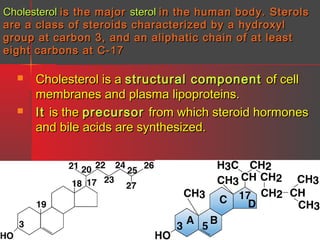
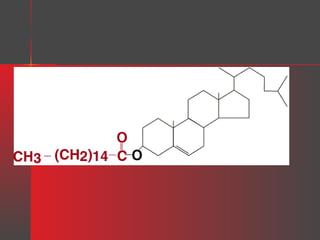
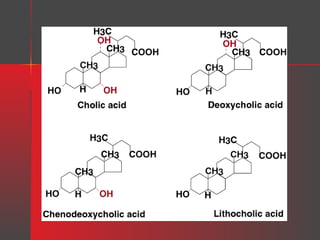
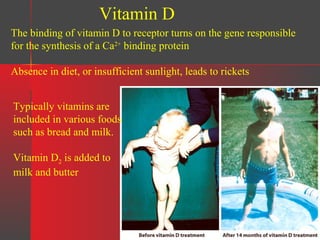
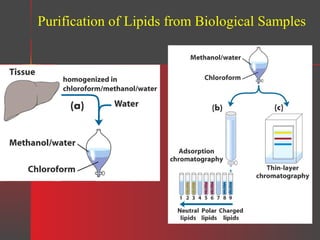
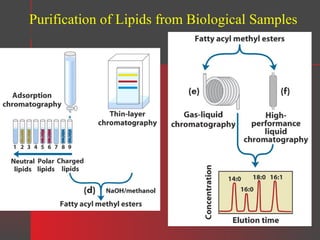
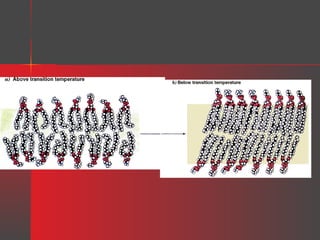
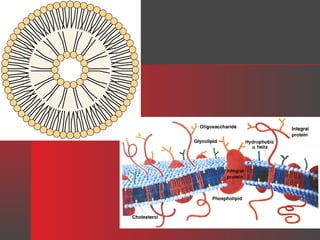
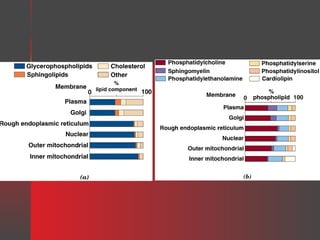
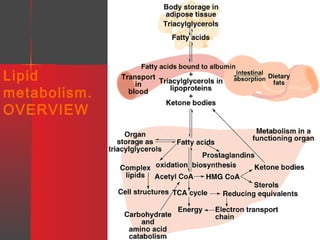
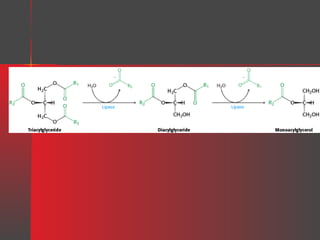
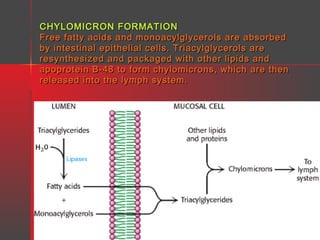
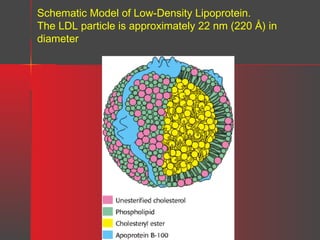
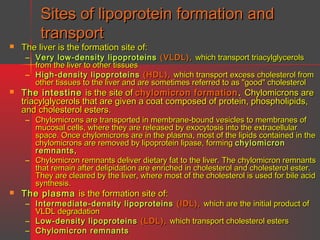
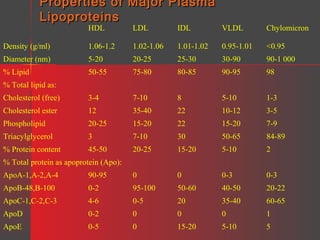
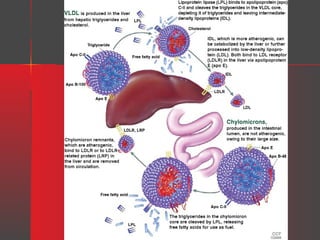
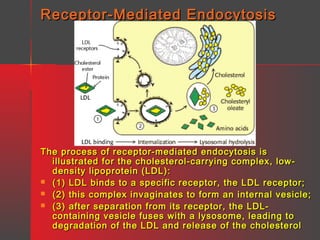
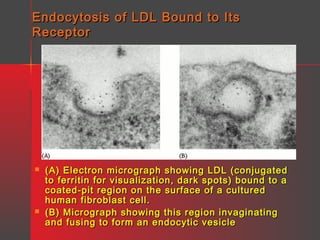
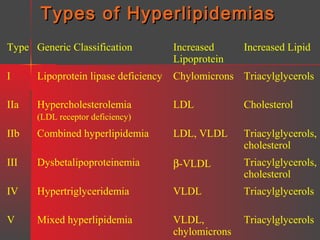
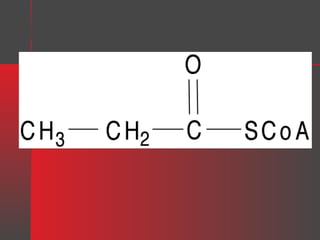
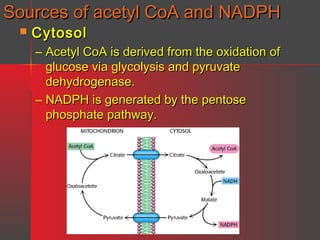
