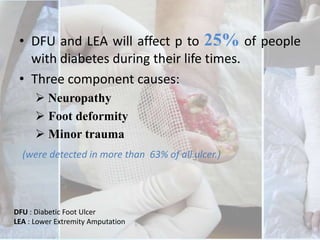
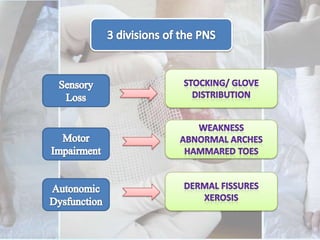
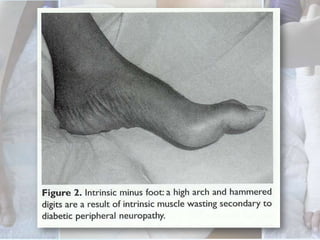
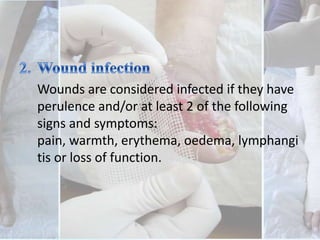
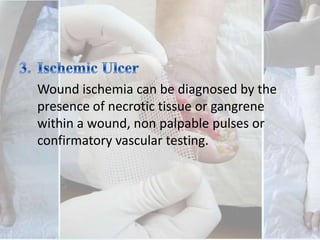
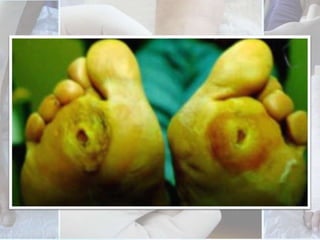
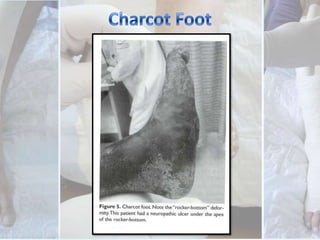
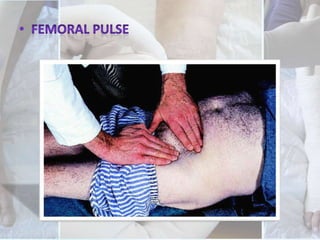
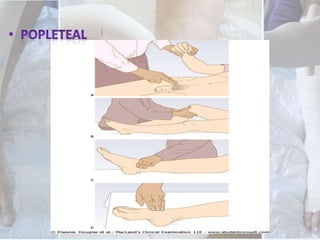
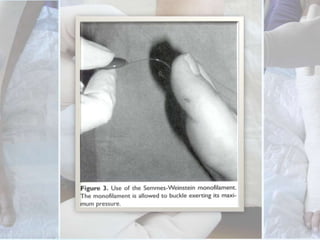
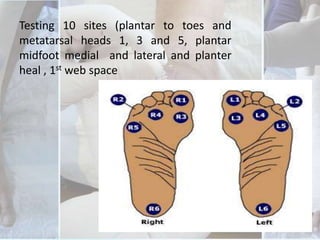
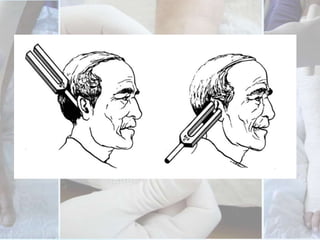
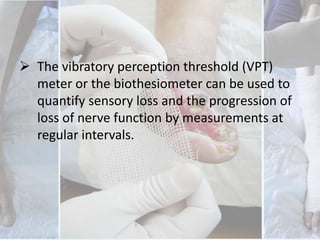
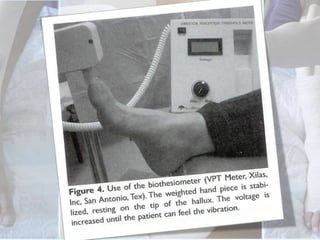
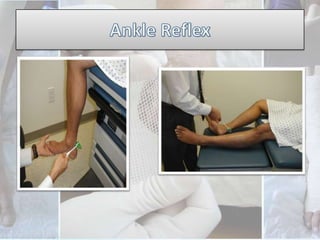
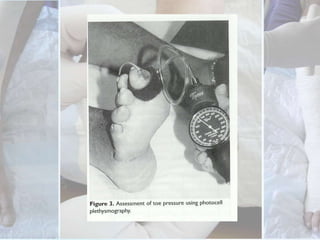
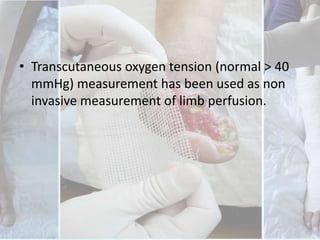
This document discusses the examination of diabetic feet, which are at risk for ulcers and lower extremity amputation. There are three main causes of diabetic foot complications: neuropathy, foot deformity, and minor trauma. It is important for clinicians to check for loss of protective sensation, foot deformities, and history of foot problems. The foot examination should inspect for deformities, ulcers, skin and nail integrity, and evaluate sensation using tests like monofilament and vibration. Vascular assessment includes checking pulses, ankle-brachial index, and other blood flow measurements. A thorough diabetic foot exam can detect problems and help prevent further complications.