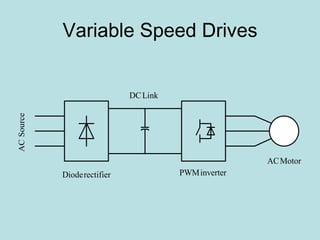
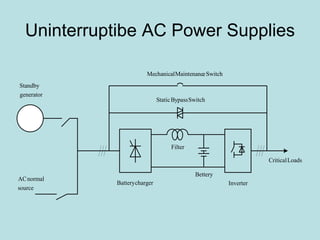
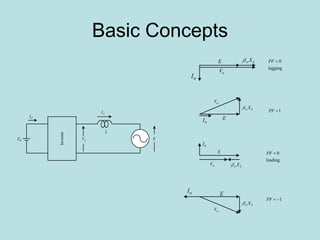
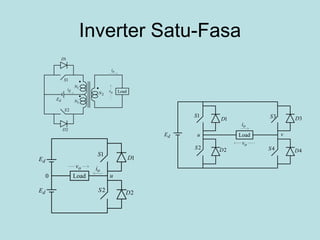
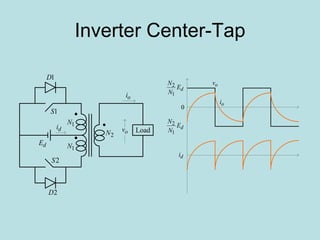
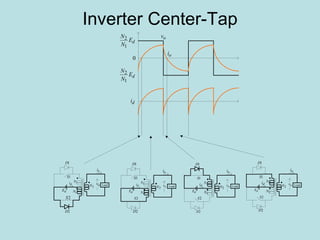
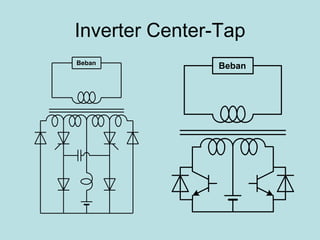
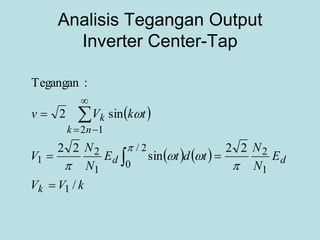
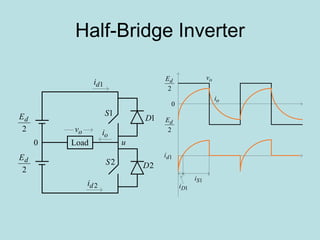
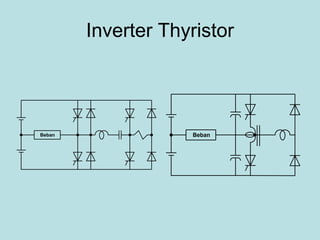
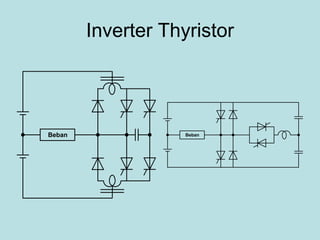
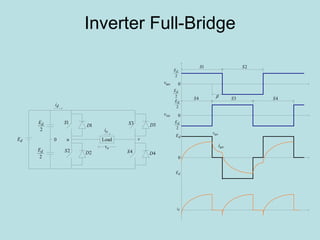
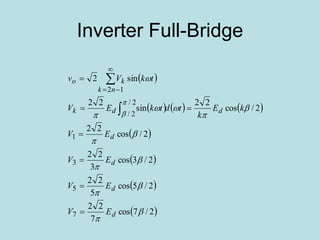
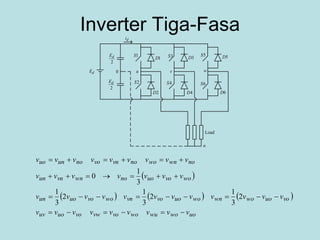
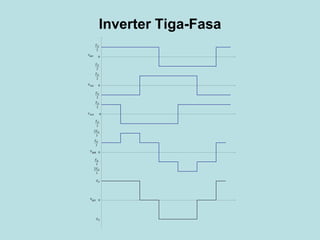
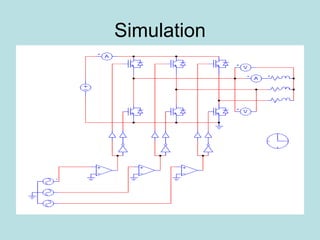
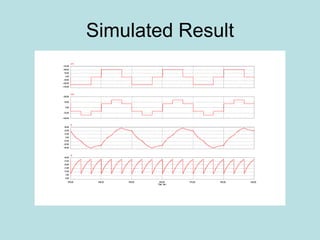
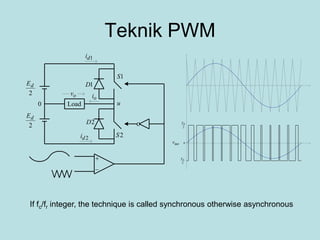
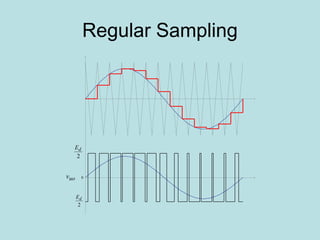
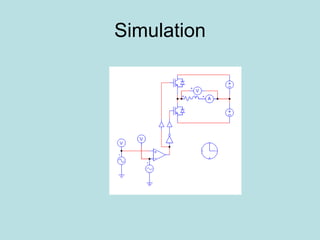
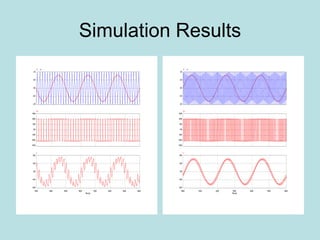
