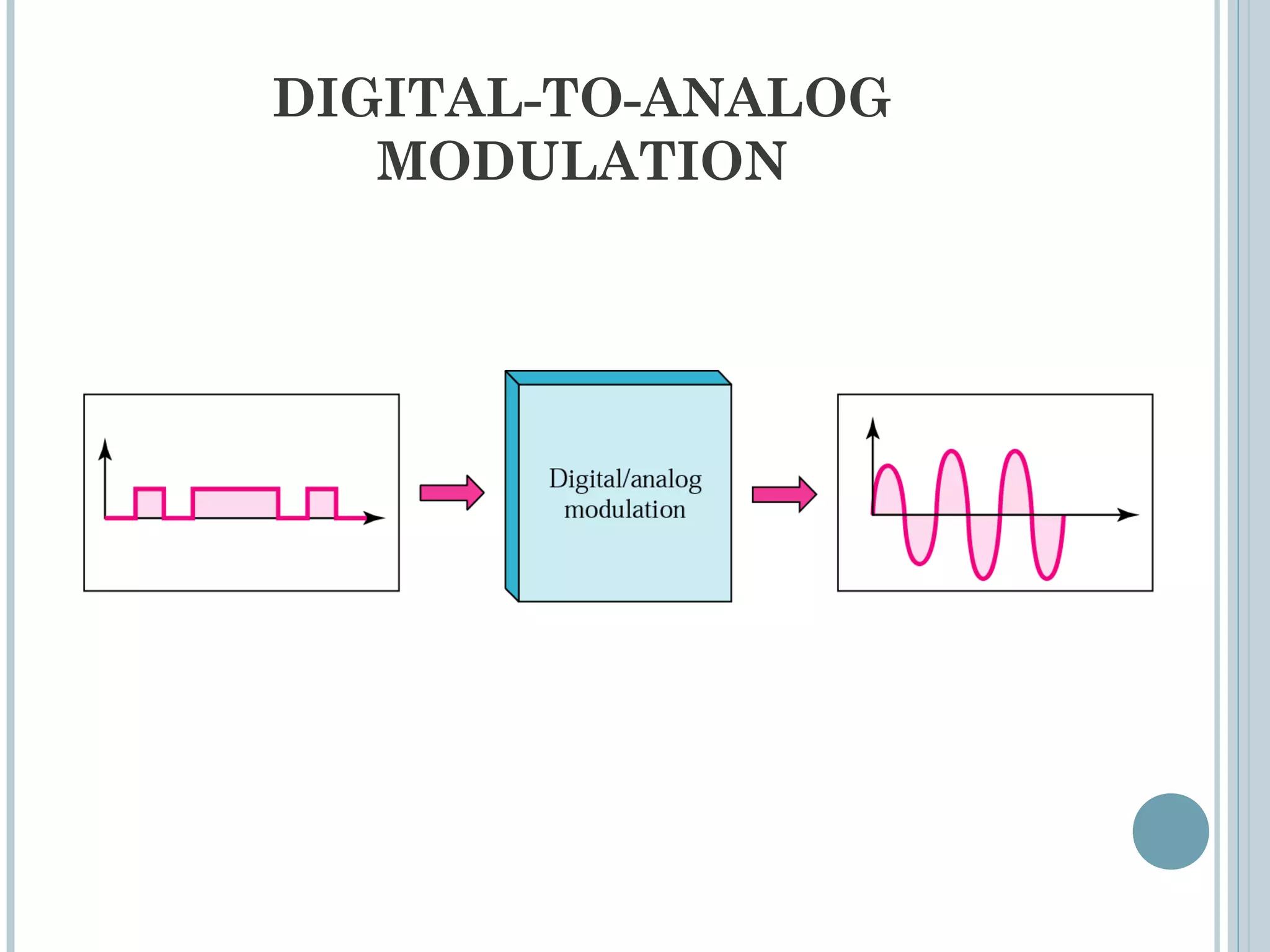
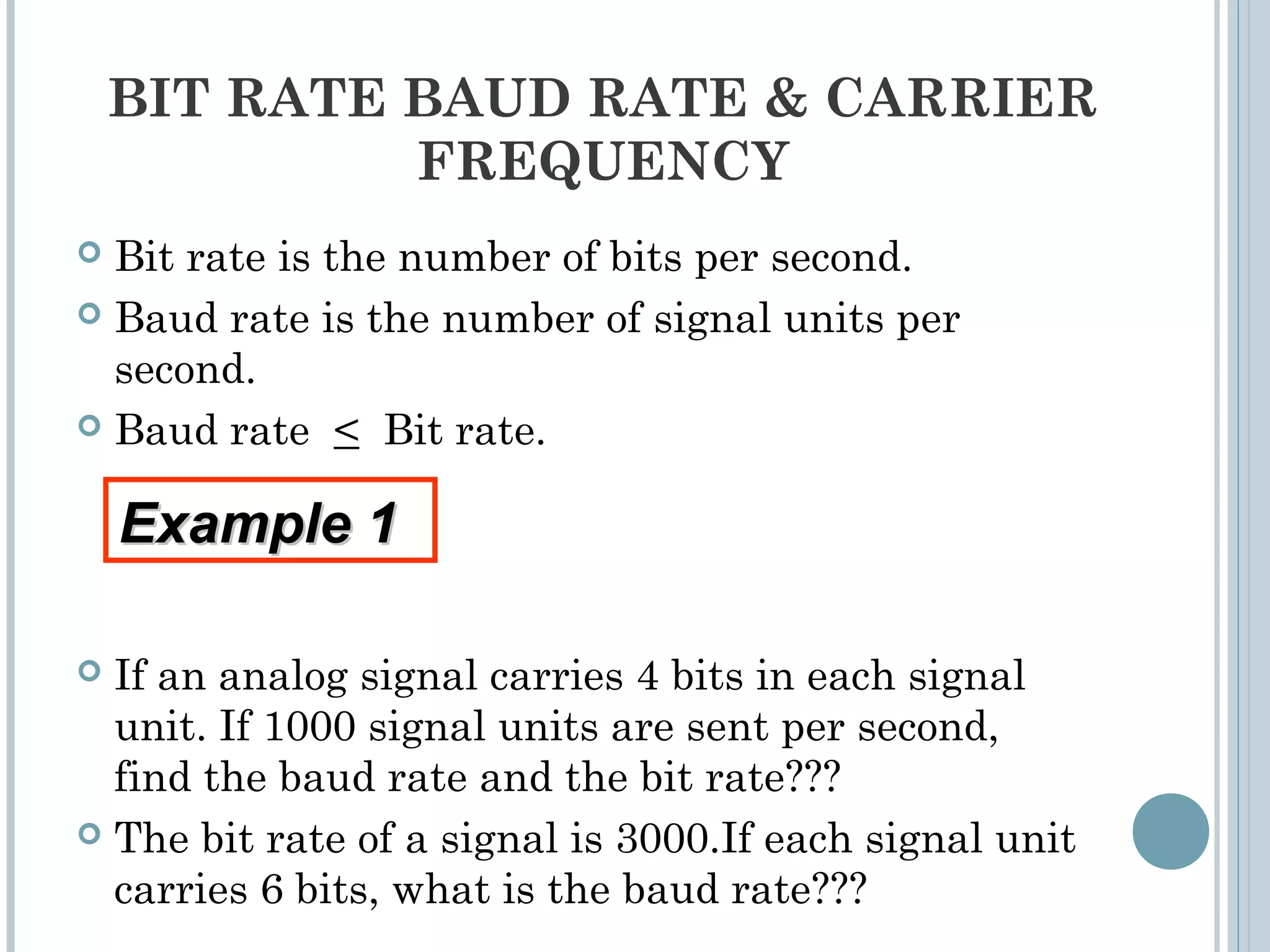
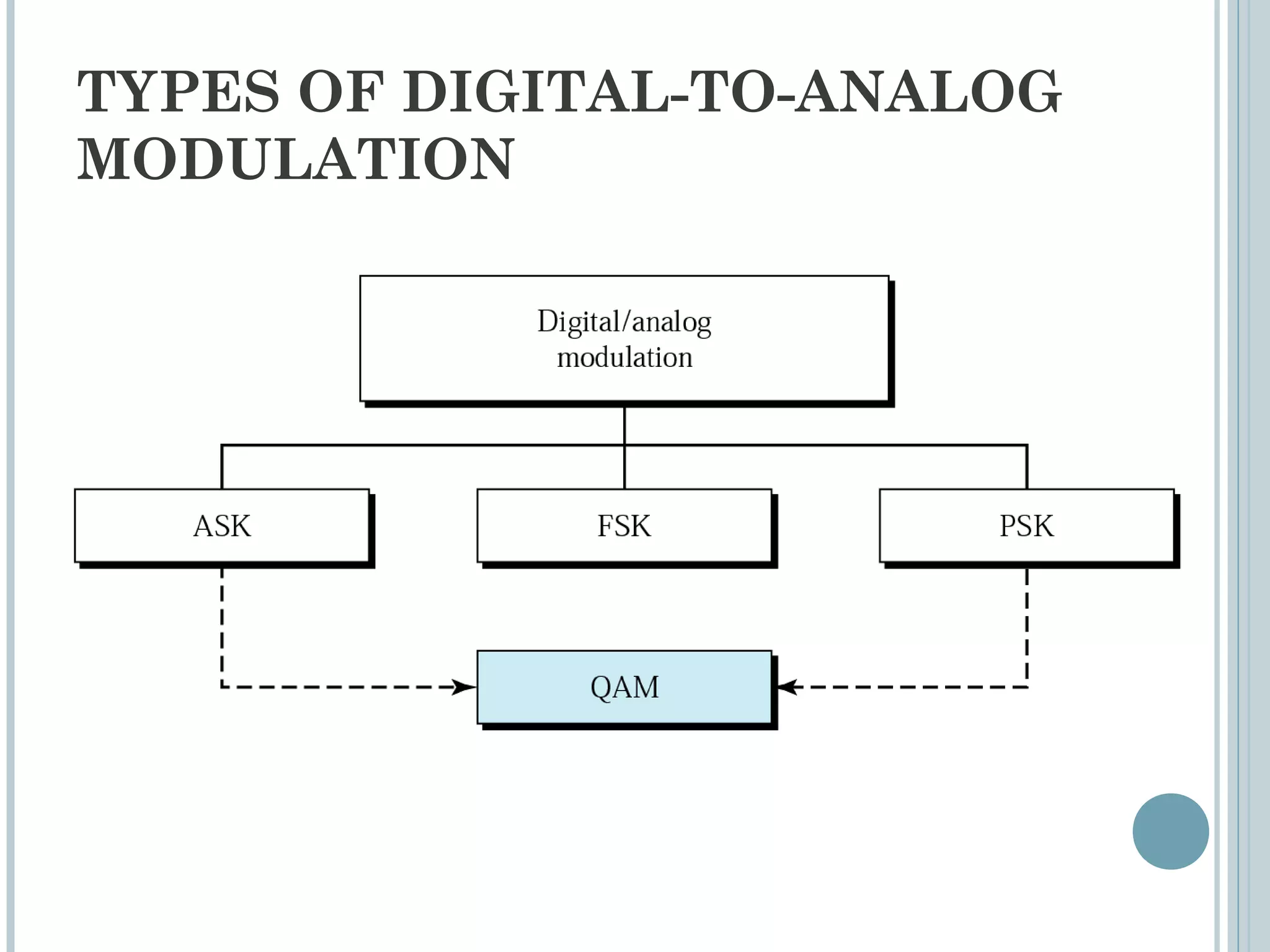
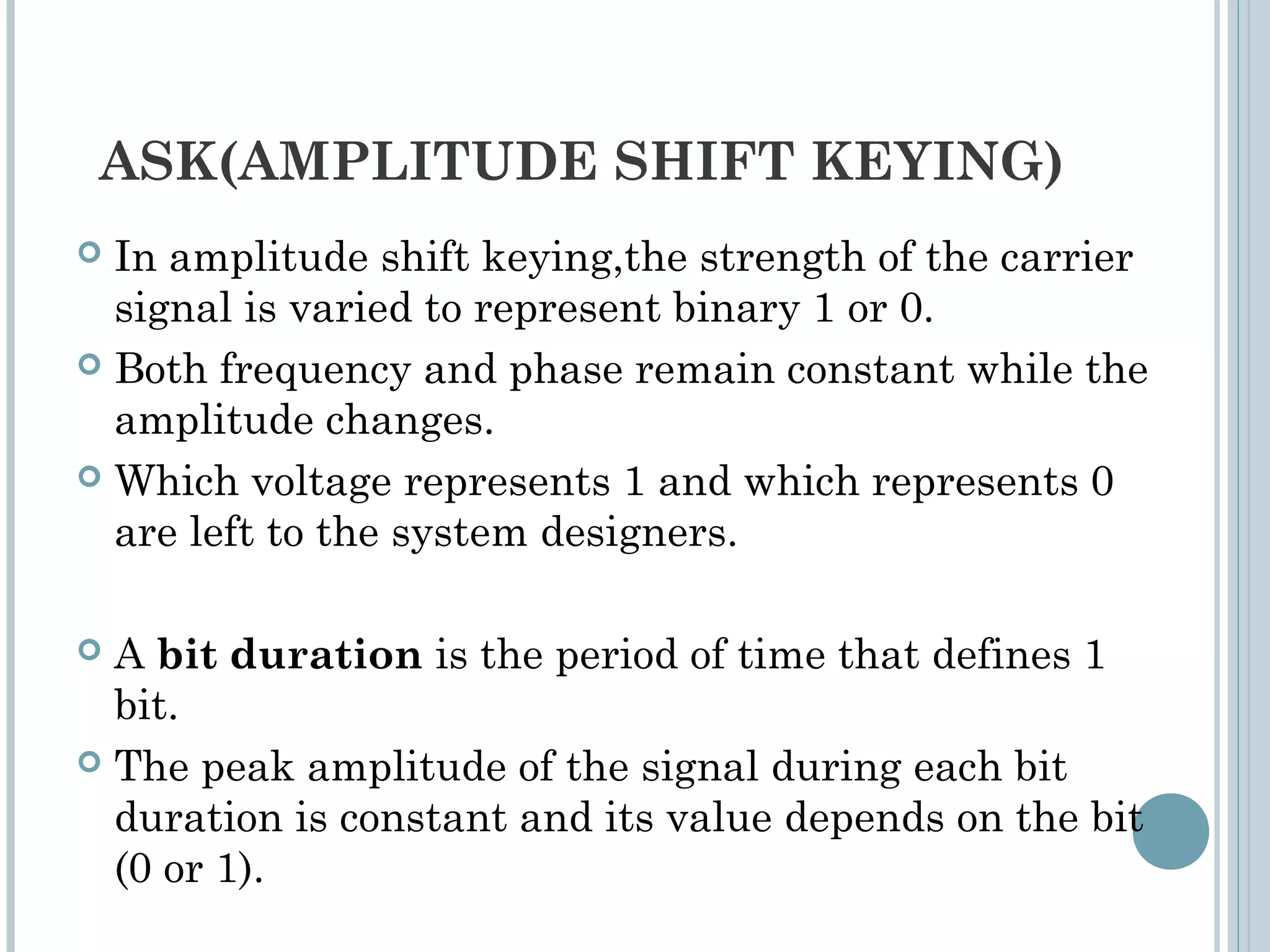
