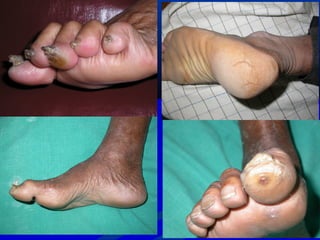
1) 5-15% of diabetics develop foot ulcers, and 70% of healed ulcers recur within 5 years. 85% of non-traumatic lower limb amputations occur due to diabetic foot ulcers.
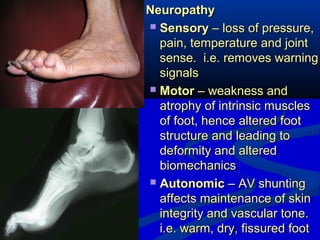
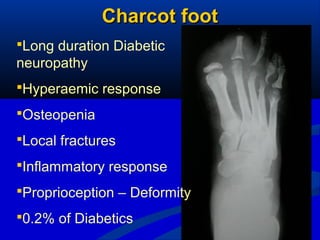
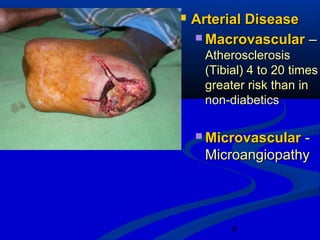
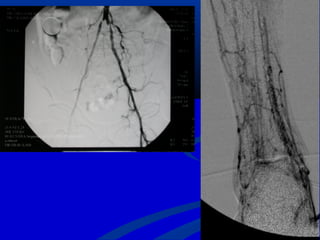
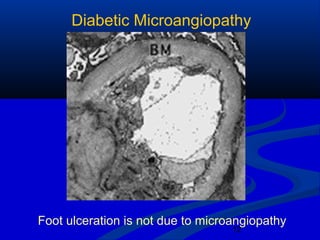
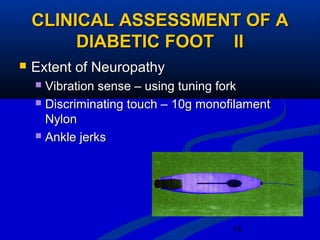
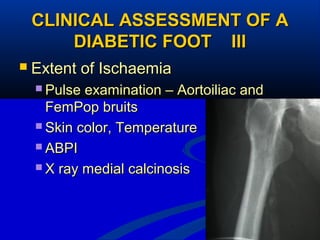
2) The main causes of diabetic foot ulcers are neuropathy, arterial disease, and an abnormal wound healing response. Neuropathy causes loss of sensation while arterial disease increases risk of atherosclerosis.
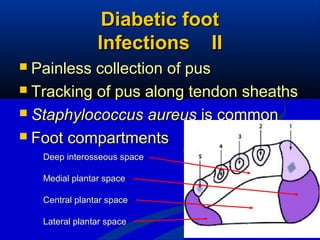
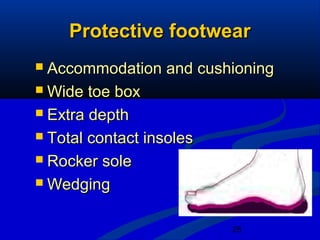
3) Management of diabetic feet focuses on prevention through patient education, regular examination and protective footwear. Treatment involves aggressive wound care, antibiotics, and sometimes surgery or amputation in severe cases.