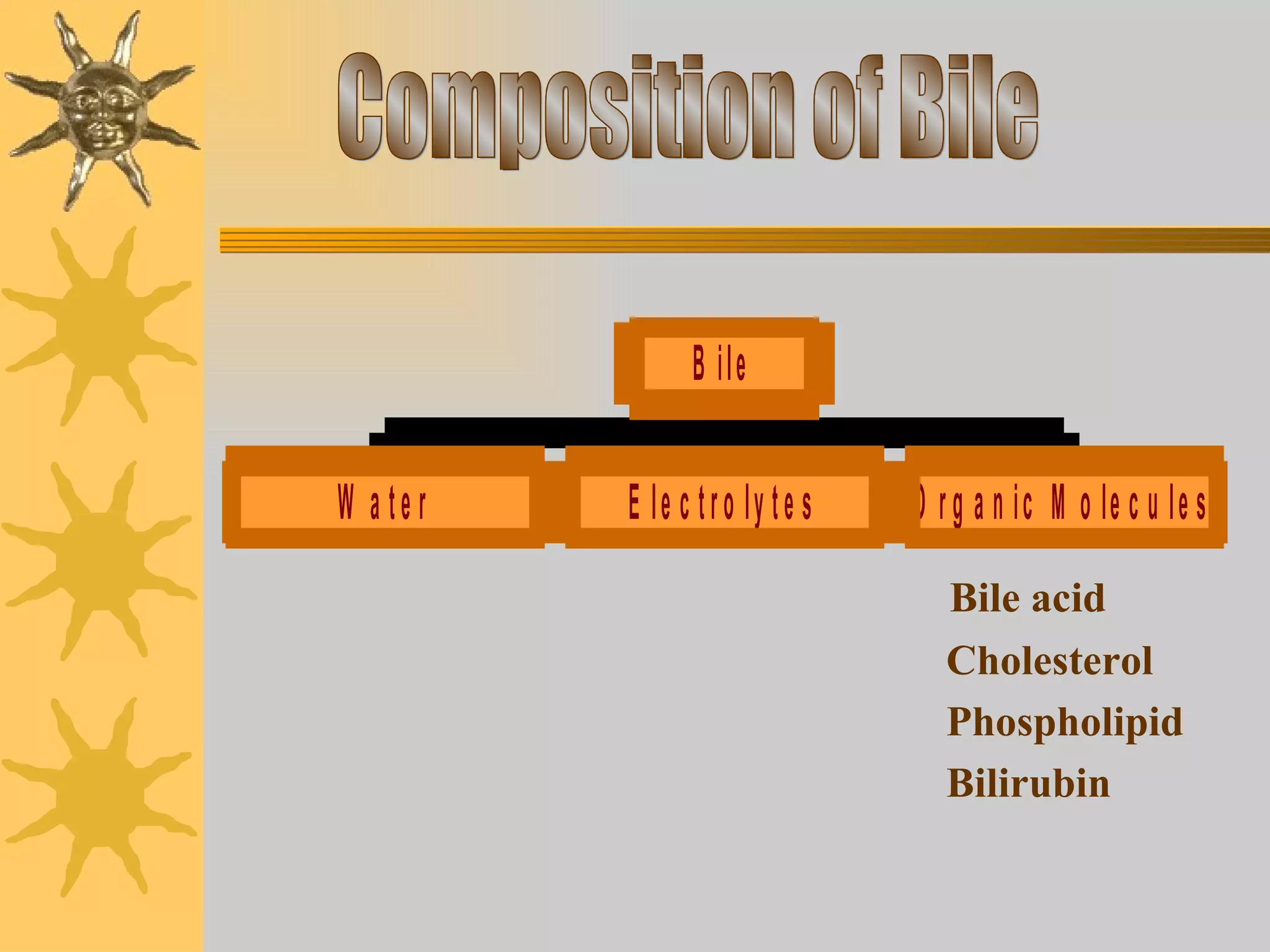
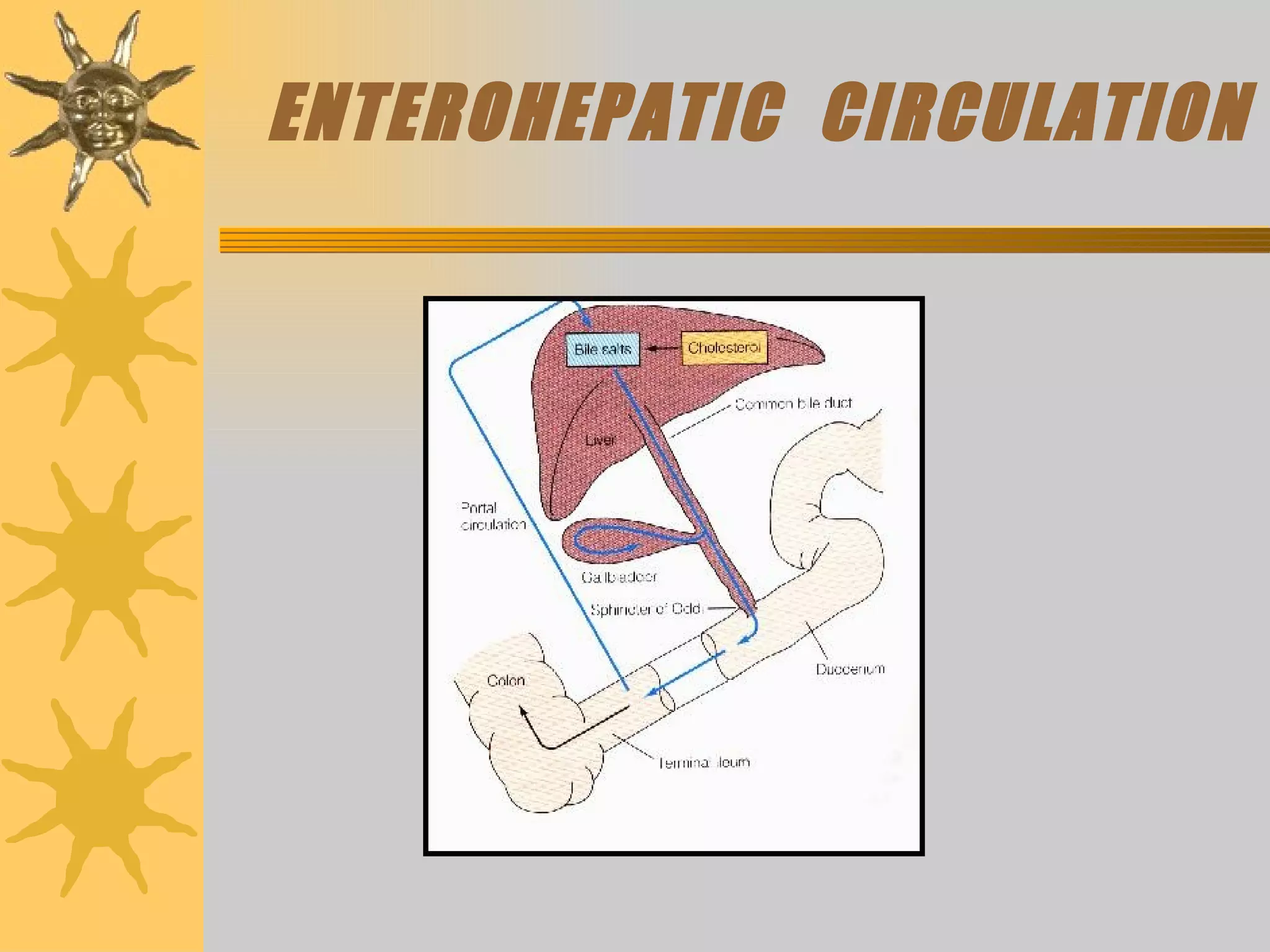
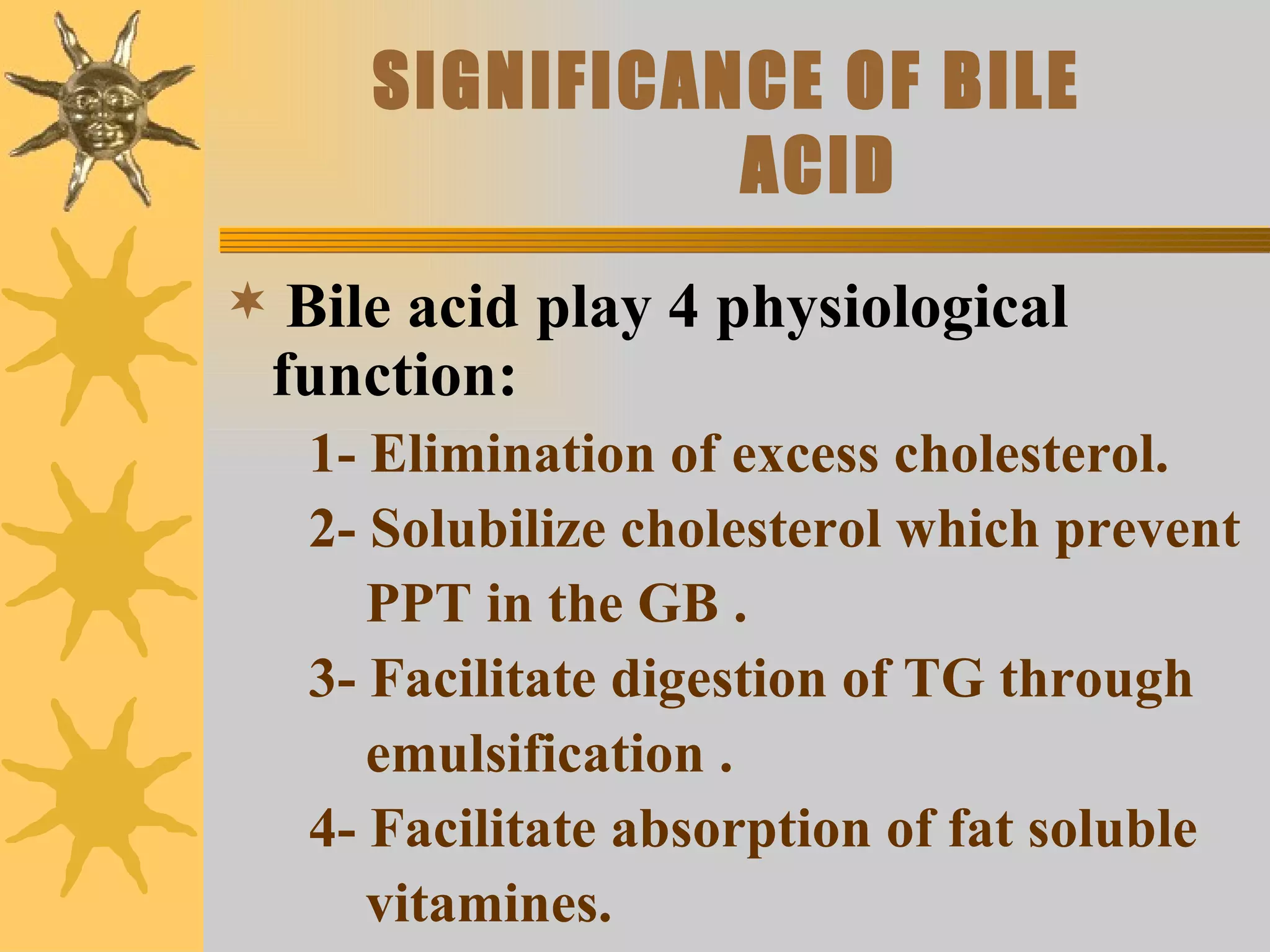
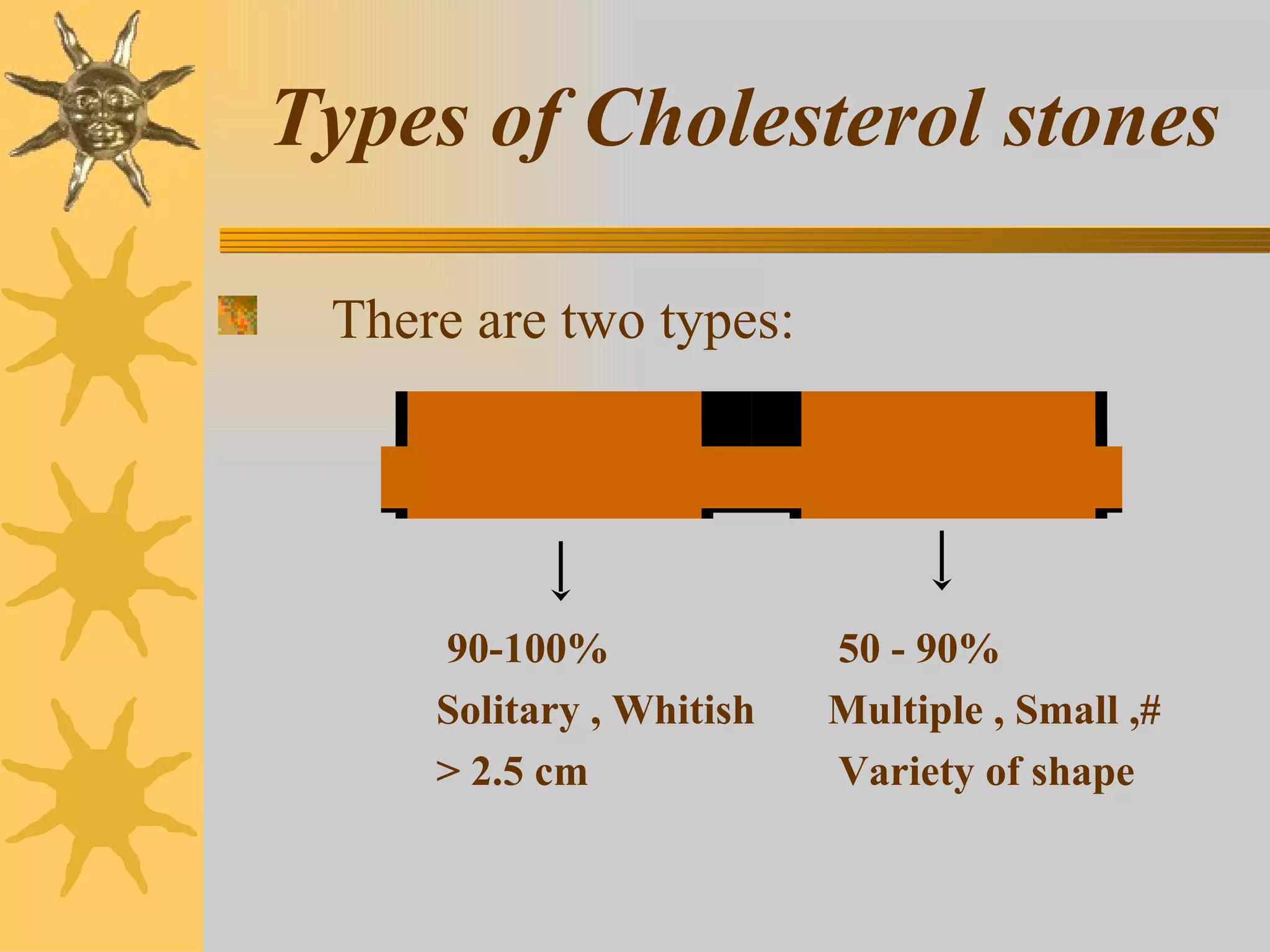
The document discusses the pathogenesis of gallstones. It begins by describing the anatomy of the liver and its role in bile synthesis. Bile is composed of cholesterol, bile acids, phospholipids, and bilirubin. Cholesterol in bile can precipitate to form gallstones under certain conditions. Gallstones are usually either cholesterol stones or pigment stones, with different risk factors and pathophysiological mechanisms for each. Gallstones may be asymptomatic but can also lead to complications if they block bile ducts or the pancreas.