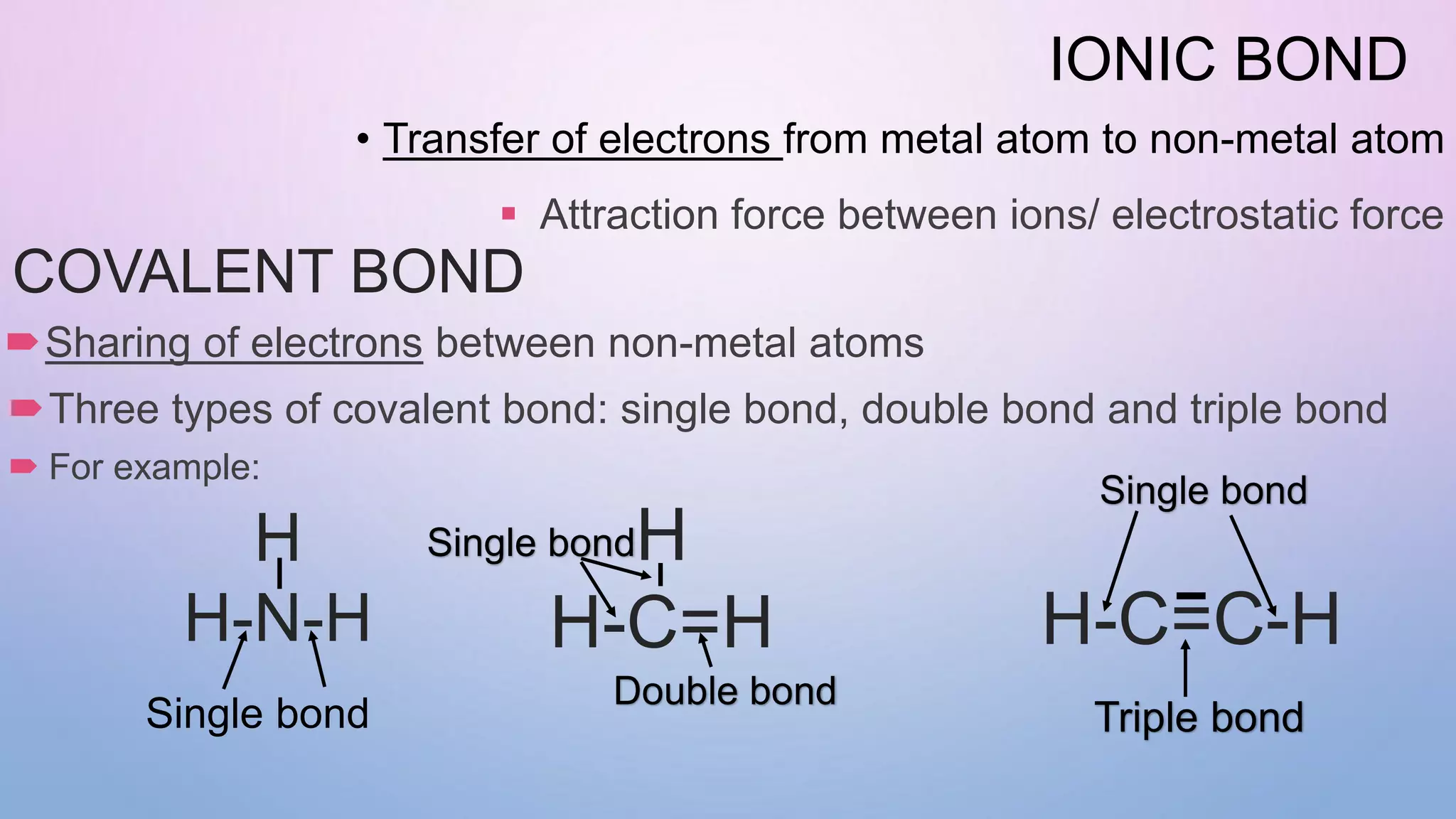
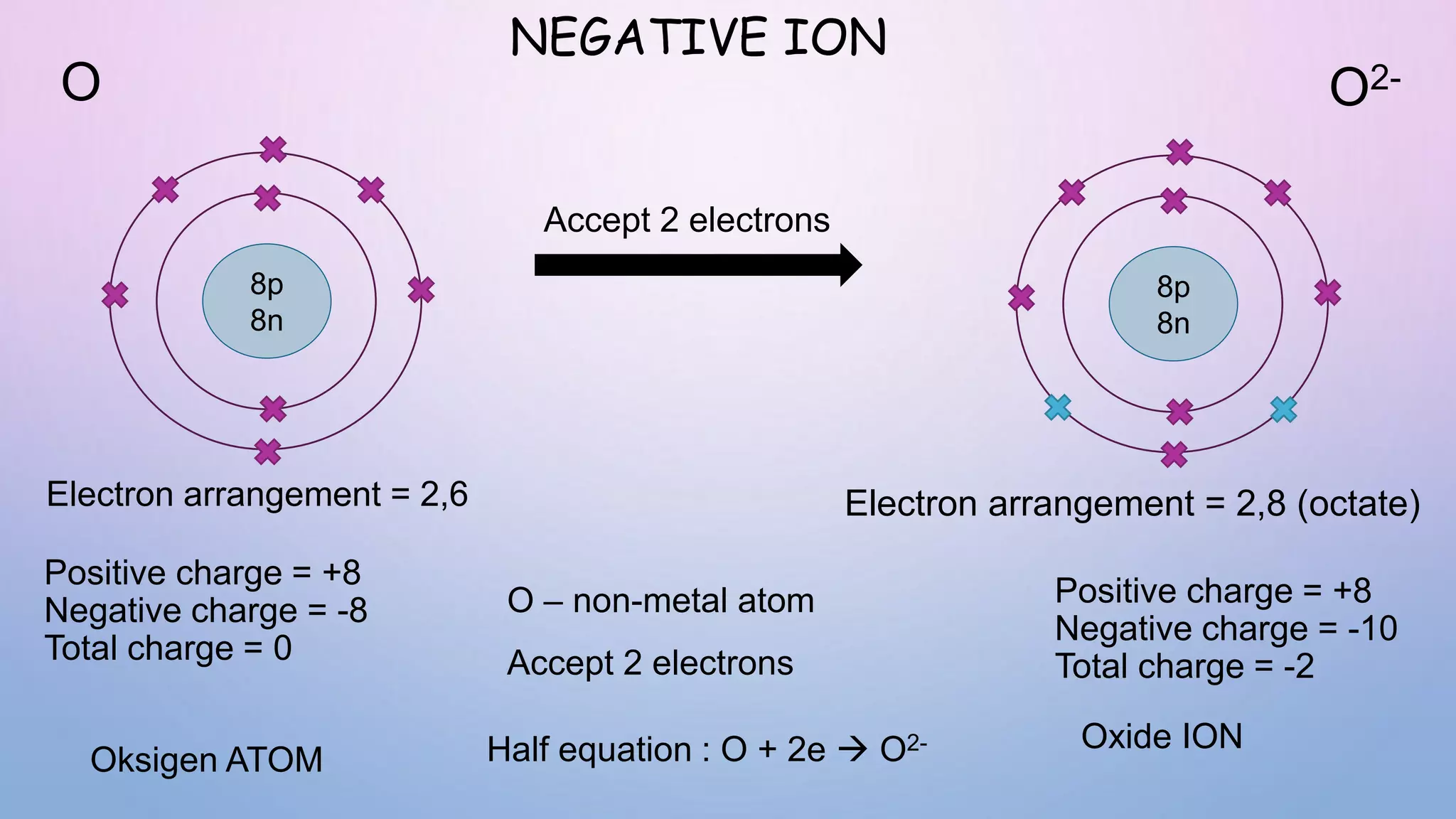
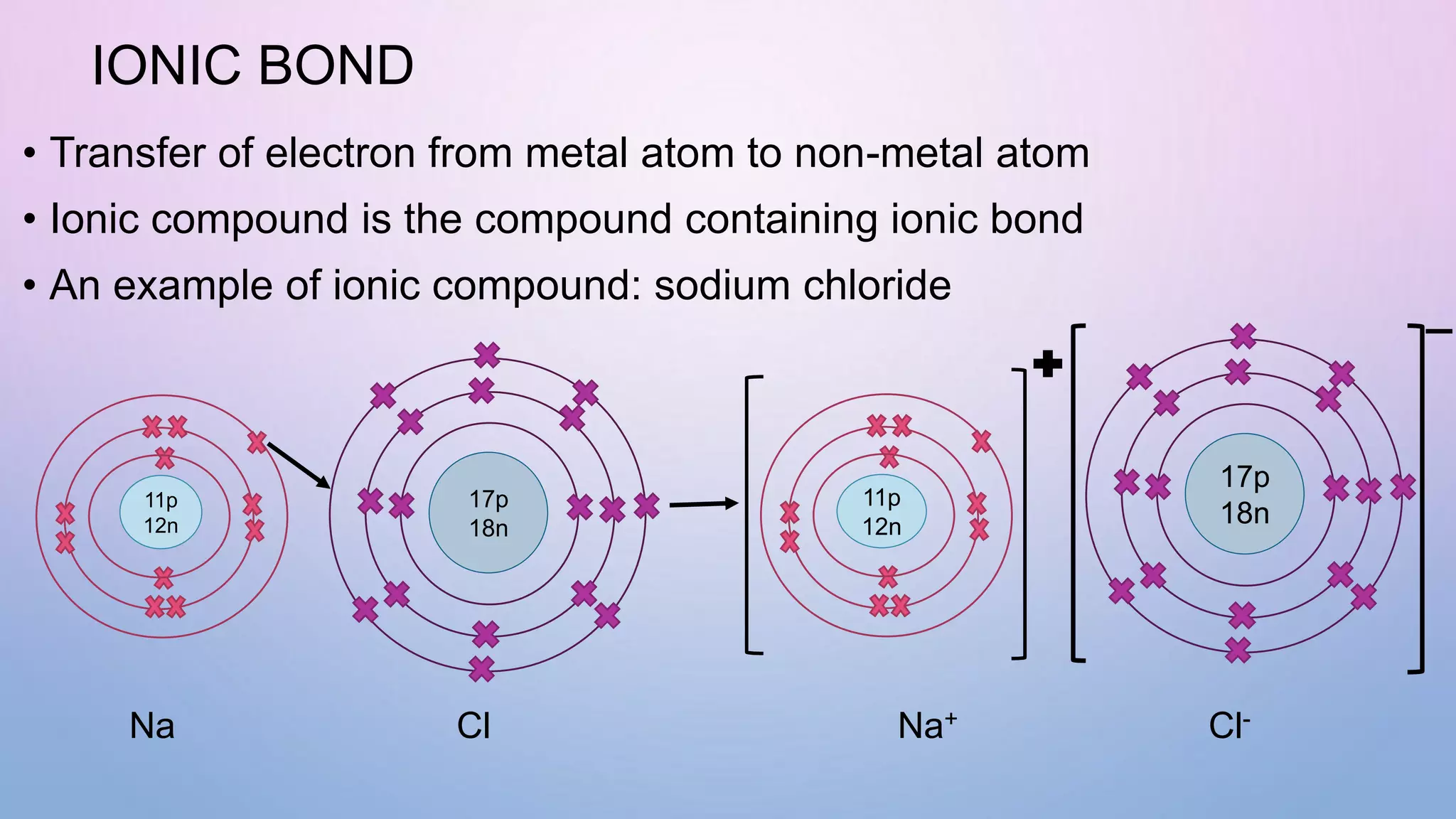
