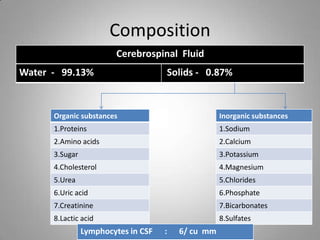
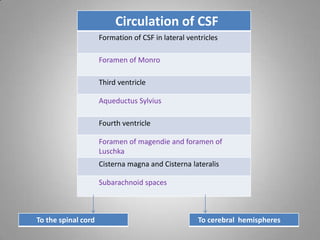
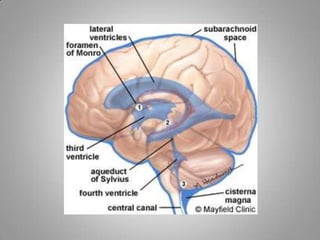
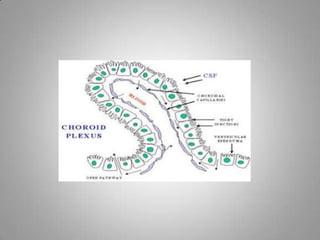
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) circulates through the brain, spinal cord, and subarachnoid space. It is produced by the choroid plexus in the ventricles and is absorbed by the arachnoid villi into the dural sinuses. CSF acts as a protective buffer and aids in nutrient exchange; its composition is similar to extracellular fluid with higher sodium than potassium levels. CSF pressure varies with body position and can be measured via lumbar puncture for diagnostic purposes.