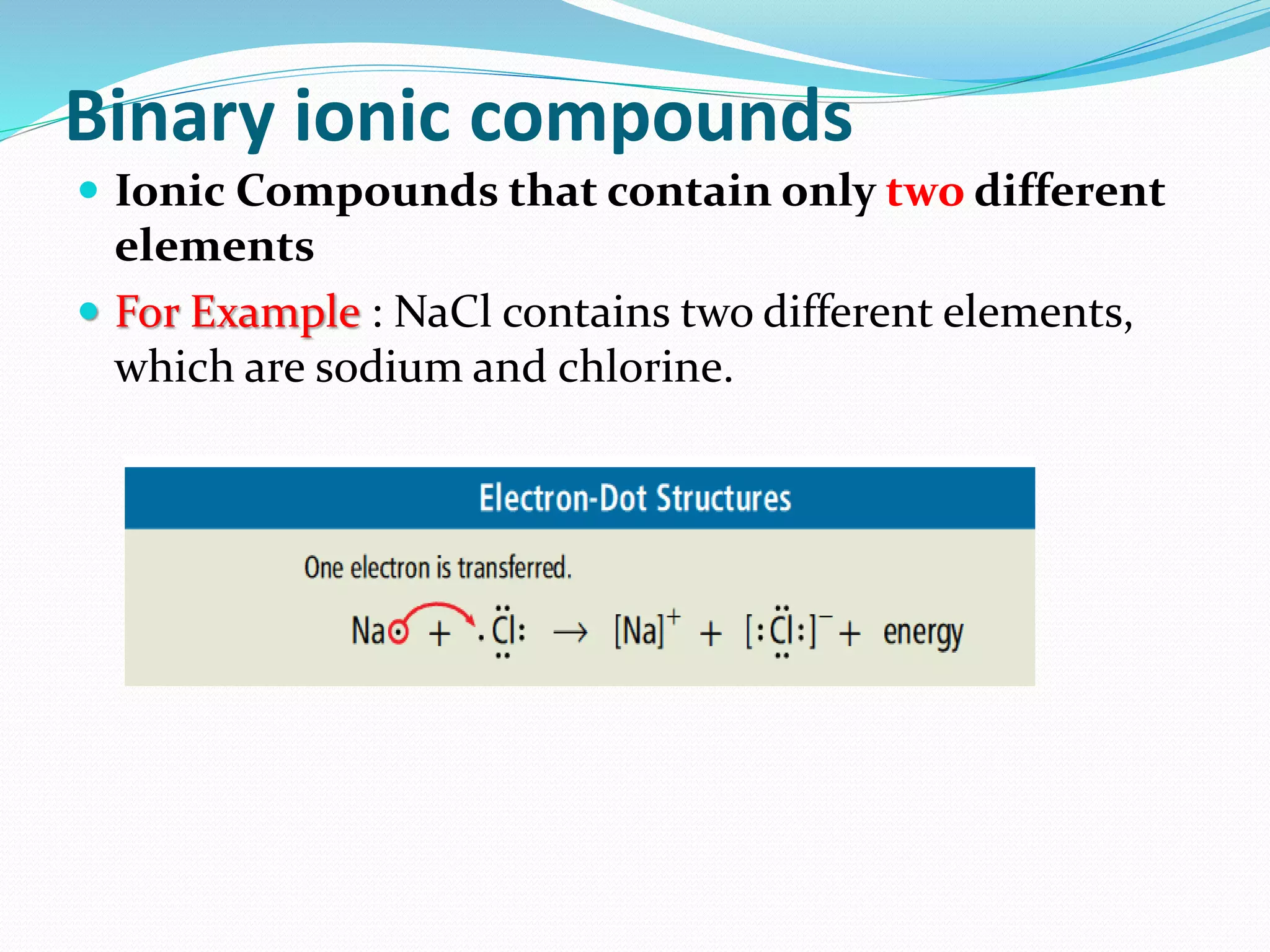
This document describes the formation and properties of ionic compounds. Ionic bonds form when oppositely charged ions attract each other to form electrically neutral compounds. Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points because the ionic bonds between ions require a large amount of energy to overcome. The ions are tightly packed in a crystal lattice structure. Physical properties like conductivity depend on whether the ions are free to move or locked in place. Smaller or more highly charged ions result in stronger ionic bonds and higher lattice energies.