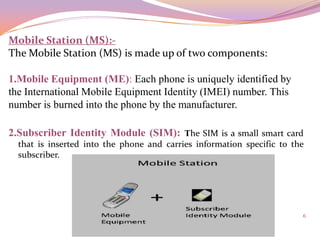
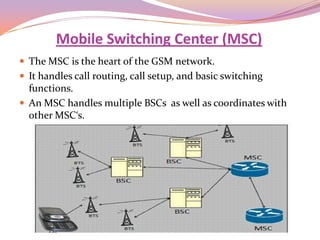
This document discusses the use of a sniffer device to detect lost mobile phones. It begins with an introduction to cellular systems including mobile stations, base transceiver stations, base station controllers, and mobile switching centers. It then explains that a sniffer is a mobile base station with a directional antenna and tracking software that can detect lost phones by their IMEI number. The sniffer works by intercepting signals from lost phones and locating them through GPS. While useful for finding lost phones cost effectively, sniffers have privacy and security disadvantages.