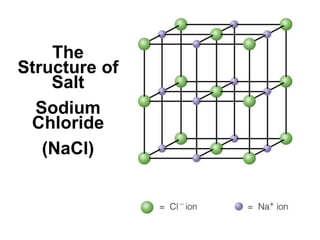
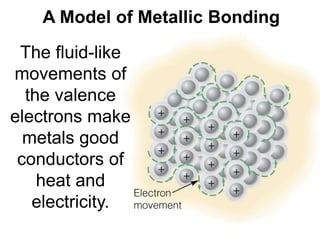
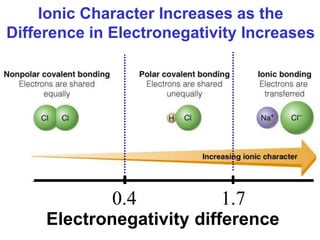
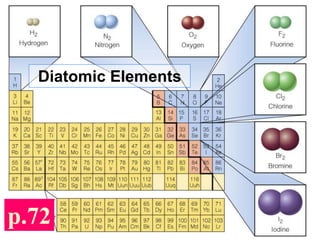
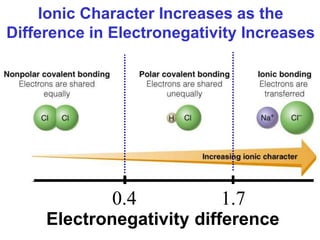
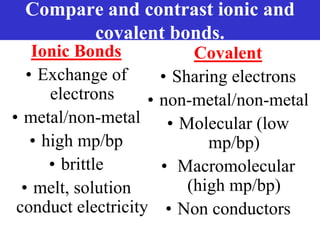
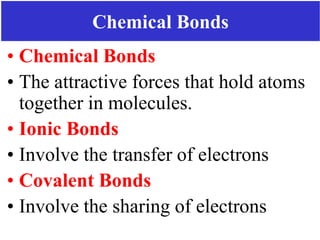
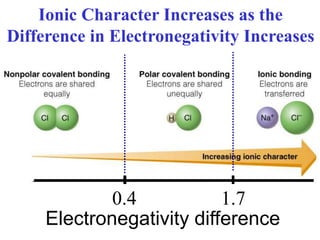
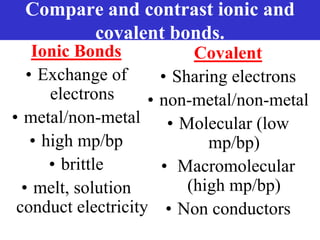
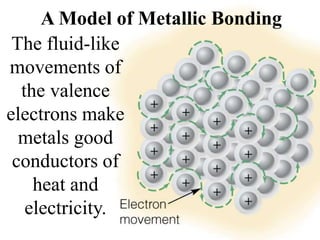
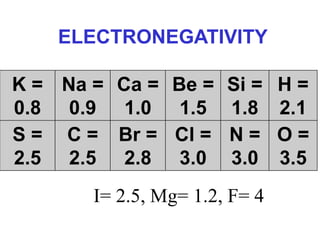
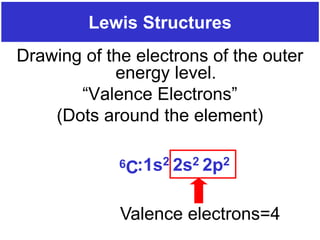
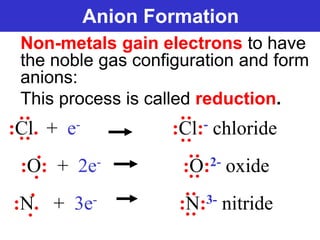
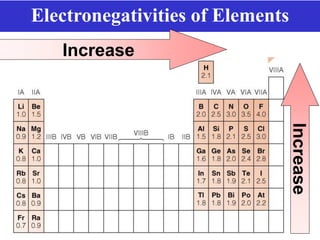
The document discusses different types of chemical bonds including ionic bonds and covalent bonds. Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between metals and non-metals, resulting in ionic compounds with high melting and boiling points that conduct electricity when melted or in solution. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between non-metal atoms, resulting in molecules with low melting and boiling points that do not conduct electricity. The document also discusses metallic bonding and how metal atoms are held together by valence electrons that are delocalized throughout the structure.