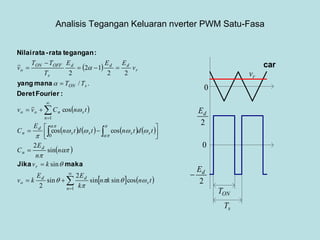
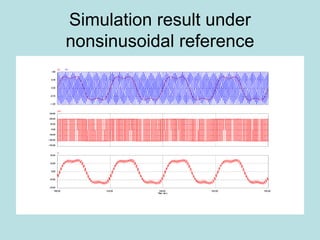
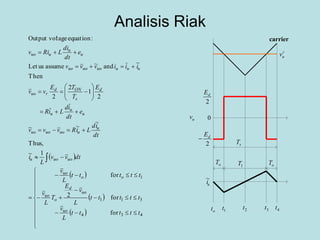
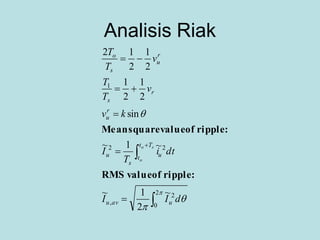
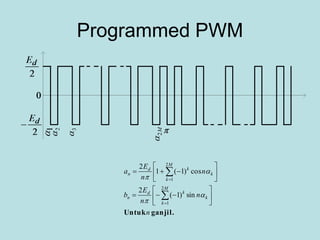
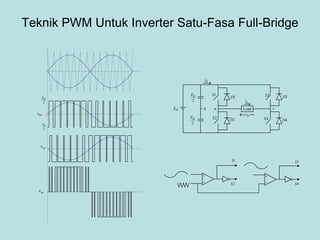
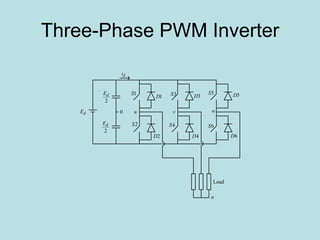
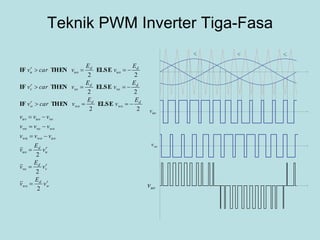
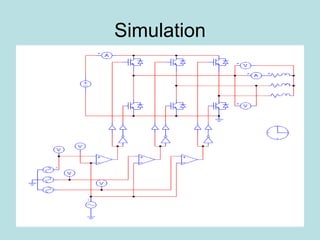
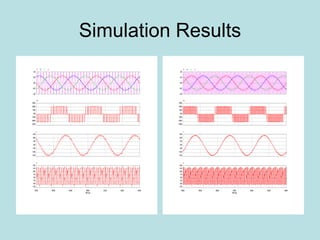
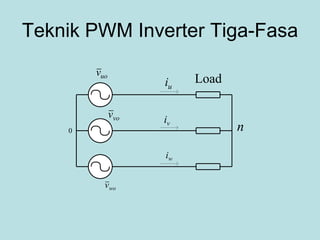
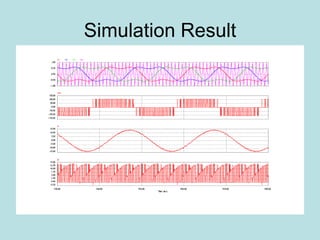
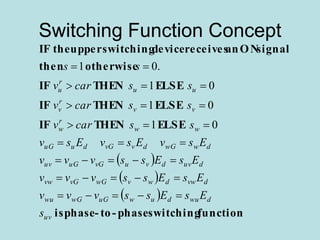
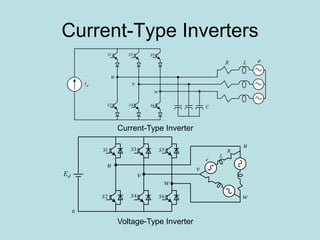
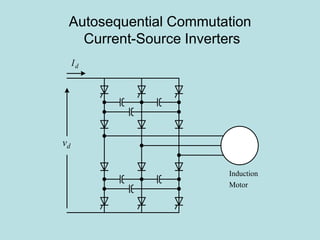
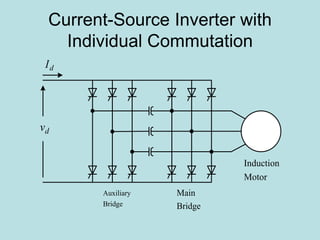
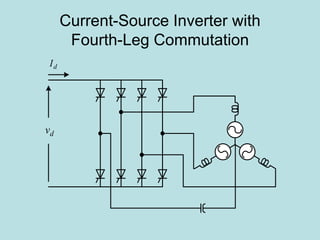
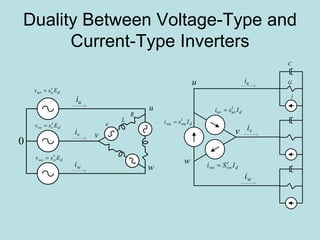
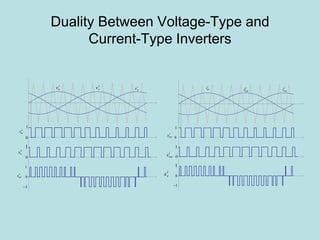
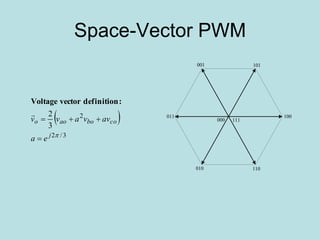
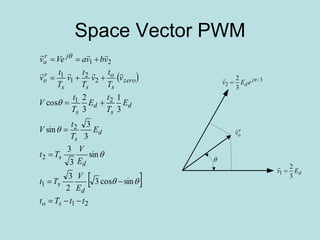
