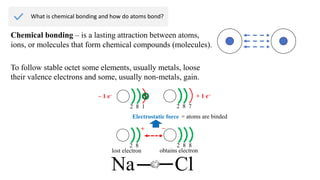
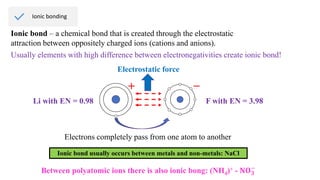
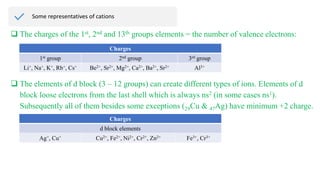
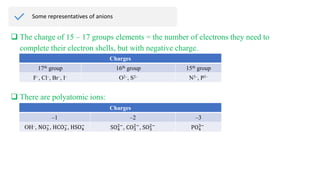
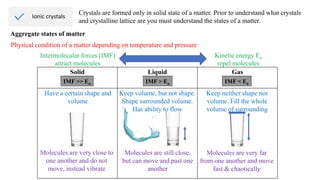
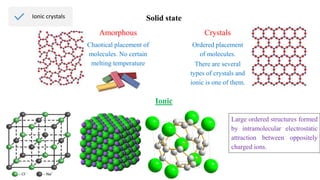
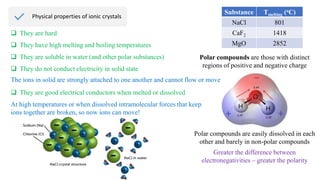
Ionic bonding occurs through the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions. Cations form when metals lose electrons, while anions form when nonmetals gain electrons. Ionic bonds are usually seen between metals and nonmetals. Ionic crystals form ordered structures with ions packed together. Ionic crystals have high melting points, are hard, and conduct electricity when molten or dissolved due to the ions being able to move.