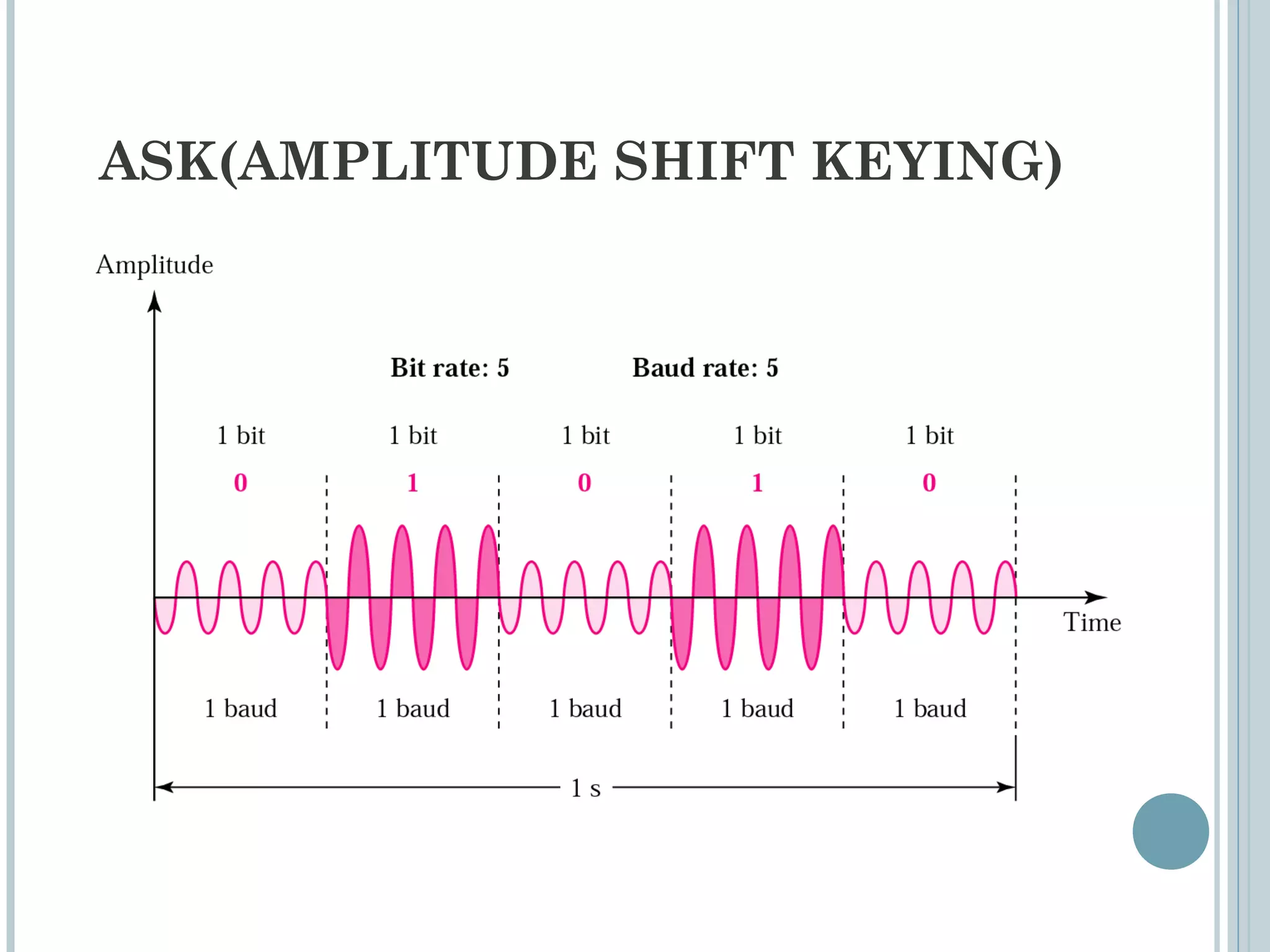
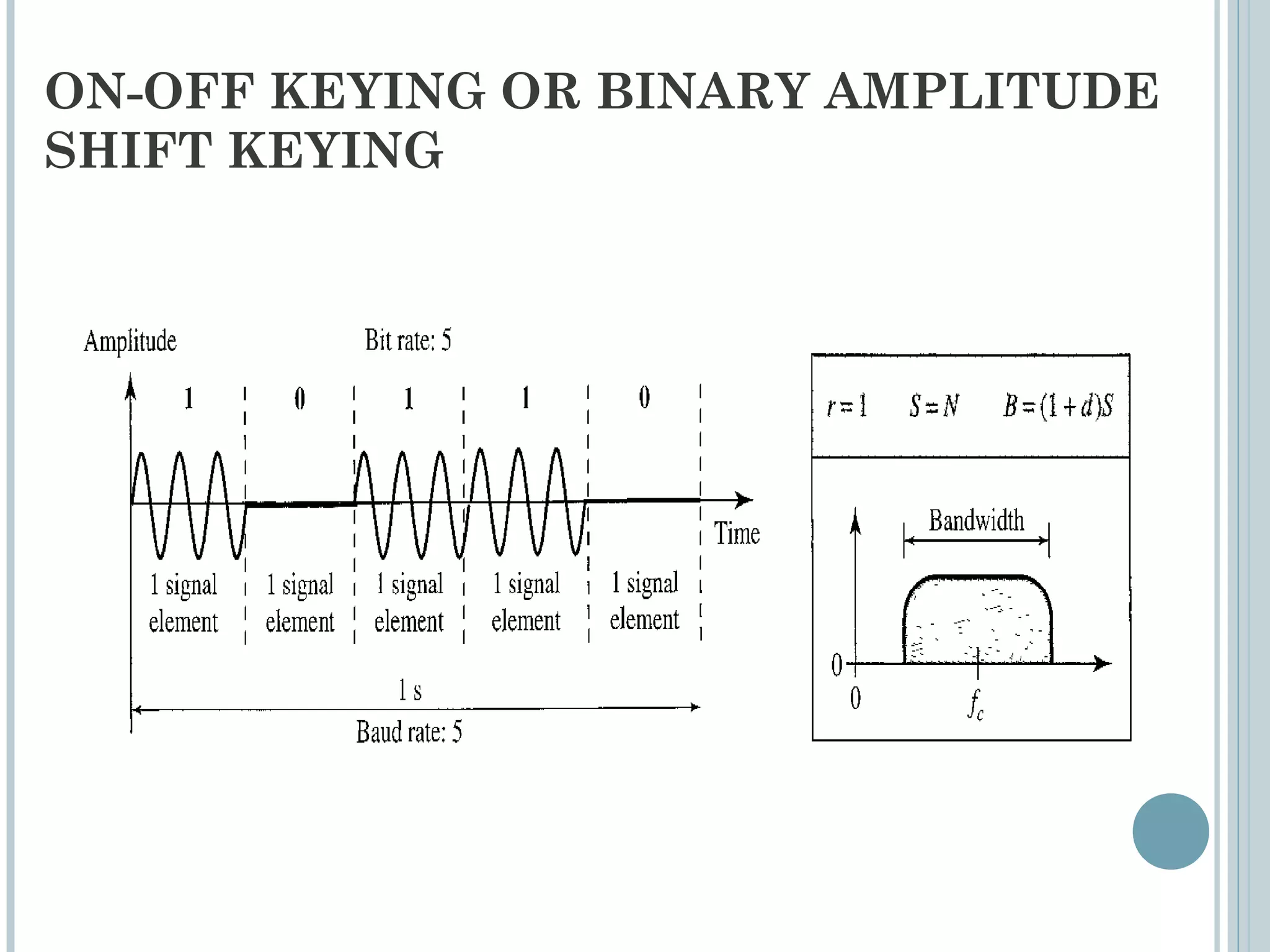
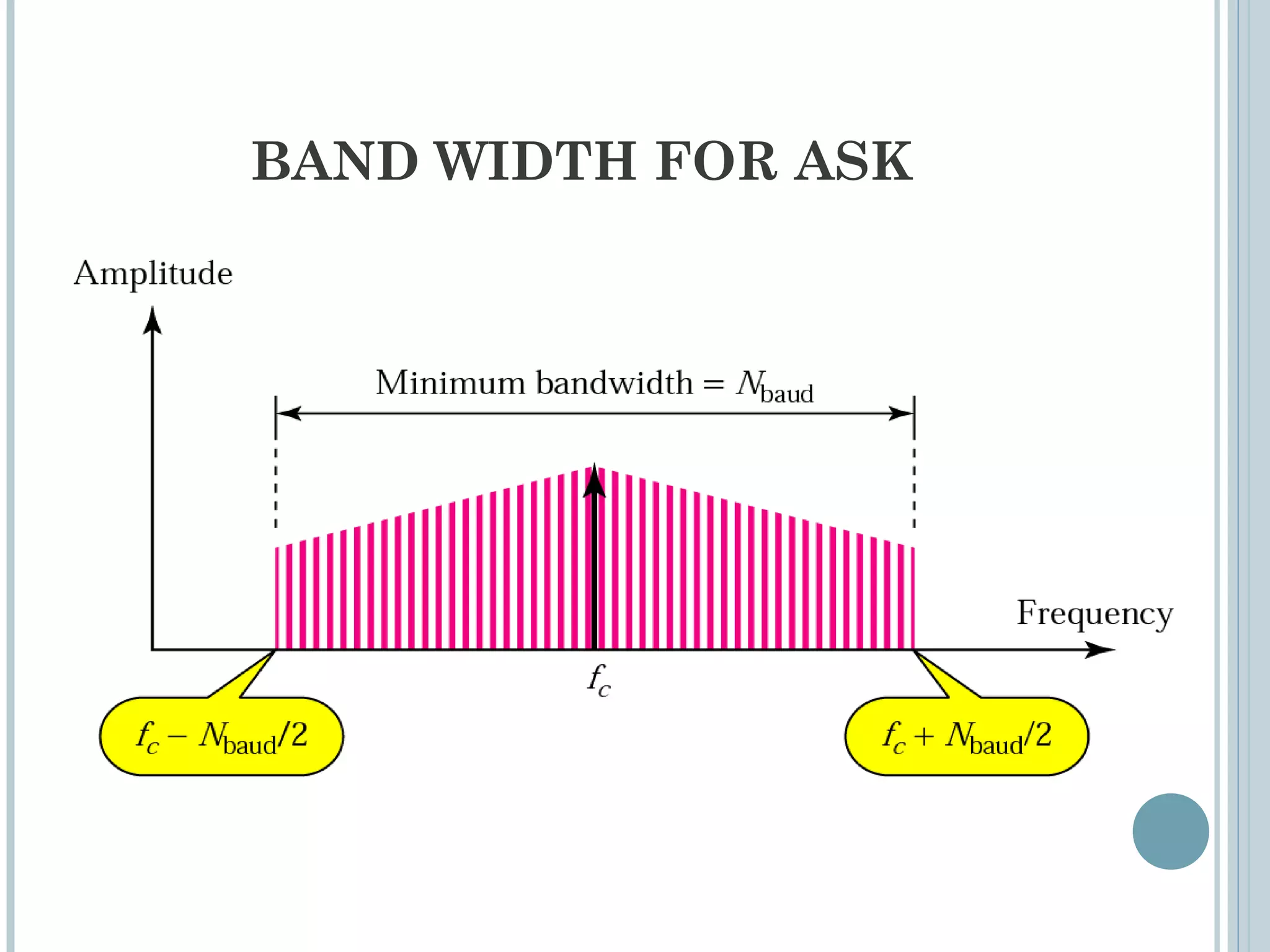
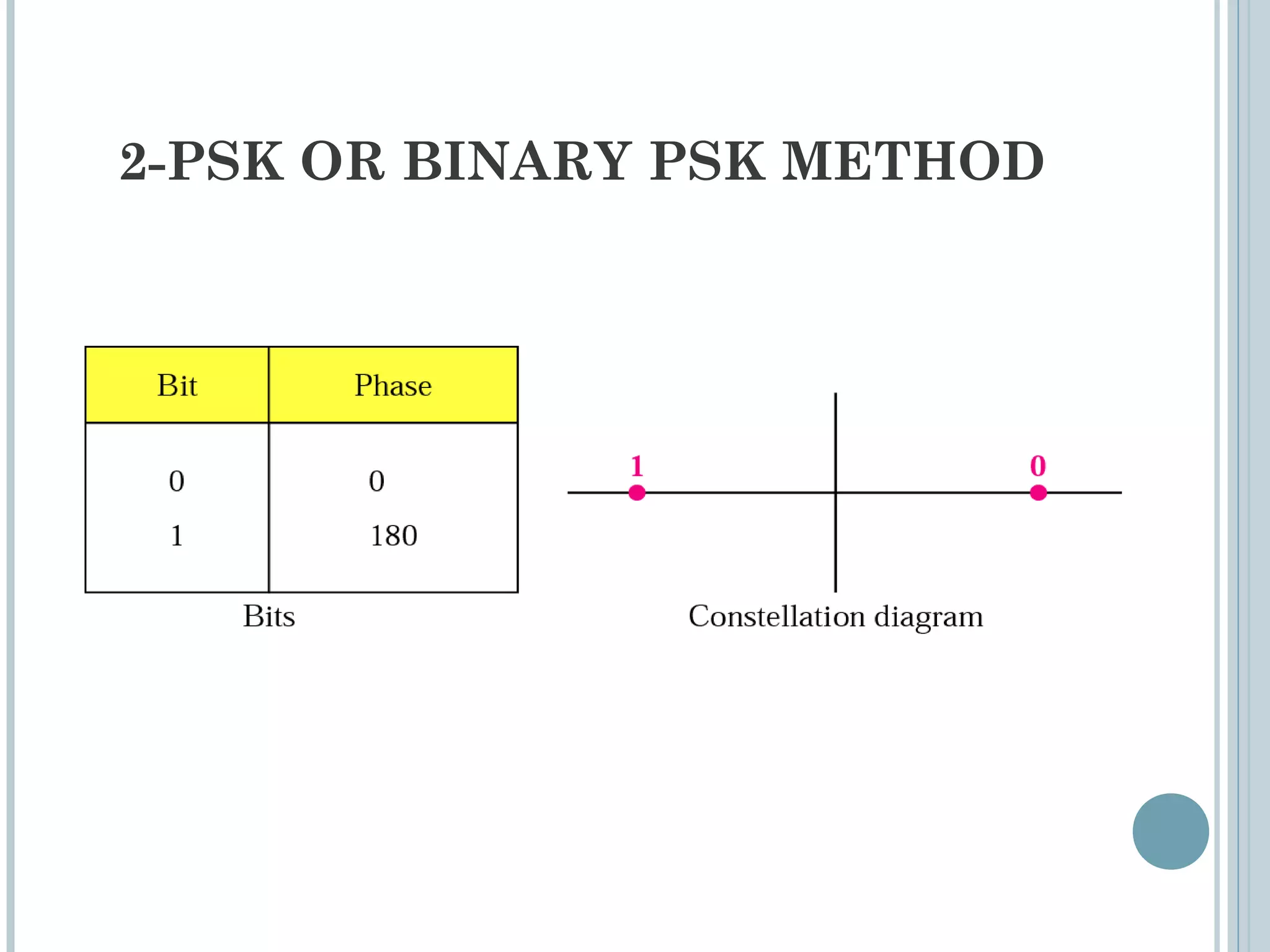
