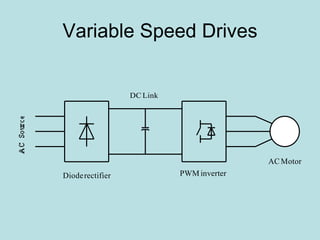
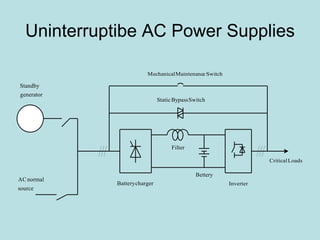
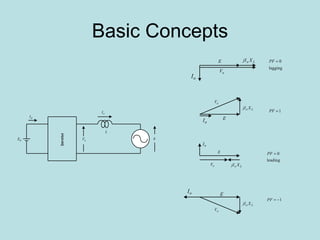
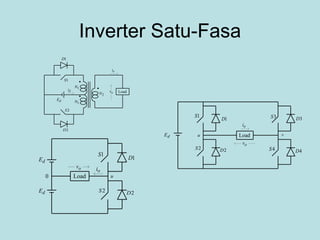
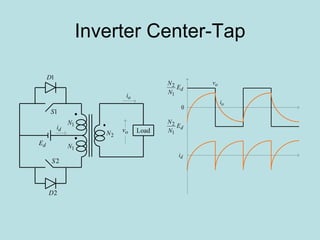
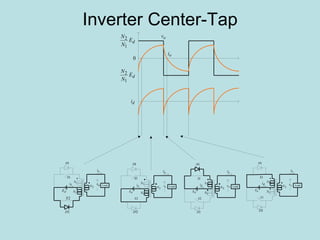
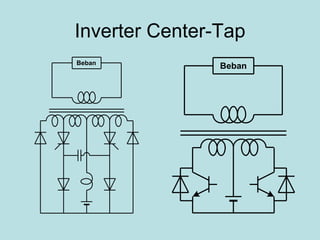
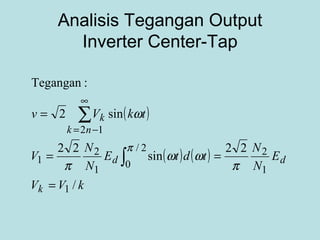
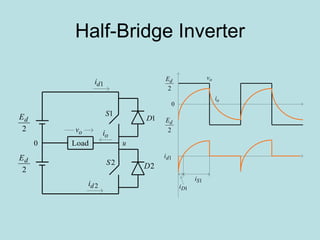
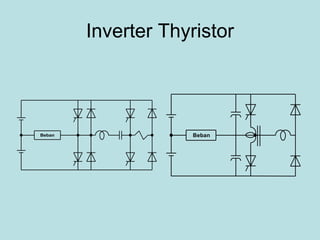
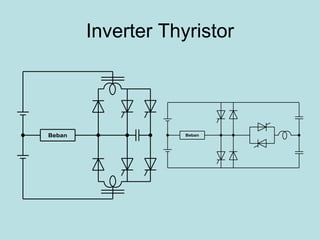
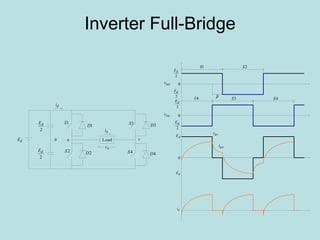
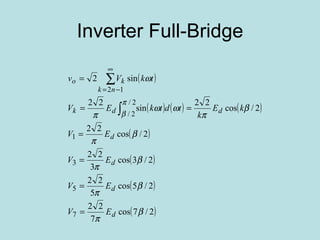
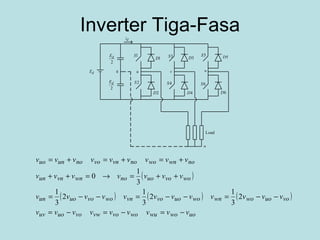
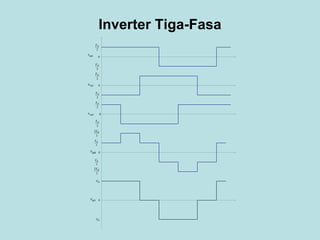
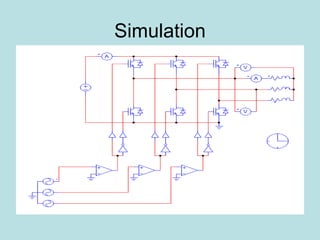
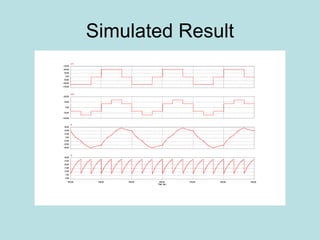
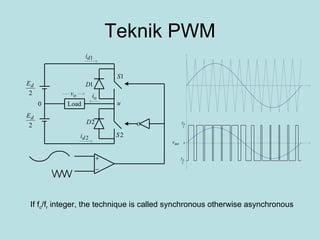
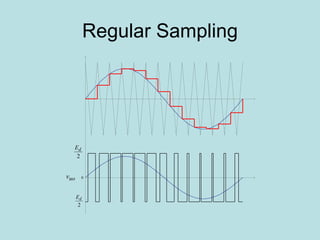
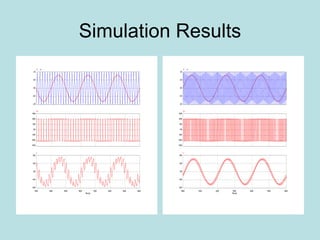
