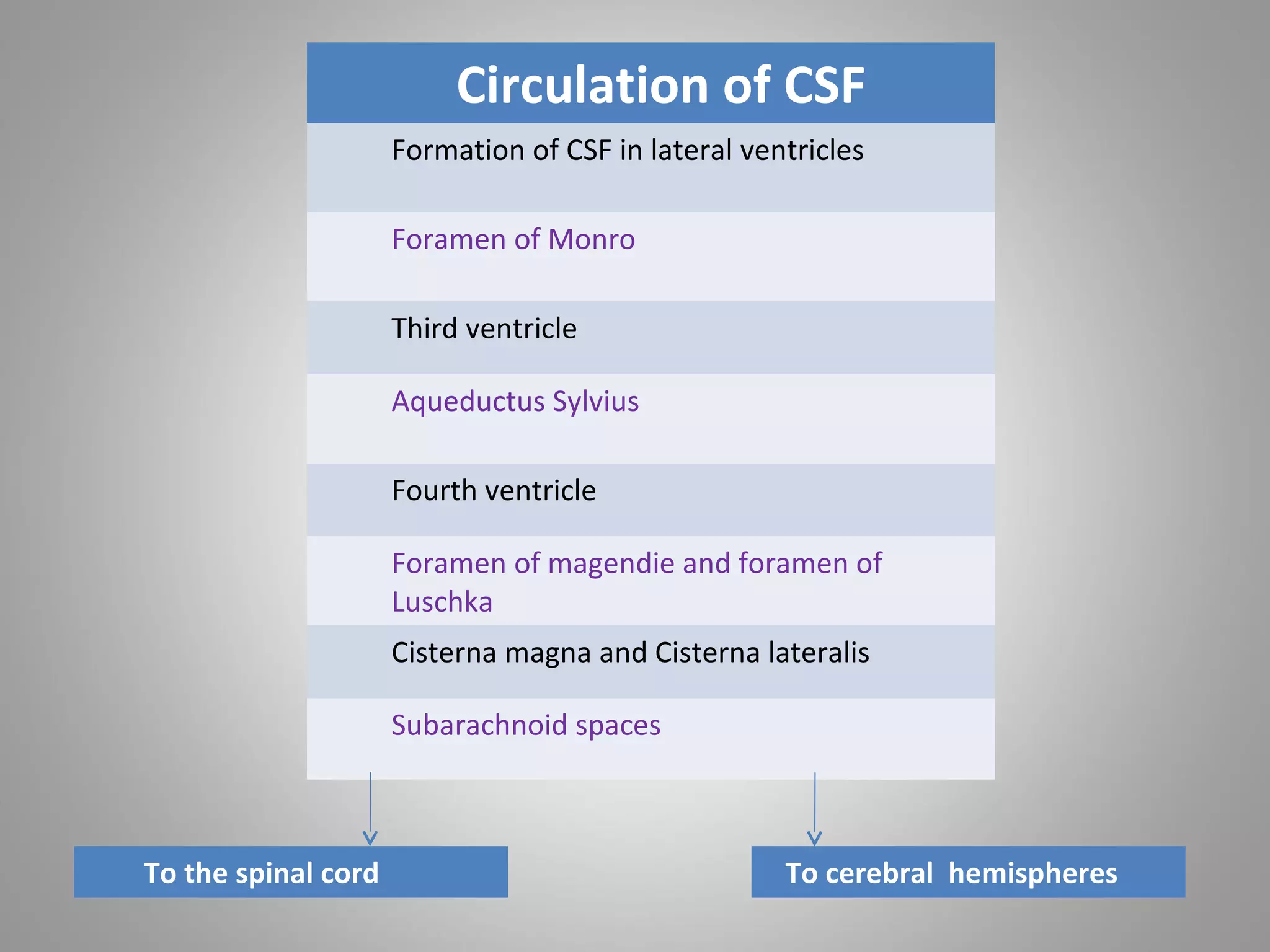
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) circulates through the brain, spinal cord, and subarachnoid space. It is composed primarily of water but also contains electrolytes, proteins, sugars, and lymphocytes. CSF is produced by the choroid plexus in the ventricles and circulates from the ventricles through the brain and spinal cord before being absorbed into the bloodstream by the arachnoid villi and spinal veins. It acts as a cushion and medium of exchange to protect the brain and spinal cord and transport nutrients and waste. Hydrocephalus is a condition where excess CSF accumulates in the brain, which can cause headaches, vomiting, brain atrophy, and other symptoms.