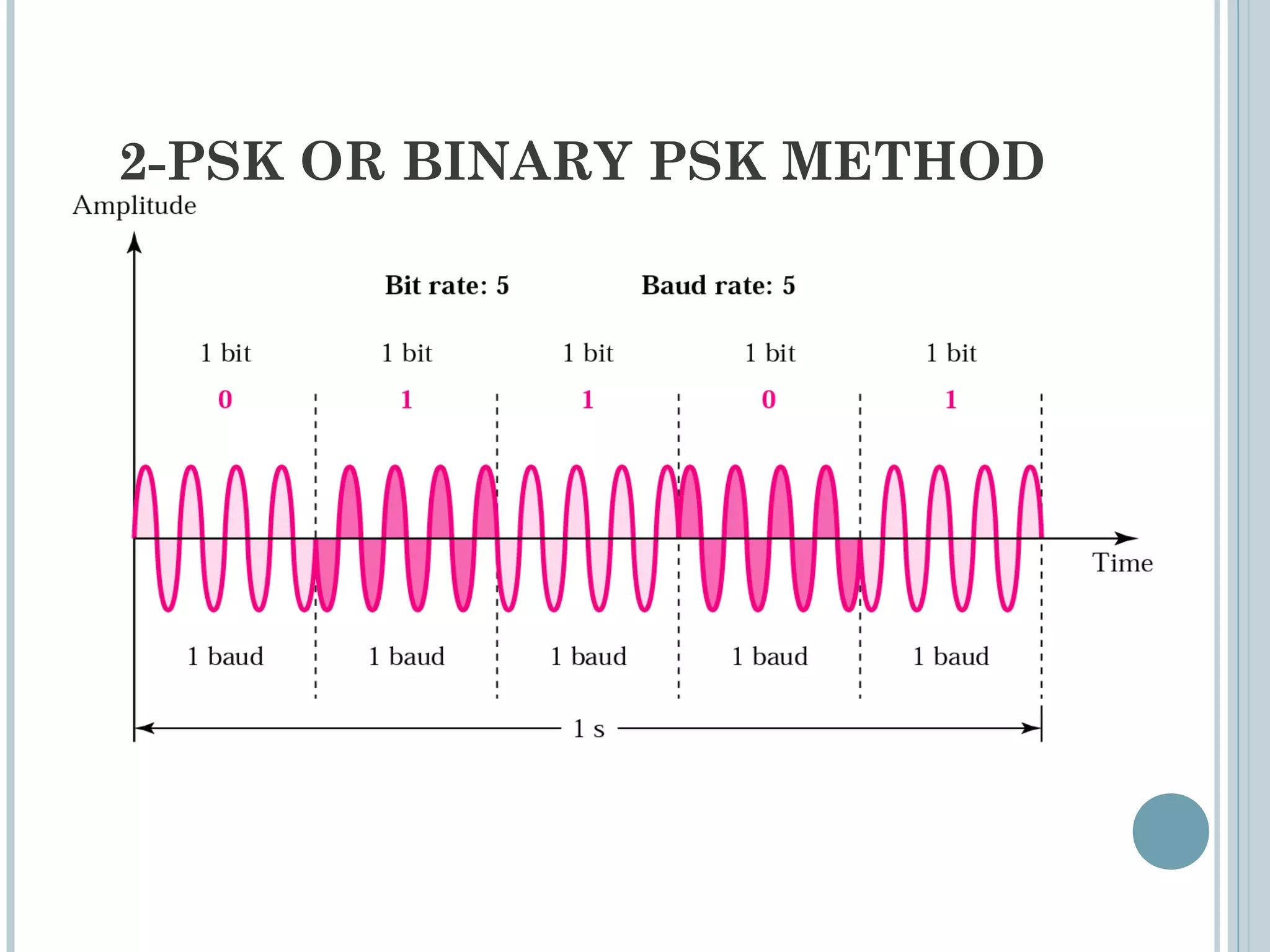
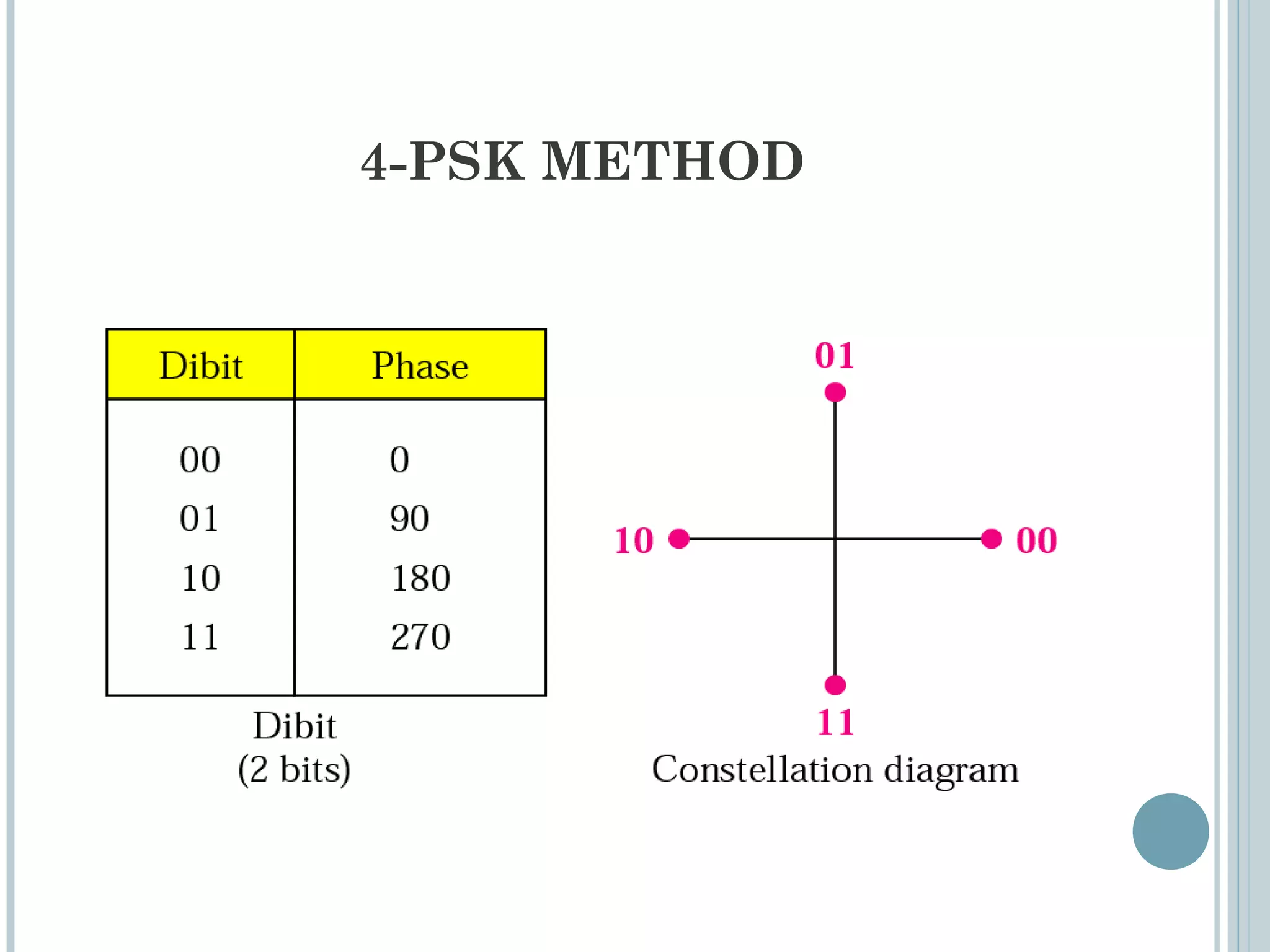
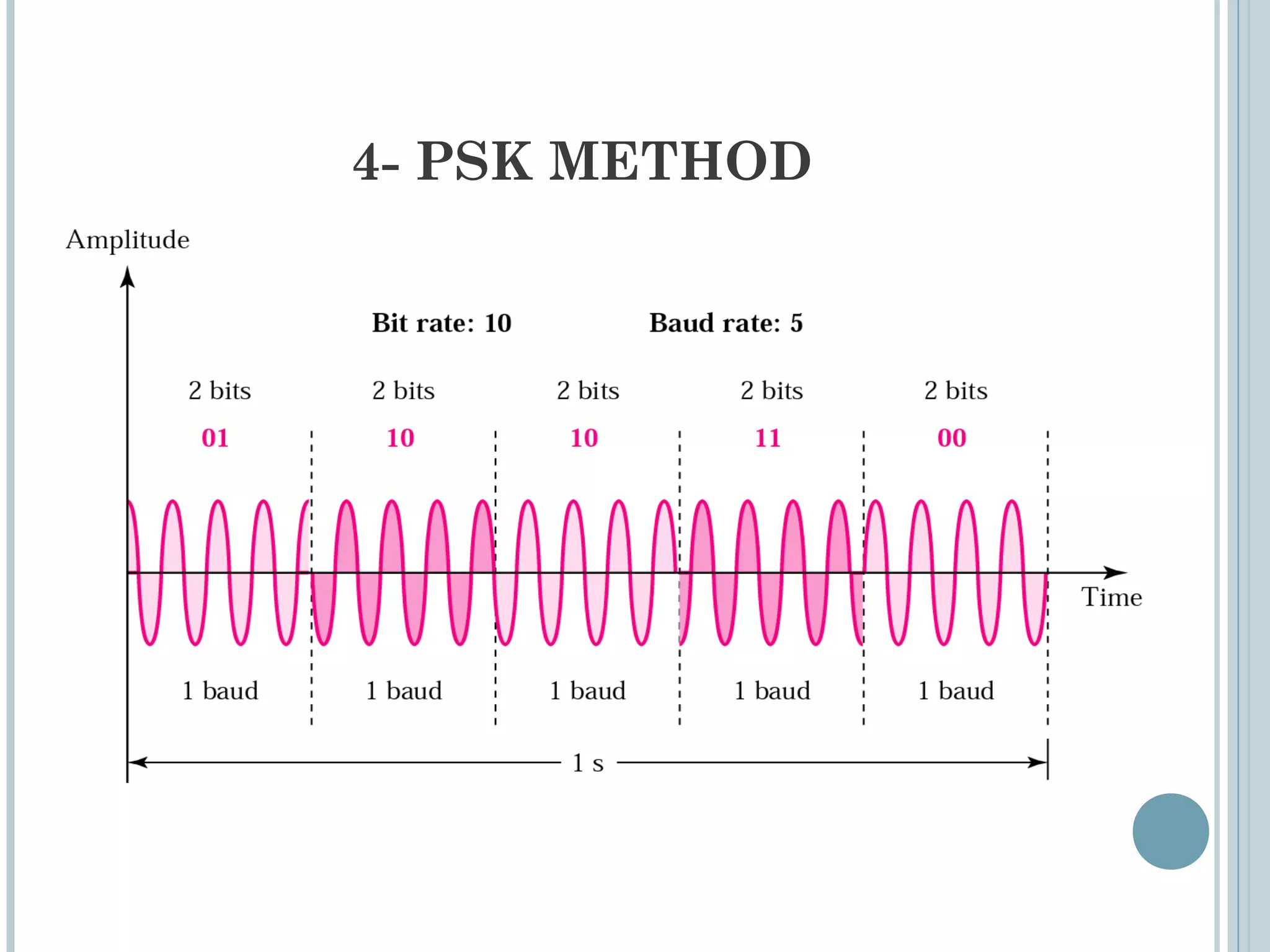
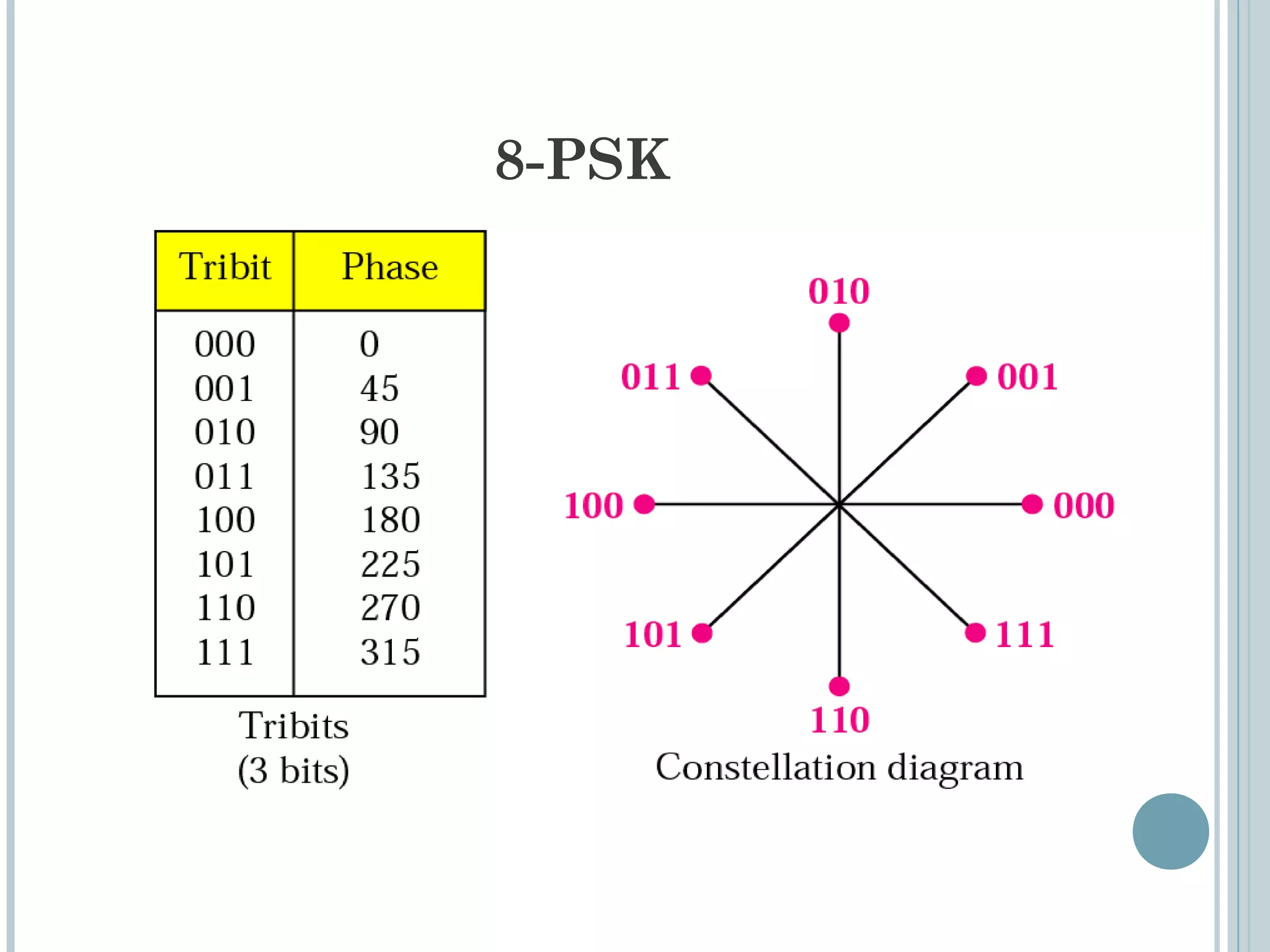
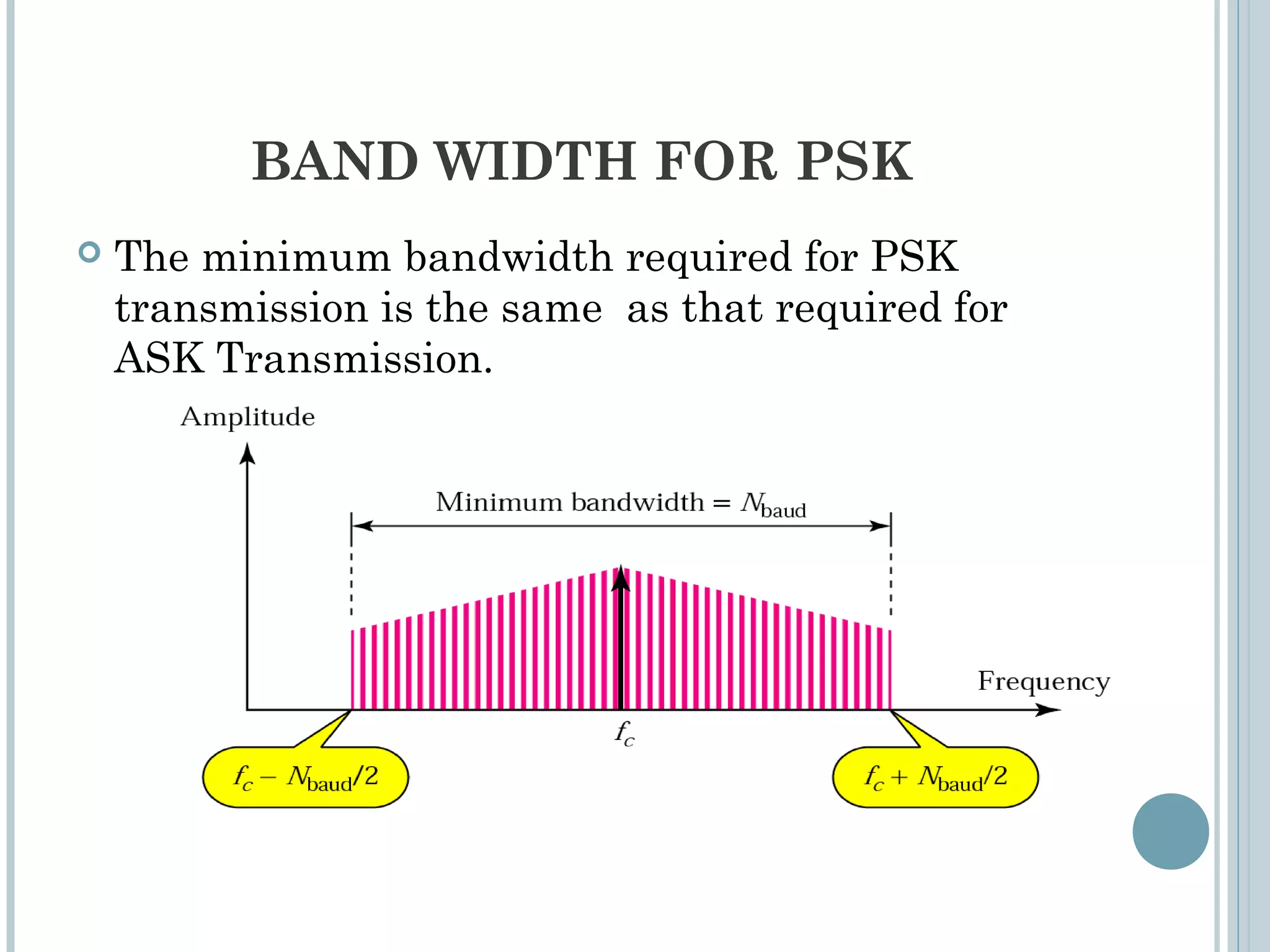