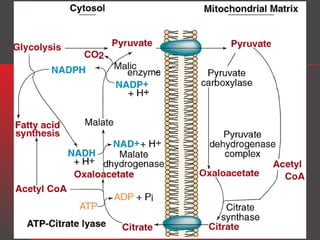
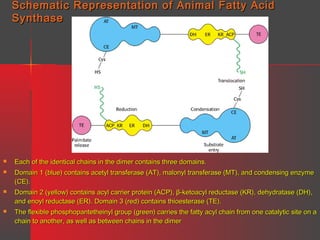
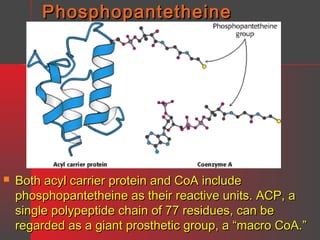
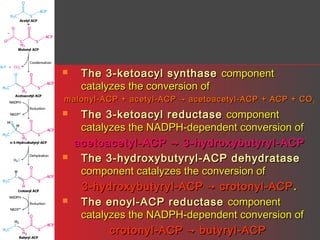
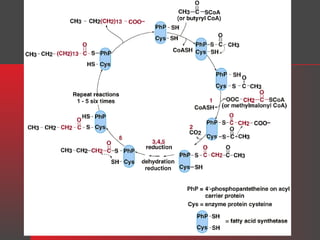
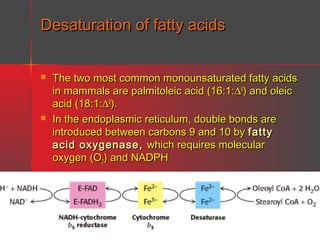
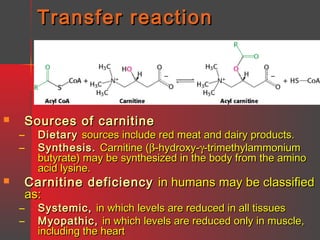
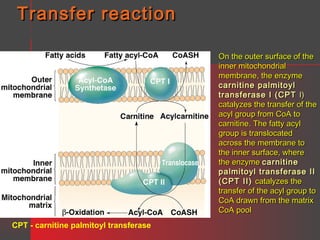
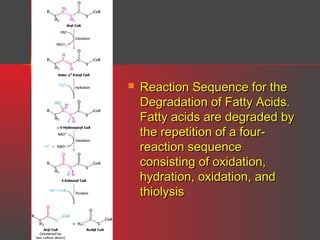
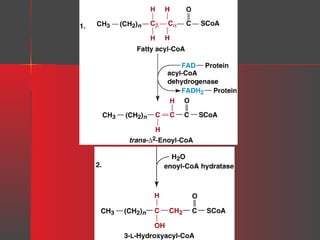
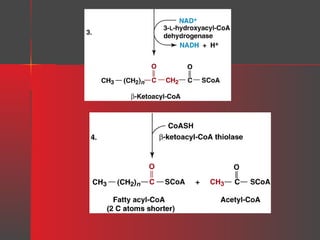
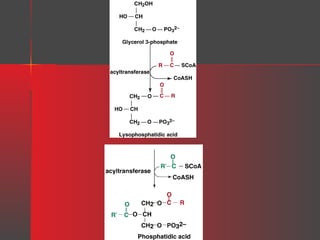
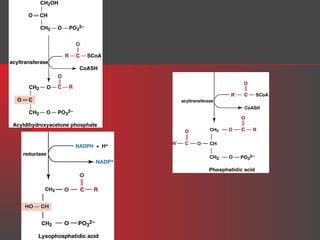
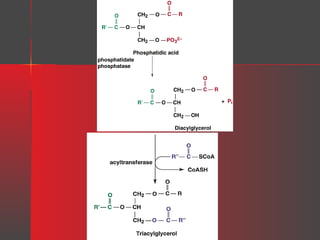
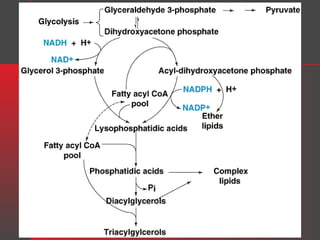
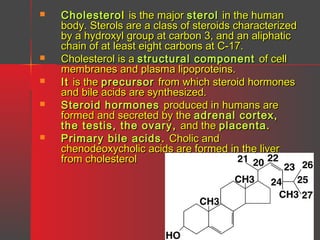
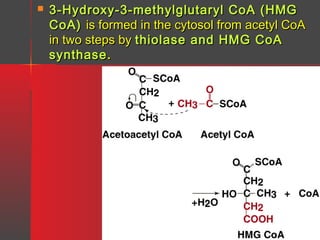
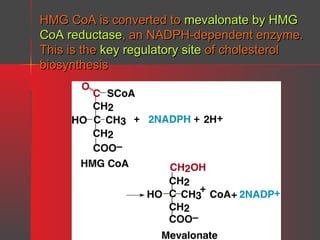
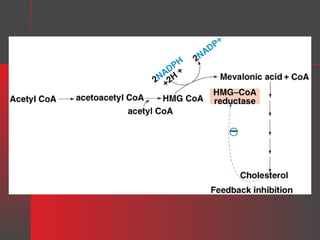
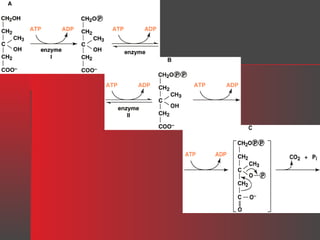
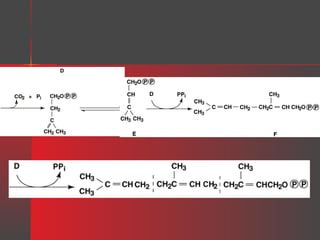
