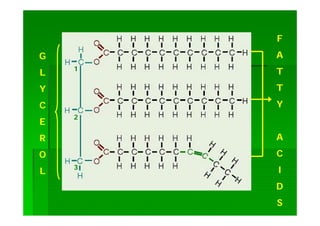
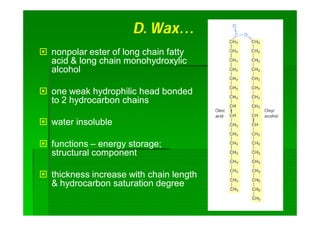
Lipids are biomolecules that are not soluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. They are formed through condensation reactions between fatty acids and alcohols. The main types of lipids include fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, waxes, fats and oils, and steroids. Lipids serve important structural and energy storage functions in organisms. They are the main components of biological membranes and are stored as triglycerides in adipose tissue to be used as an energy source when needed.