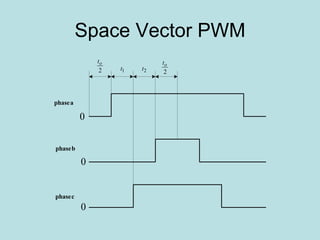
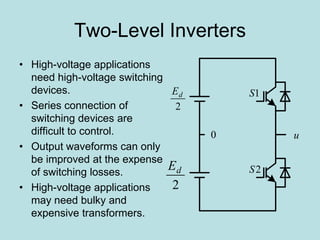
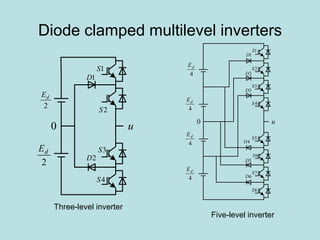
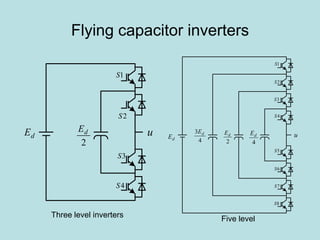
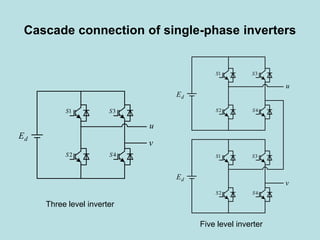
Inverter (Konverter DC – AC) are used for various applications such as AC motor control, UPS systems, active power filters, and flexible AC transmission systems. There are several types of inverters classified by number of phases, DC source, commutation method, output wave shaping technique, and number of output voltage levels. Basic inverter topologies include single phase, half bridge, full bridge, and three phase inverters. Pulse width modulation techniques are used to generate quasi-sinusoidal output voltage waveforms from the inverters. Simulation results show that higher switching frequencies produce more sinusoidal output currents.