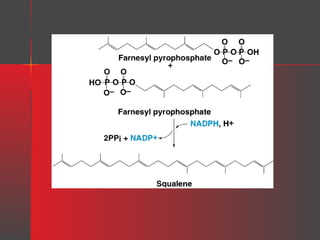
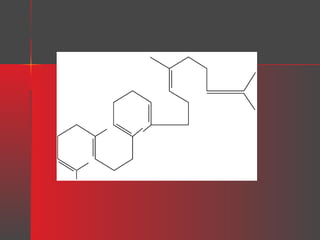
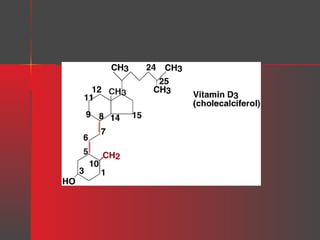
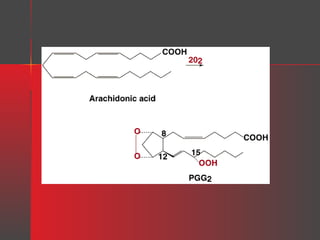
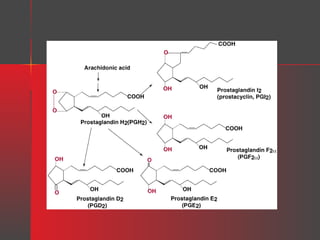
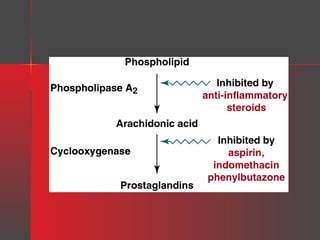
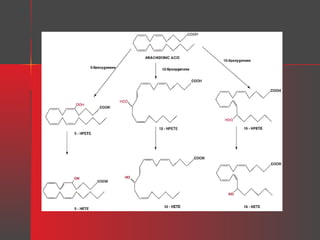
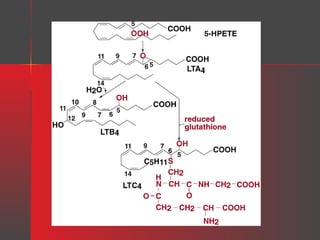
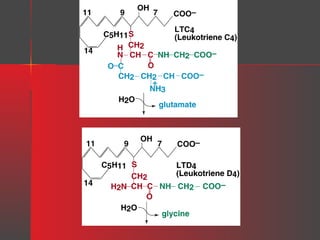
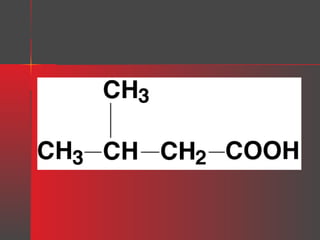
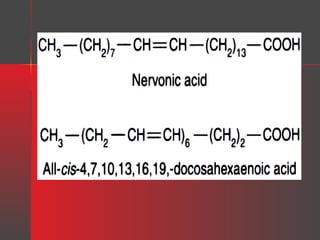
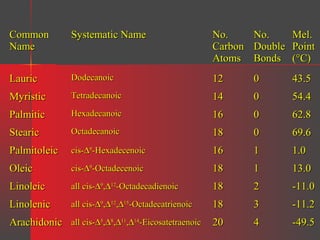
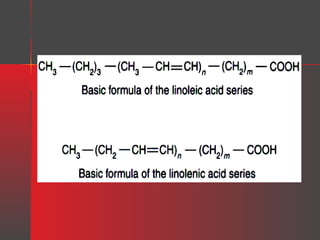
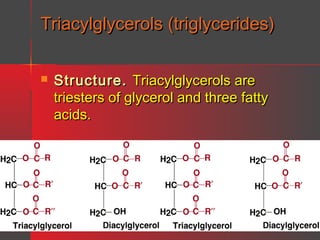
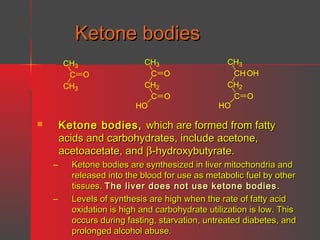
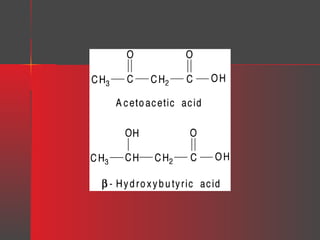
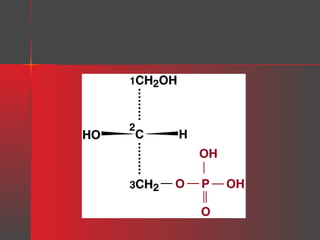
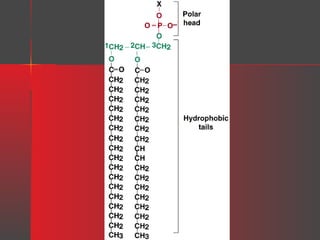
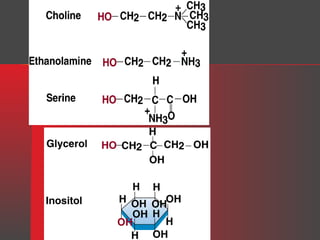
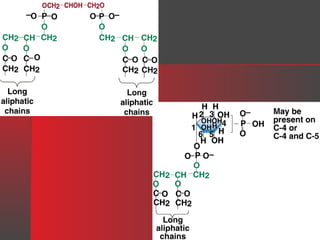
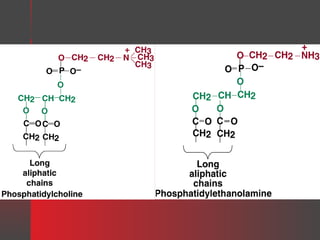
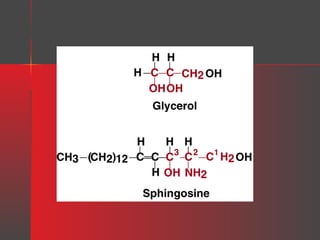