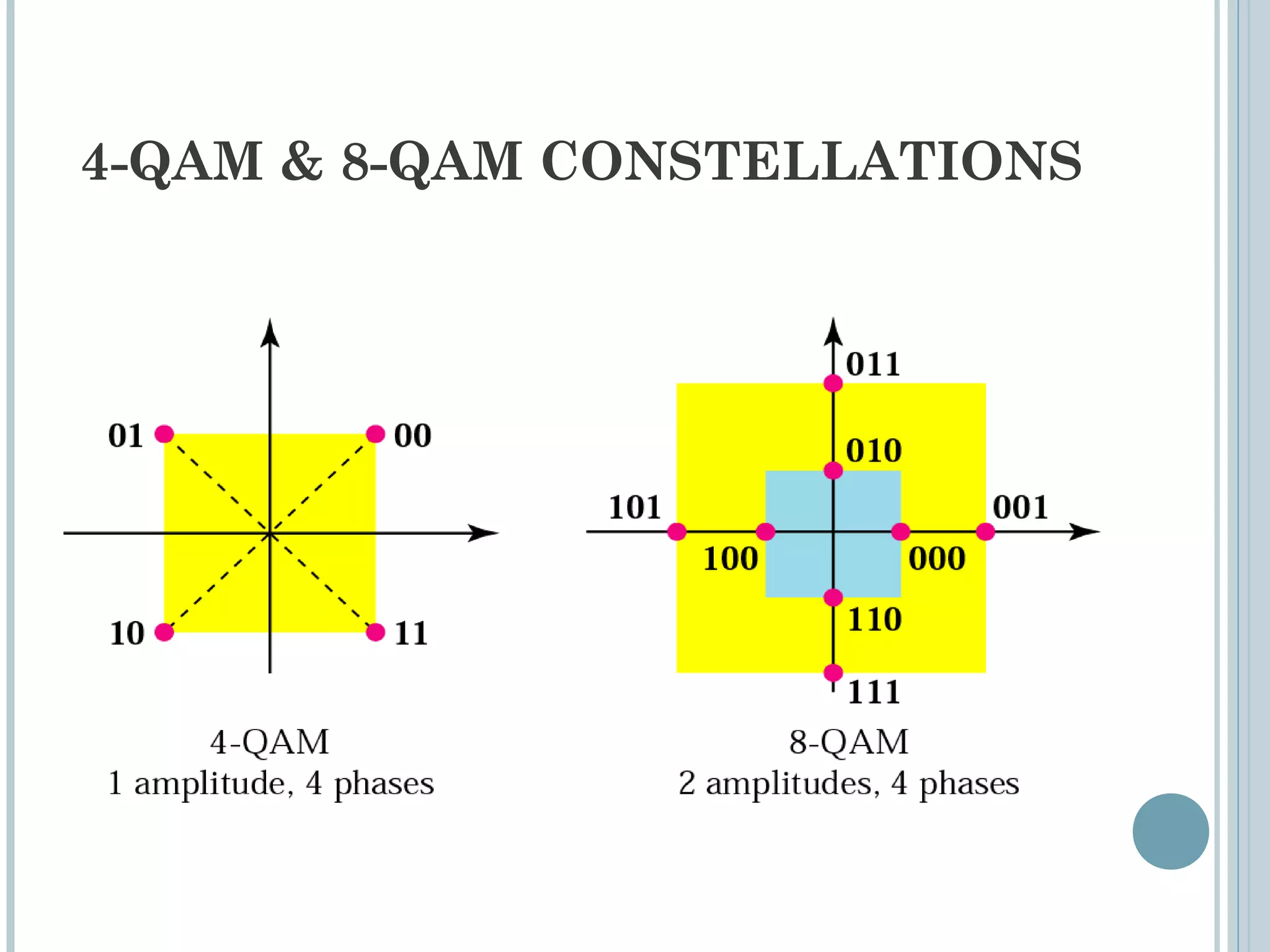
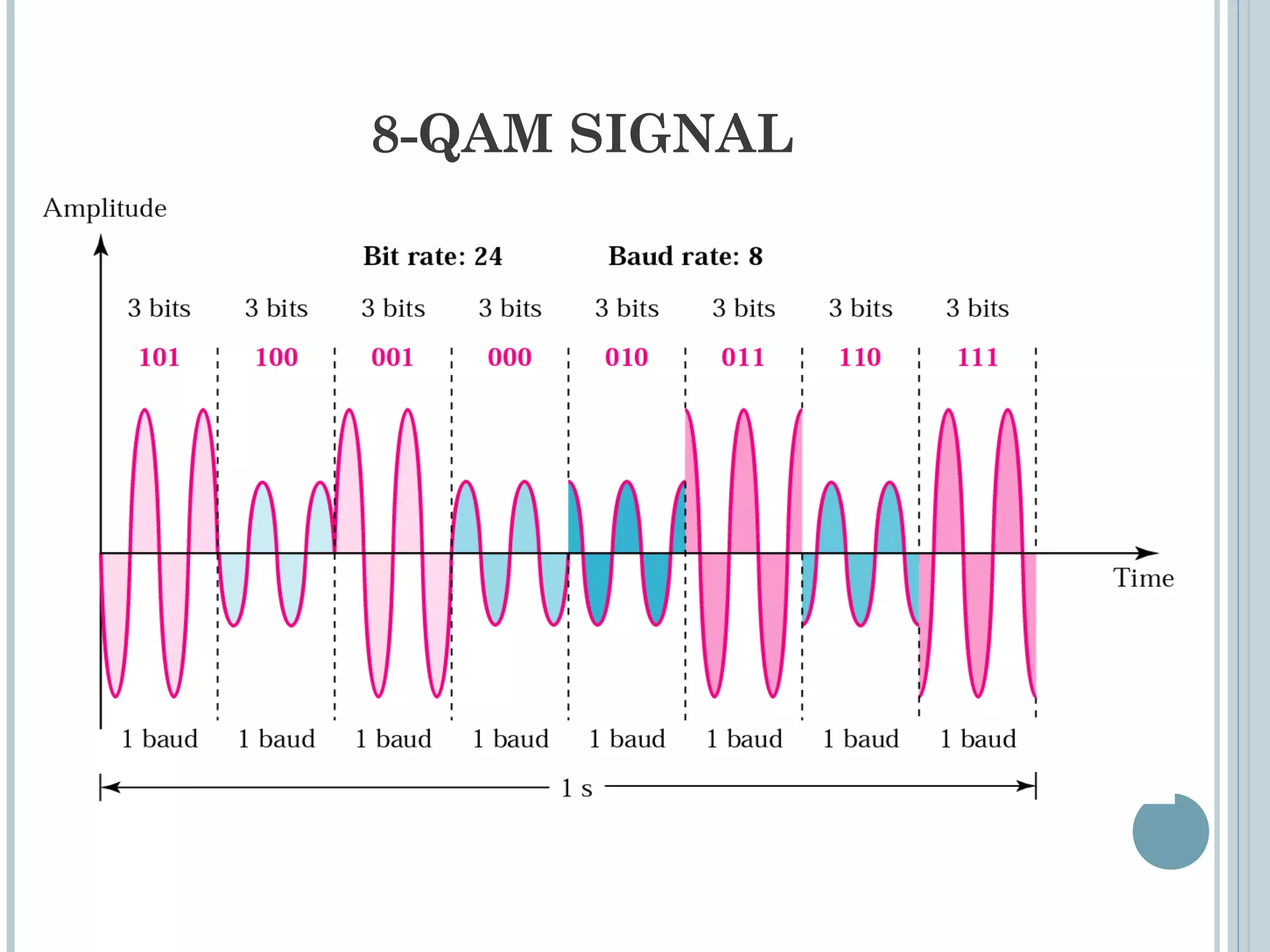
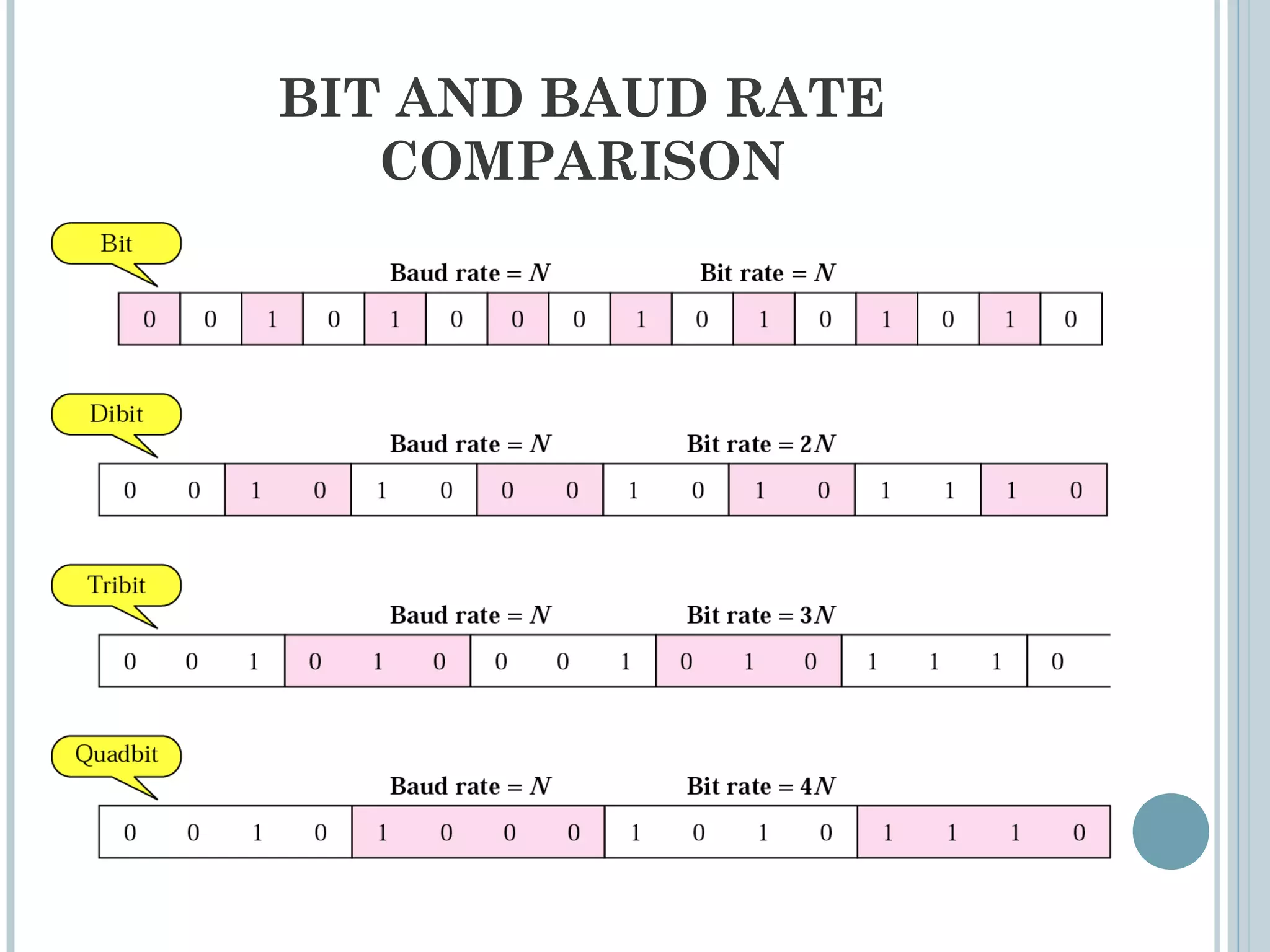
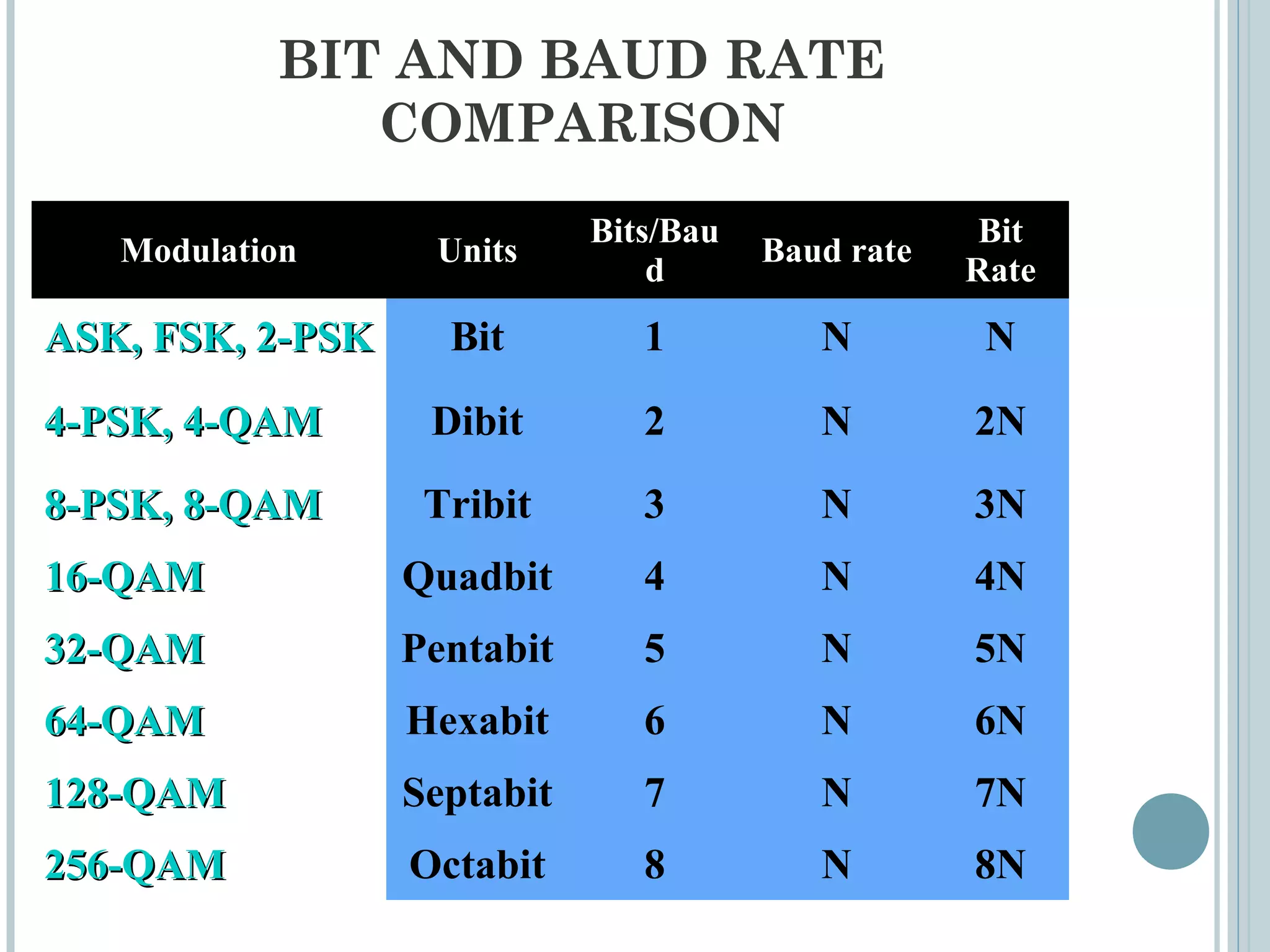