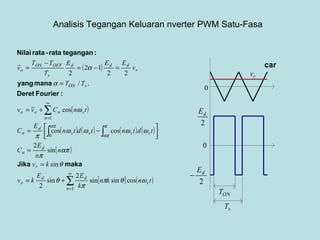
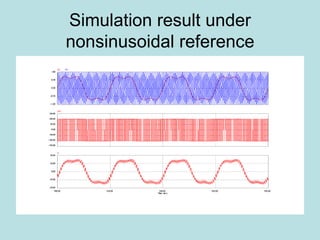
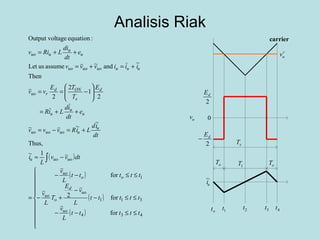
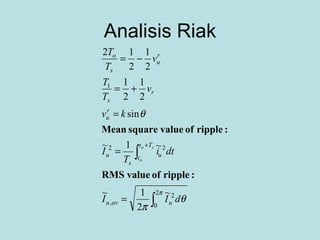
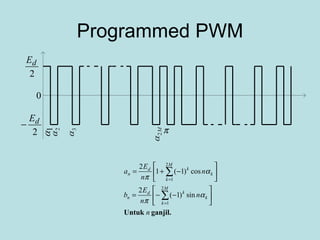
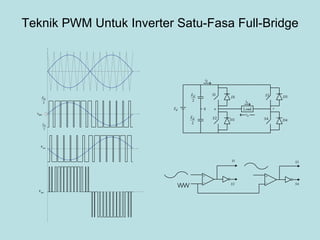
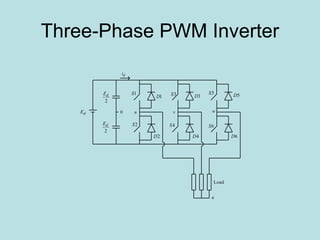
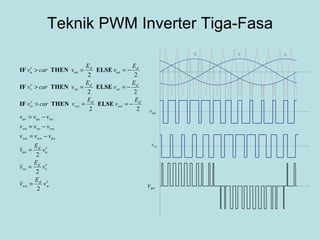
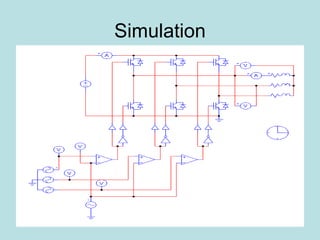
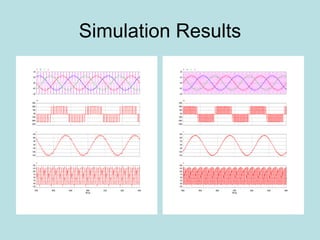
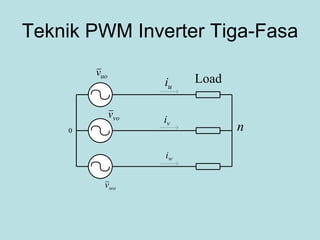
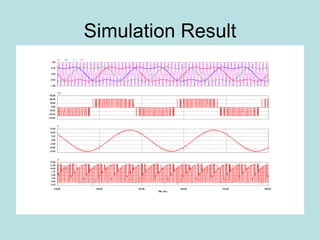
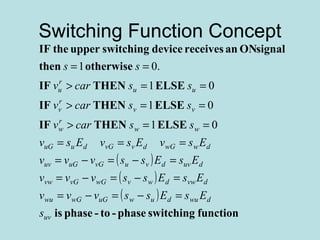
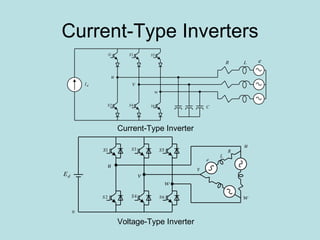
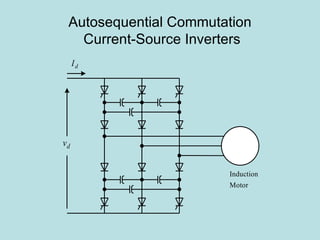
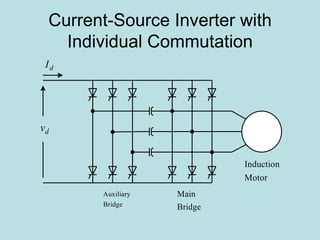
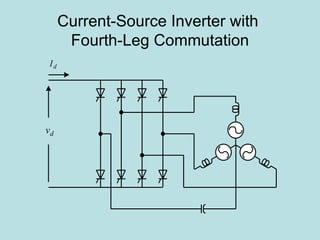
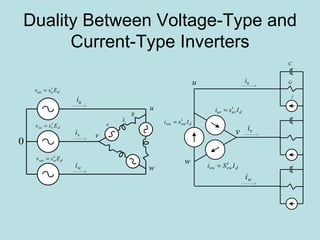
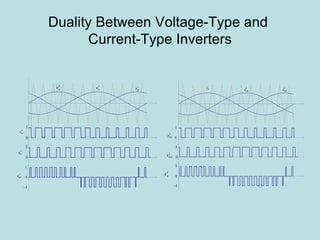
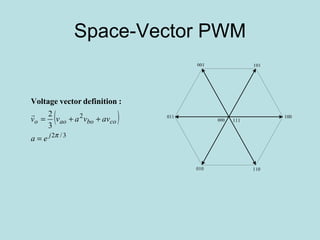
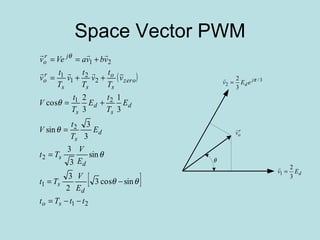
