Embed presentation




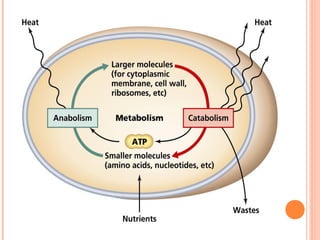
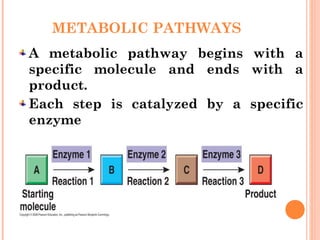
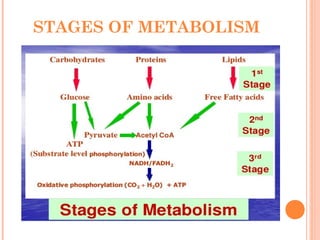
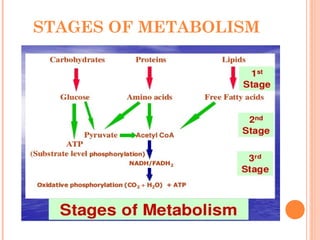
The document introduces metabolism as the sum of all chemical reactions within an organism that allows it to grow and maintain itself, and describes the two main types as catabolism which breaks down complex molecules to release energy and anabolism which uses that released energy to synthesize complex molecules from simpler precursors. Metabolic pathways involve a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions that transform a starting molecule into a product, and metabolism occurs through stages of breaking down molecules, activating precursors, and assembling complex structures.









