Embed presentation
Download to read offline

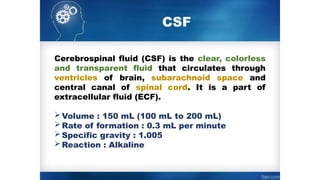
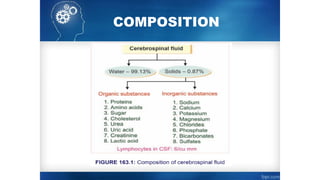

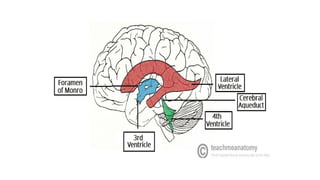
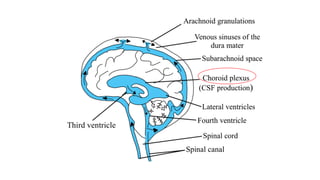
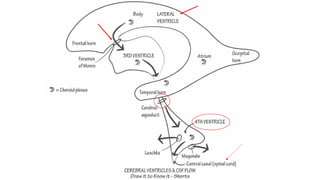
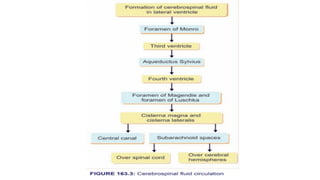




Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless fluid that circulates in the brain and spinal cord, with a volume of approximately 150 ml and a formation rate of 0.3 ml per minute. It is produced by choroid plexuses in the ventricles and serves several functions, including protecting the brain from injury, regulating cranial volume, and facilitating substance exchange between blood and brain tissues.