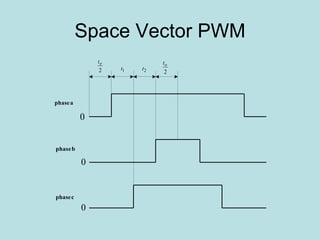
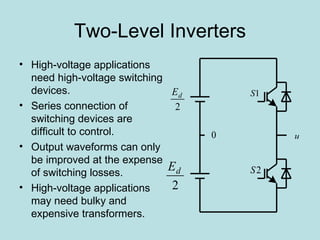
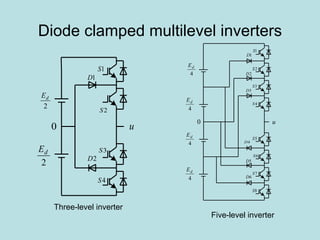
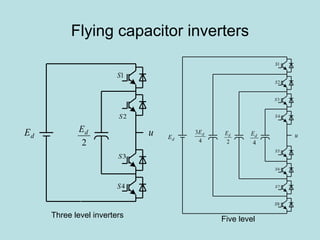
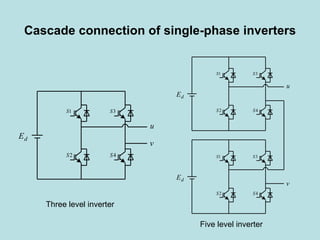
The document discusses different types of inverters classified based on number of phases, DC source, commutation method, AC wave shape, output voltage levels, and topologies like center-tap, half-bridge, full-bridge, and three-phase inverters. It also covers pulse width modulation techniques like regular sampling, programmed PWM, space vector PWM, and current-type inverters which are commonly used in applications like AC motor drives, UPS systems, and solar inverters. Current-type inverters are gaining popularity for medium voltage applications due to advantages like sinusoidal currents and short-circuit protection.