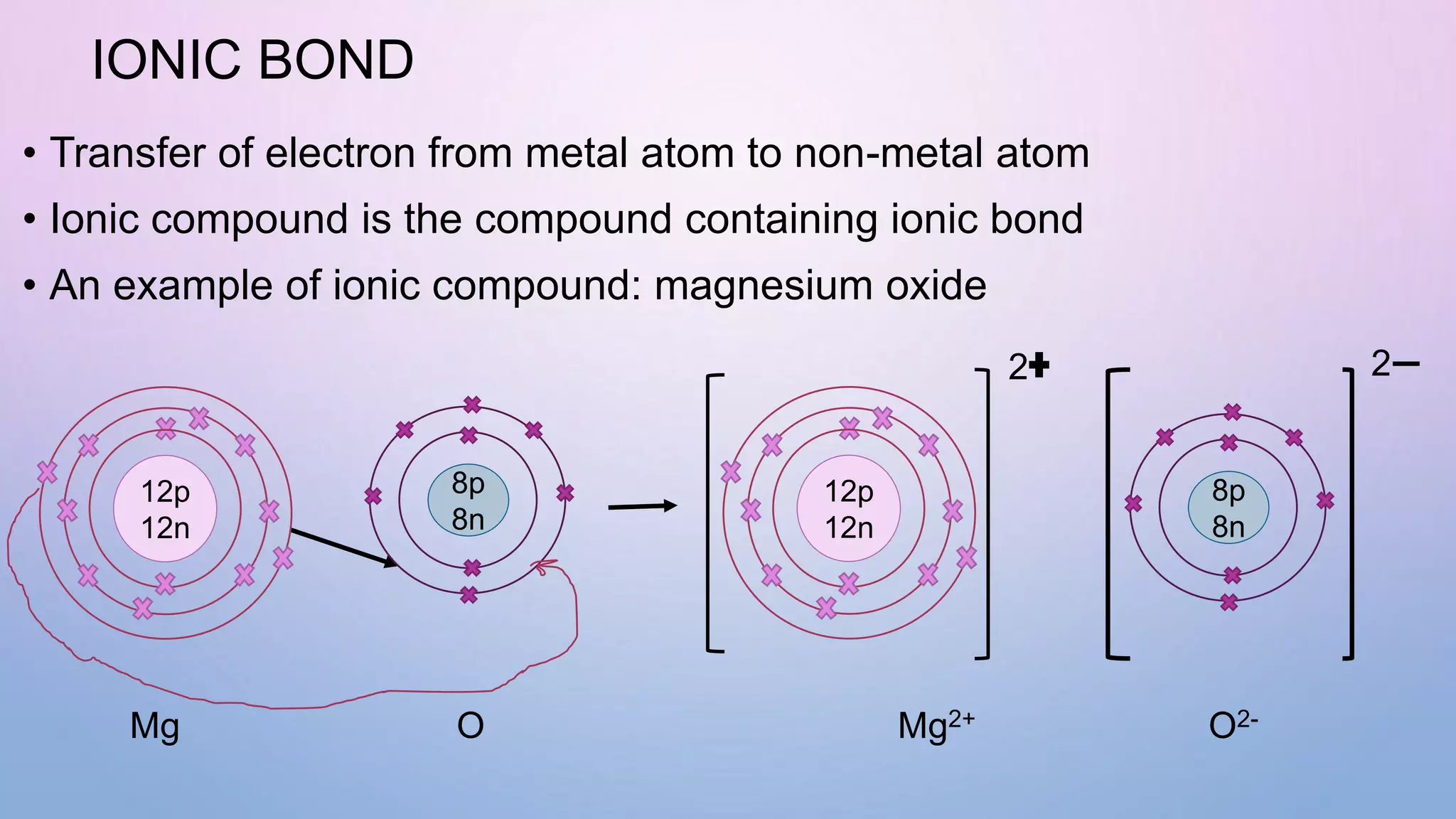
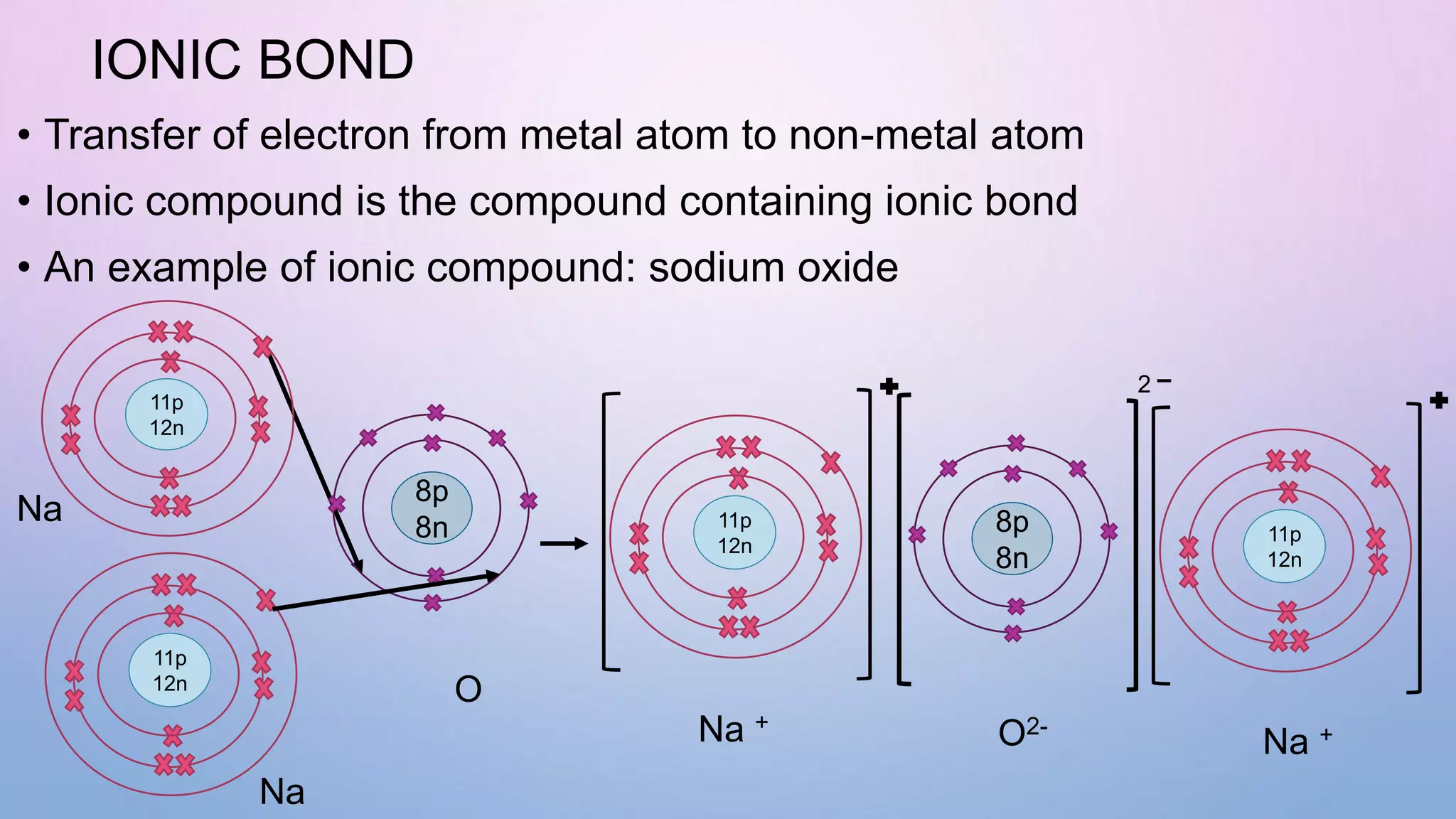
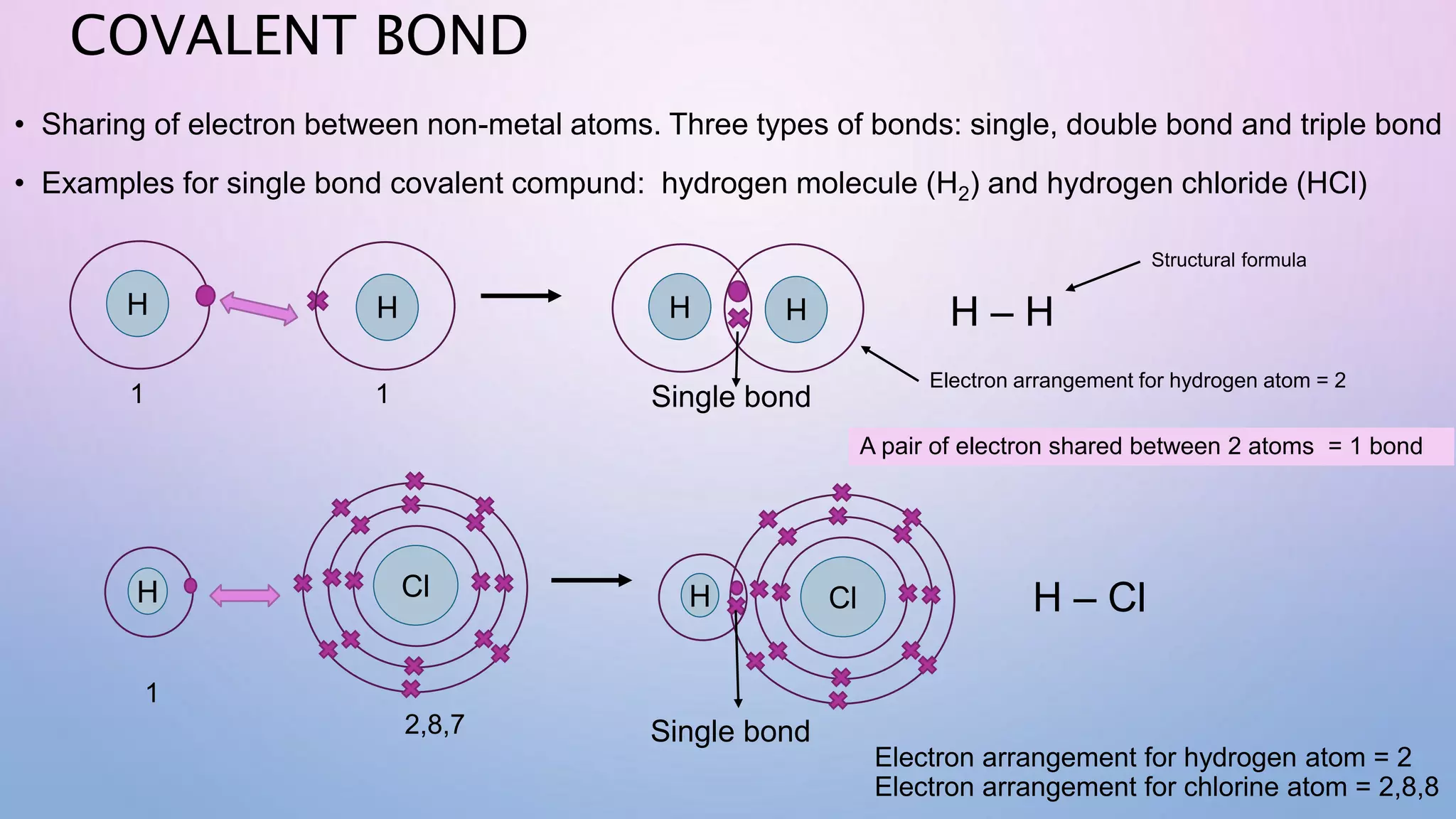
