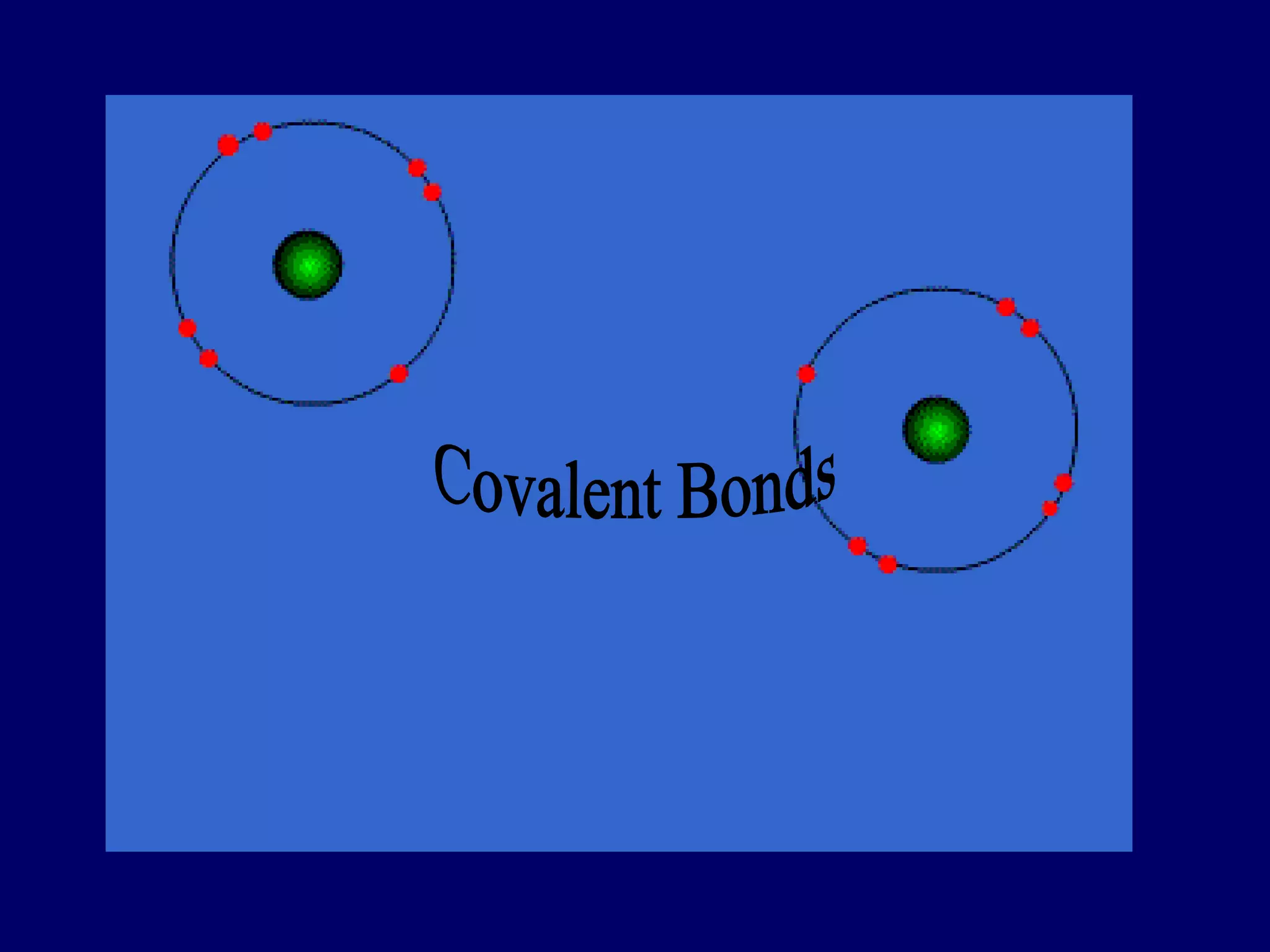
This document discusses three main types of chemical bonding: ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds. Ionic bonds form between metals and nonmetals through the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, producing charged ions. Covalent bonds form between nonmetals of similar electronegativity through the sharing of electron pairs. Metallic bonds form between metallic elements through a shared "electron cloud" that holds the atoms together strongly.