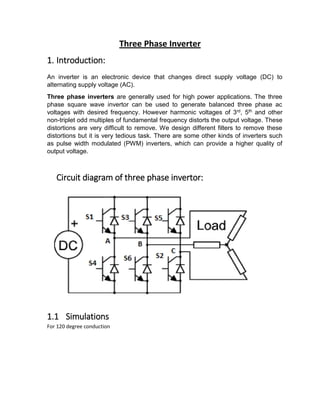
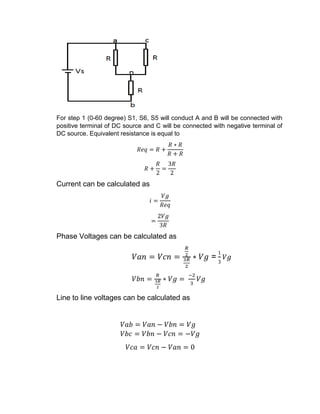
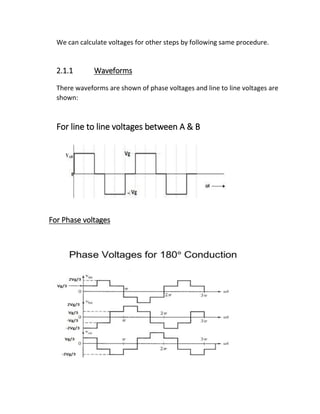
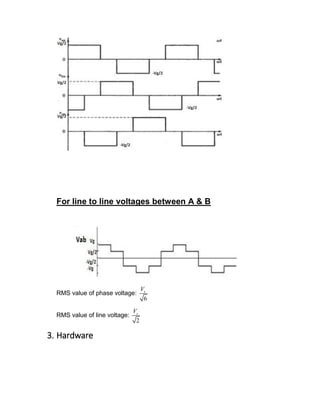
This document describes a three phase inverter that converts DC voltage to AC voltage. There are two main modes of conduction for a three phase inverter - 180 degree conduction and 120 degree conduction. 180 degree conduction involves three switches being on at a time, while 120 degree conduction only has two switches on at a time. The document provides circuit diagrams and equations to calculate the output voltages under each conduction mode. Waveforms are also shown to illustrate the phase and line voltages.