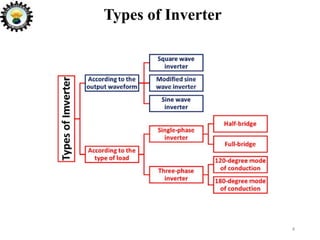
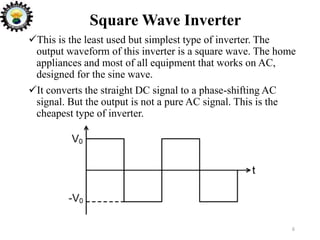
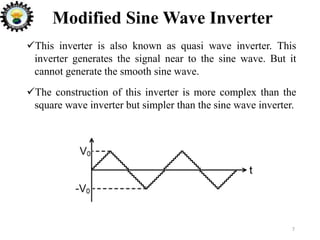
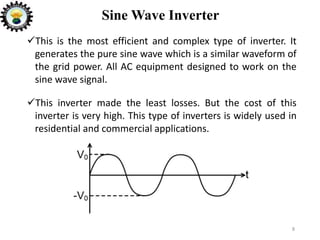
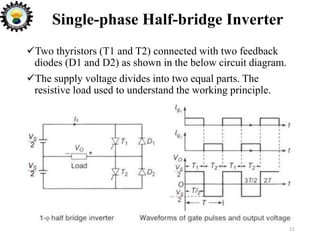
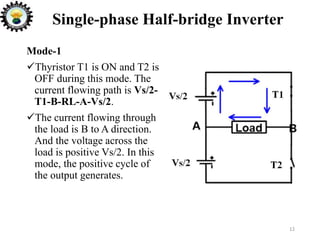
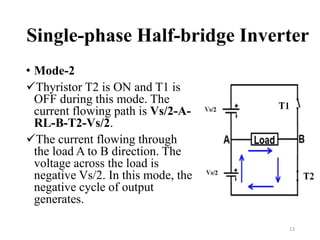
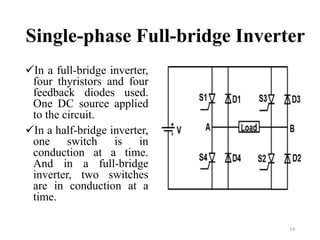
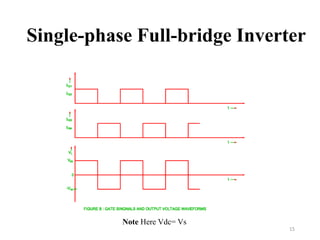
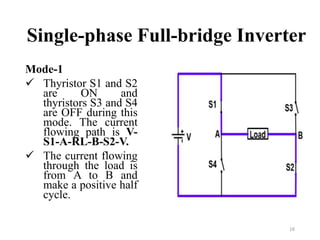
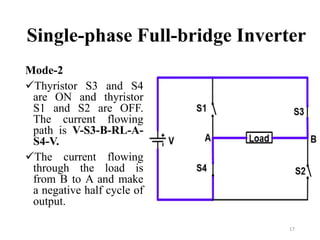
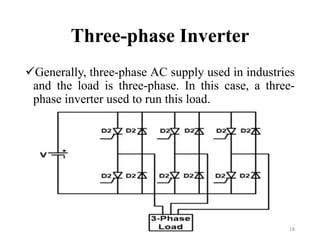
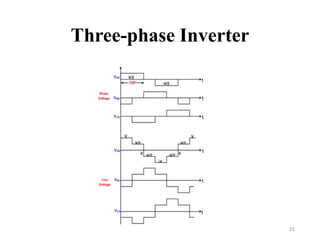
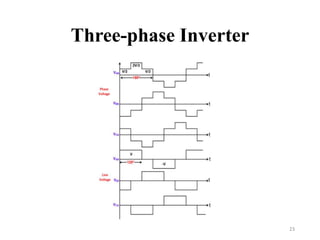
The document is an introduction to power electronics focusing on inverter units, detailing the types of inverters including square wave, modified sine wave, and sine wave inverters, as well as single-phase and three-phase variants. It explains the operation principles, configurations, and applications of these inverters, and includes important questions and multiple-choice questions for further understanding. Overall, the document serves as a comprehensive educational resource on inverter technology for electrical engineering students.