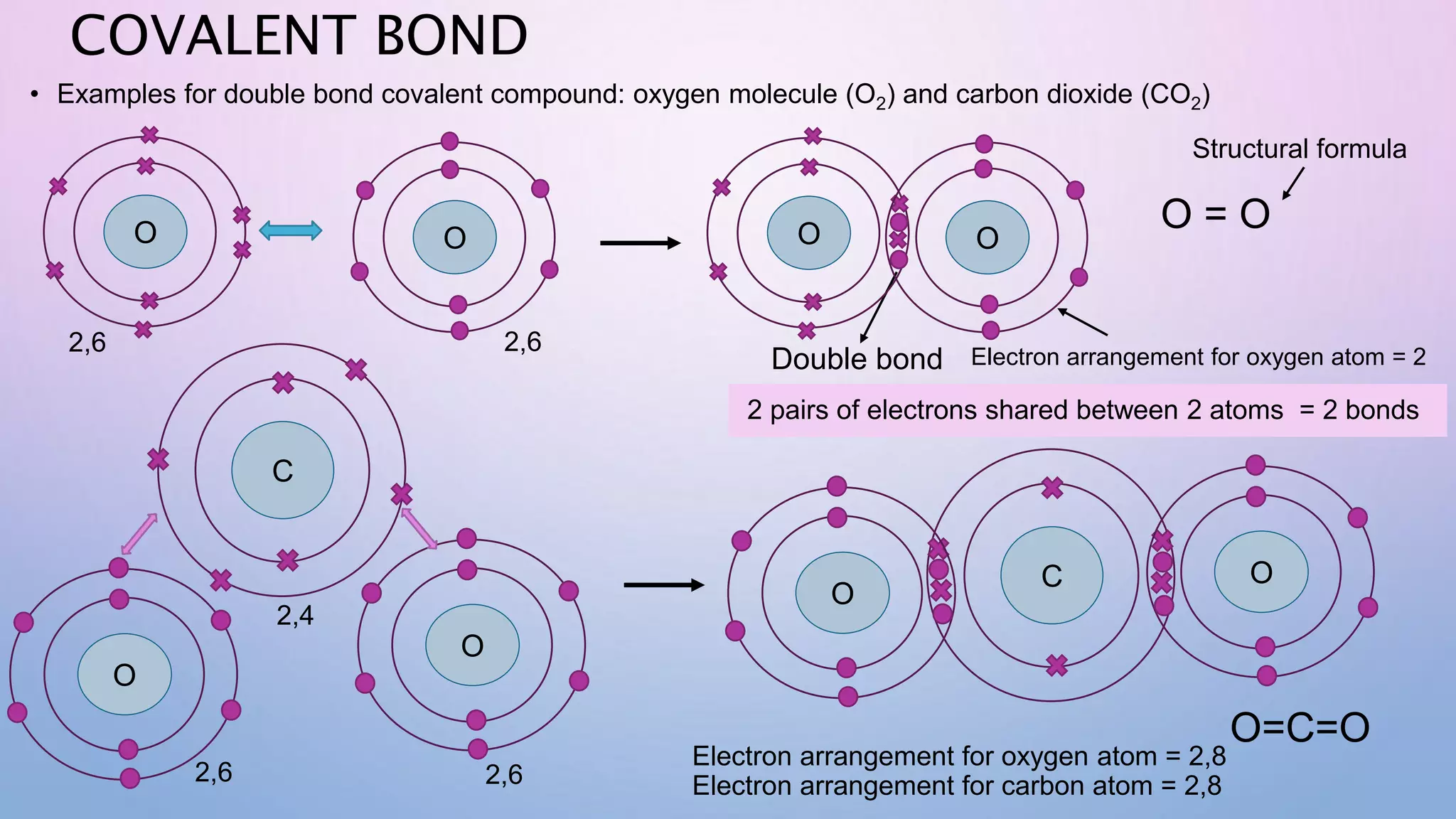
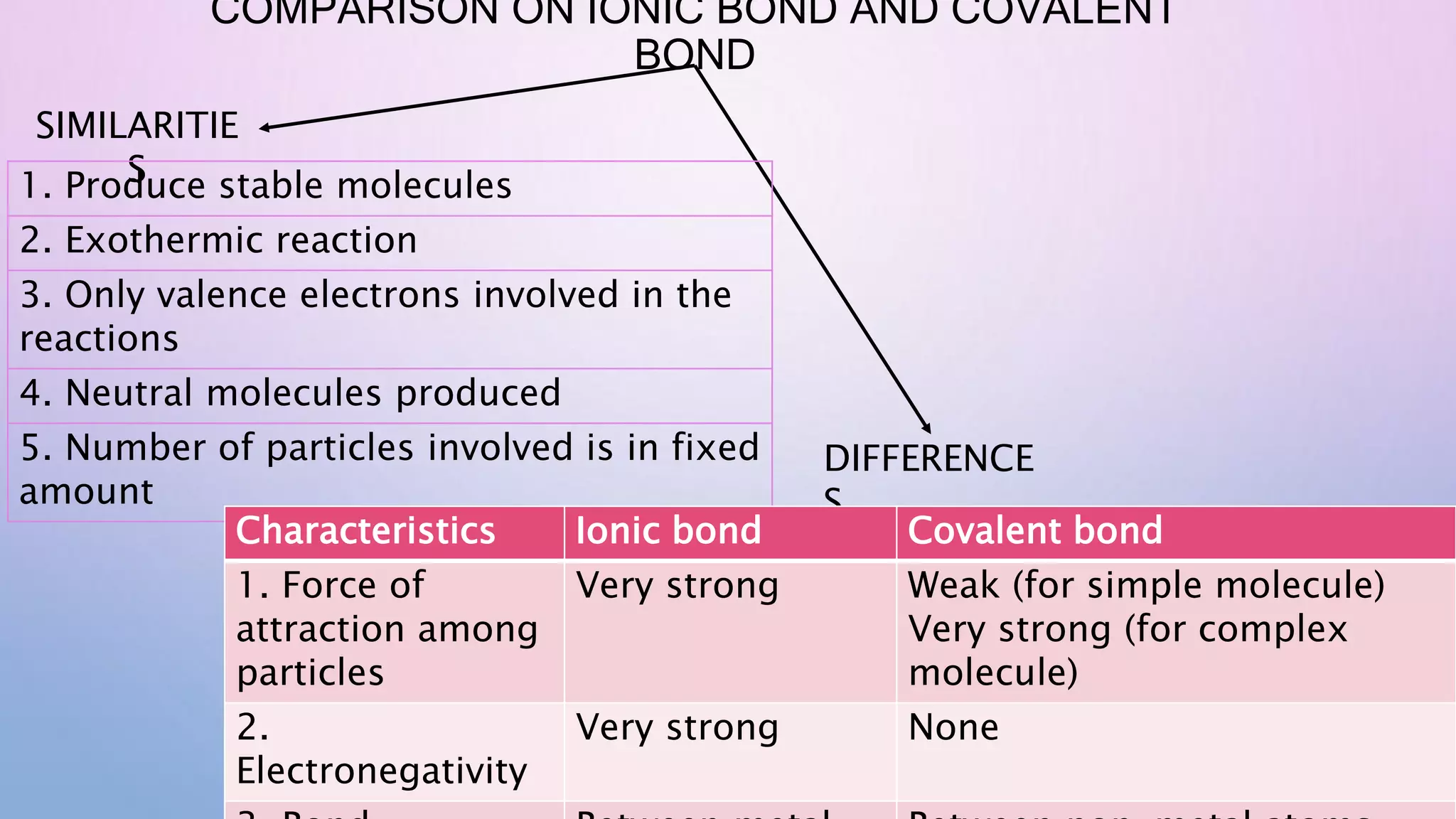
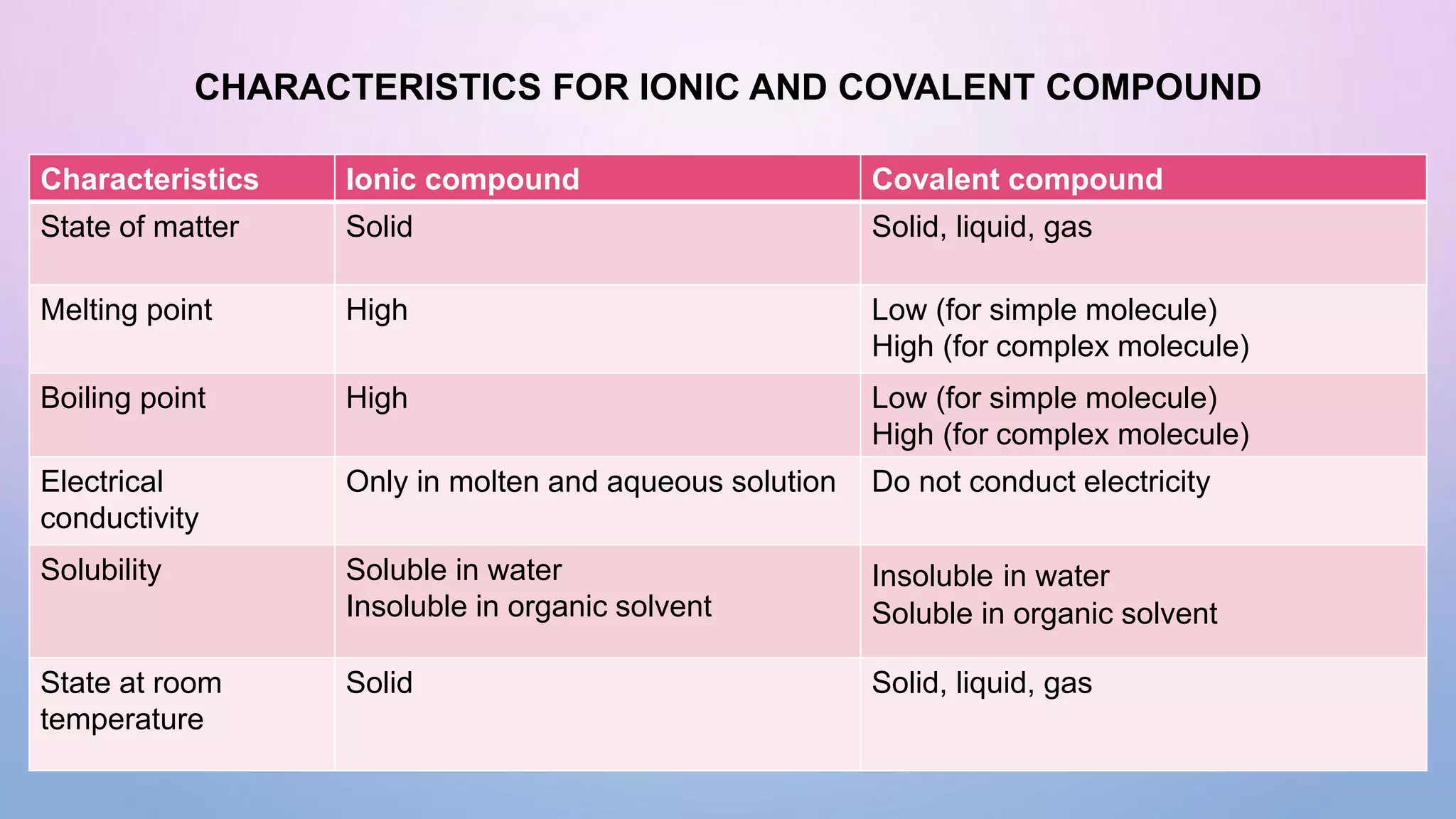
Ionic bonds form when electrons are transferred from a metal atom to a non-metal atom, creating oppositely charged ions. Covalent bonds form through the sharing of electrons between non-metal atoms. Ionic compounds contain ionic bonds and transfer electrons, while covalent compounds share electrons. Examples of ionic compounds are sodium chloride and magnesium oxide, while examples of covalent compounds are hydrogen gas, oxygen gas, and carbon dioxide. Ionic compounds are generally solids with high melting points that conduct electricity when molten or dissolved, while covalent compounds can be solids, liquids or gases with varied properties depending on molecular complexity.