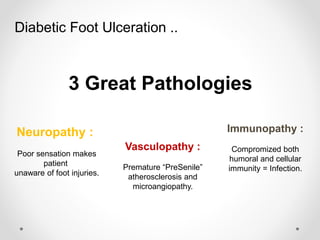
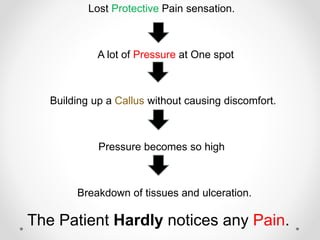
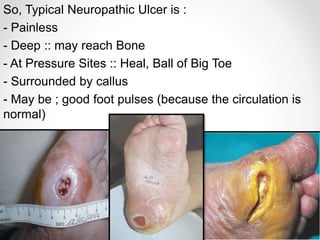
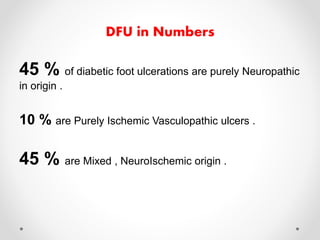
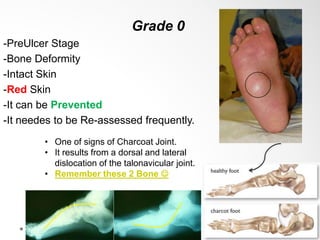
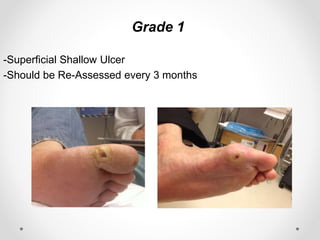
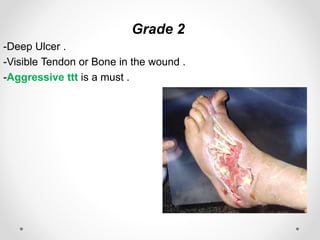
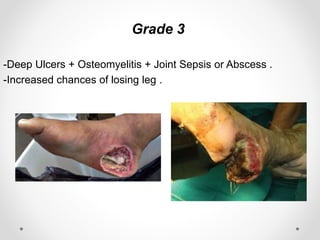
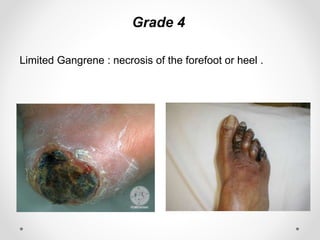
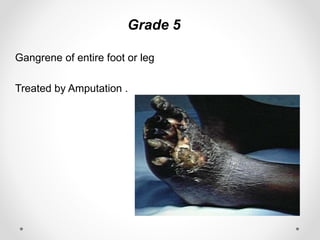
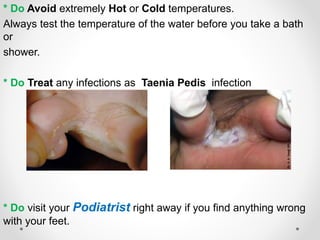
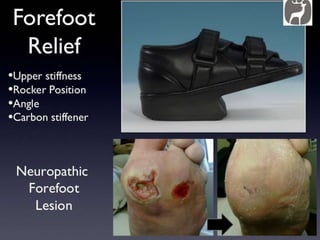
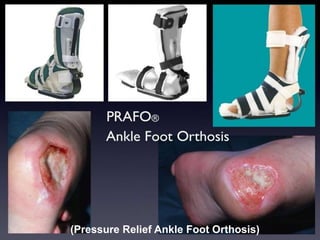
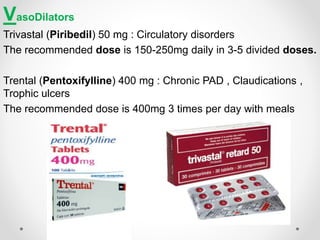
Diabetic foot disease is one of the most significant complications of diabetes. It involves foot ulcers associated with neuropathy and/or peripheral arterial disease in patients with diabetes. There are three main pathologies that contribute to diabetic foot disease: neuropathy, which causes loss of sensation and makes patients unaware of foot injuries; vasculopathy, which involves premature hardening of the arteries; and immunopathy, which compromises the body's immune response and increases risk of infection. Medical treatment of diabetic foot disease focuses on risk identification, foot examination, patient education, and management of diabetes, foot care, and medications to promote circulation and prevent ulcers.