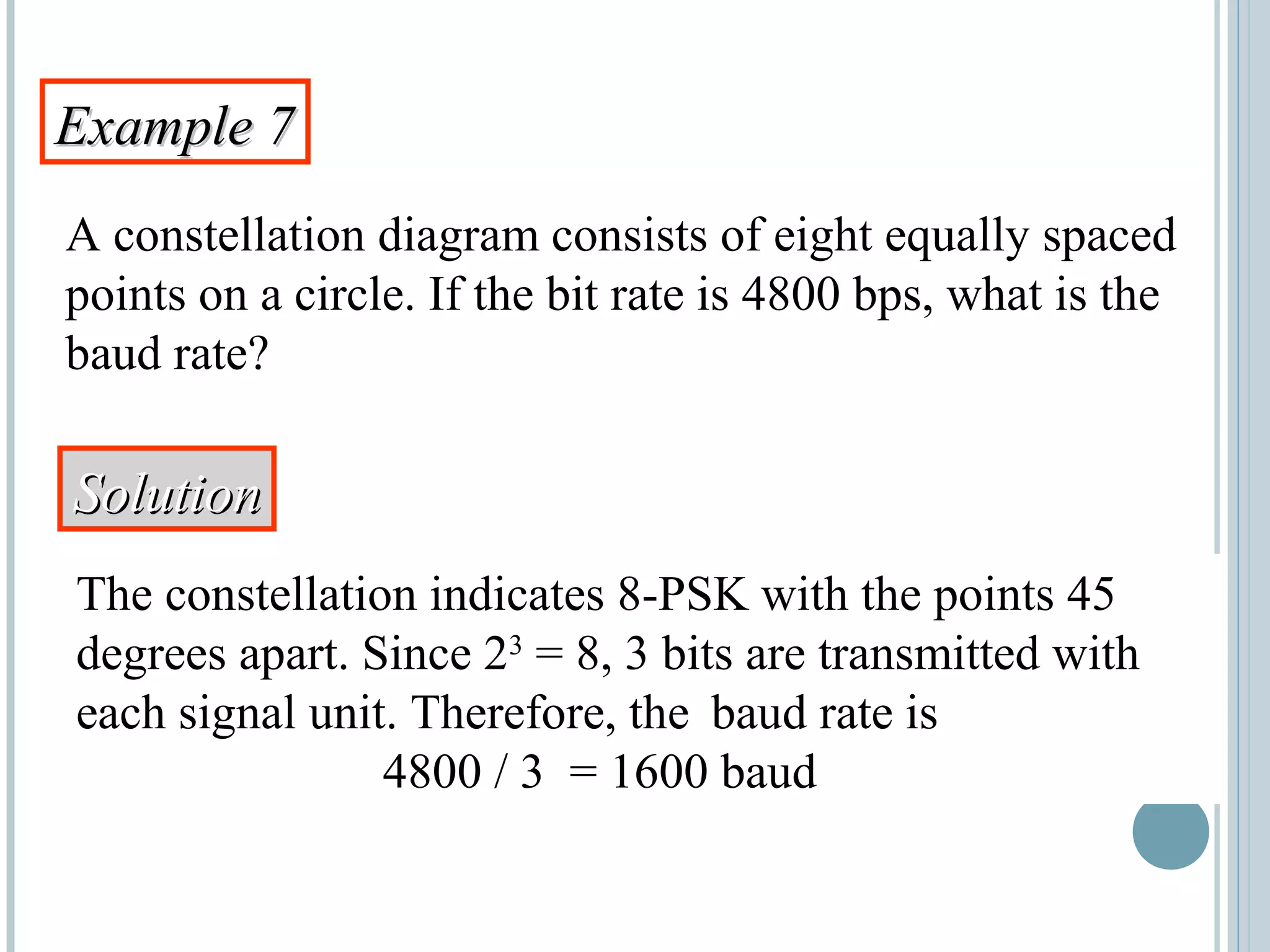
This document provides an overview of digital-to-analog modulation techniques used in data communications including: Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK), Frequency Shift Keying (FSK), Phase Shift Keying (PSK), and Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM). It defines these techniques, discusses their advantages and limitations, and provides examples of calculating bit rates and bandwidth requirements. Key points covered include how digital data is modulated onto an analog carrier signal, the relationship between bit rate and baud rate, and how more advanced modulations like QAM combine aspects of ASK and PSK.