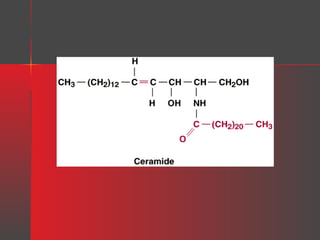
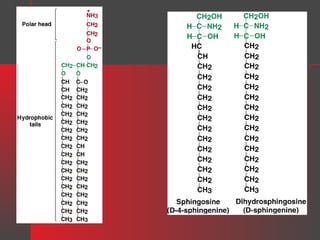
Lipids have a hydrophobic nature due to hydrocarbon chains. They are insoluble in water but soluble in nonpolar solvents. Major lipids include fatty acids, triacylglycerols, phospholipids, cholesterol, and steroid hormones. Fatty acids are used for energy storage and membrane components. Triacylglycerols store fatty acids as an energy source. Phospholipids are major membrane components. Cholesterol is important for membrane structure and steroid hormone synthesis. Lipids are digested into fatty acids and monoacylglycerols then absorbed into intestinal cells to form chylomicrons which transport lipids through lymph and blood.
















![Gangliosides
Nature
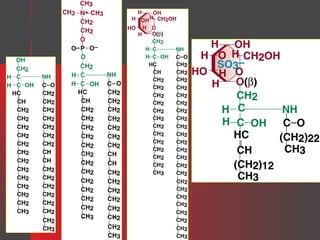
Gangliosides are glycosphingolipids that contain one or more
neuraminic acid residues, usually as the N-acetyl derivative [i.e., Nacetylneuraminic acid (NANA)], which is sialic acid. They are
found in high concentration in ganglion cells of the CNS and in lower
concentration in the membranes of most cells.
Nomenclature
The letter G is used to denote a ganglioside, with M, D, T, or Q to
indicate, respectively, mono-, di-, tri-, or quatrosialic acid contents.
Numerical subscripts are based on their chromatographic migration.
For example:
–
–
–
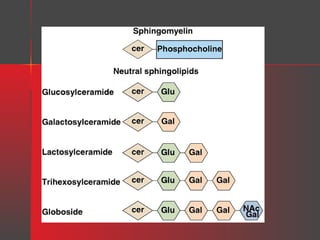
GM1 = Gal-(N-AcGal)-Gal-Glc-Cer
GM2 = (N-AcGal)-Gal-Glc-Cer
GM3 = Gal-Glc-Cer
where Cer = ceramide, Glc = glucose, Gal = galactose, and N-AcGal = Nacetylgalactosamine.
(N-AcGal)-Gal-Glc-Cer
For example, the GM2 ganglioside is:
NANA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lipids-131127064146-phpapp02/85/Lipids-35-320.jpg)