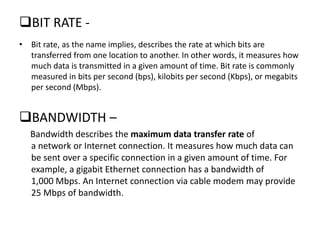
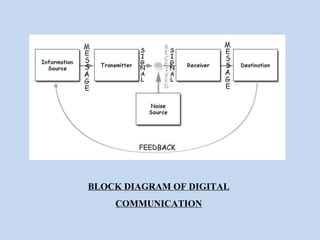
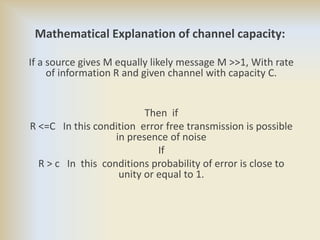
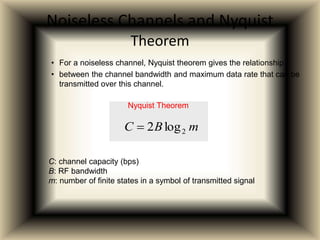
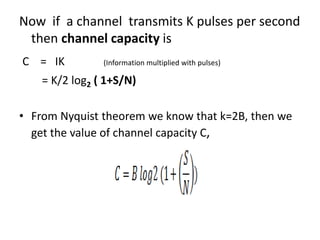
Channel capacity is the maximum rate at which information can be reliably transmitted over a communication channel, constrained by factors like bandwidth and noise power. The document explains key concepts such as bit rate, bandwidth, and digital communication, along with Shannon's mathematical framework for determining channel capacity. It concludes that Shannon's theory applies broadly across various fields beyond telecommunications, underscoring its significance in information theory.