Design Factors in Orthodontic Appliance
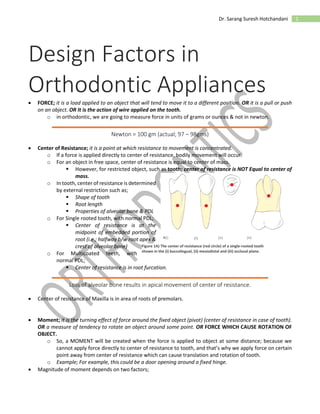
- 1. 1Dr. Sarang Suresh Hotchandani Design Factors in Orthodontic Appliances FORCE; it is a load applied to an object that will tend to move it to a different position. OR it is a pull or push on an object. OR It is the action of wire applied on the tooth. o in orthodontic, we are going to measure force in units of grams or ounces & not in newton. Newton = 100 gm (actual; 97 – 98gms) Center of Resistance; it is a point at which resistance to movement is concentrated. o If a force is applied directly to center of resistance, bodily movement will occur. o For an object in free space, center of resistance is equal to center of mass. However, for restricted object, such as tooth; center of resistance is NOT Equal to center of mass. o In tooth, center of resistance is determined by external restriction such as; Shape of tooth Root length Properties of alveolar bone & PDL o For Single rooted tooth, with normal PDL; Center of resistance is at the midpoint of embedded portion of root (i.e.; halfway b/w root apex & crest of alveolar bone) o For Multicoated teeth, with normal PDL; Center of resistance is in root furcation. Loss of alveolar bone results in apical movement of center of resistance. Center of resistance of Maxilla is in area of roots of premolars. Moment; it is the turning effect of force around the fixed object (pivot) (center of resistance in case of tooth). OR a measure of tendency to rotate an object around some point. OR FORCE WHICH CAUSE ROTATION OF OBJECT. o So, a MOMENT will be created when the force is applied to object at some distance; because we cannot apply force directly to center of resistance to tooth, and that’s why we apply force on certain point away from center of resistance which can cause translation and rotation of tooth. o Example; For example, this could be a door opening around a fixed hinge. Magnitude of moment depends on two factors; Figure 1A) The center of resistance (red circle) of a single-rooted tooth shown in the (i) buccolingual, (ii) mesiodistal and (iii) occlusal plane.
- 2. 2Dr. Sarang Suresh Hotchandani o Magnitude of force applied o Perpendicular distance from the center of resistance to line of action of force. So, moment will be created when the line of force does not pass through the center of resistance. Moment = F x d So, more force will be required to cause moment when the force is applied near to center of resistance, means if the moment arm is small more force is required to cause Moment or rotation in that tooth. The size of a moment is equal to the magnitude of the force (F) multiplied by the distance from the tooth’s center of resistance (d) from which it acts. Couple; two forces equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. o Its effect is to create pure rotation without translation. – that’s why aka couple force or pure moment. A couple, as shown on the left, is defined as two forces equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. The application of a couple produces pure rotation. In clinical application, two unequal forces applied to the crown of a tooth to control root position can be resolved into a couple and a net force to move the tooth. o If a 50-gm force were applied to a point on the labial surface of an incisor tooth 15 mm from the center of resistance, a 750 gm-mm moment (the moment of the force, or Mf) would be produced, which will cause tipping of the tooth. o To obtain bodily movement, we must apply a couple to create a moment (the moment of the couple, or Mc) equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the original movement. o One way to do this would be to apply a force of 37.5 gm pushing the incisal edge labially at a point 20 mm from the center of resistance. o This creates a 750 gm-mm moment in the opposite direction, o So, the force system is equivalent to a couple with a 12.5 gm net force to move the tooth lingually. With this force system, the tooth would not tip, but with so light a net force, there would be only a small amount of movement. o To achieve a net 50 gm for effective movement, it would be necessary to use 200 gm against the labial surface and 150 gm in the opposite direction against the incisal edge. o Controlling the forces of this magnitude with a removable appliance is very difficult, and that’s why effective root movement is much more achievable with a fixed appliance. Center of Rotation; it is the point around which rotation occurs when an object is being moved. o Center of rotation can be very close to center of resistance, but it will never coincide with center of resistance. When two forces are applied simultaneously as couple to an object, we can control the center of rotation and made to have any desired location.
- 3. 3Dr. Sarang Suresh Hotchandani Use of Forces, Moments and Couples in Tooth Movement Take an example of protruding maxillary central incisors. Now, if we apply single force of 50gm on the crown of tooth 15mm away from center of resistance, it will produce 750 gm.mm of moment/rotation; o So, the result will be crown will be retracted and apex will move in opposite direction; means protracted and its inclination will change. Because, force is not passing from center of resistance. However, we want to retract that central incisor without changing the inclination; means without rotation; o We must remove the rotation; means moment which is created by the force. Now there are various methods to overcome this moment as mentioned below; 1st way; apply the force closer to center of resistance. But clinically, it is not possible to apply force in the center of resistance. o But, if we construct appliance in such a manner that some rigid attachment that project toward the root, and then we apply force on that attachment, so that line of force passes from center of resistance. o This attachment reduces the moment arm and tipping (rotation) Figure 2 Blue; Center of Rotation - Red; Center of Resistance
- 4. 4Dr. Sarang Suresh Hotchandani So, longer the hook, more it is near to center to resistance; BUT; o There are greater chances of oral hygiene problems leading to gingival irritation or decalcification. 2nd method is to create Couple force; to avoid the tipping and overcome the moment created with single force mentioned above; o So, if we are using functional appliance, we must create the couple force on lingual direction to overcome the tipping. But this is clinically difficult. So, the best solution is to use a fixed appliance on the tooth, so the forces can be applied at two points on the facial surface. o If round wire is used, auxiliary spring is needed to produce moment of couple. (figure; 9 – 20 in Proffit) A rectangular wire fitting into a rectangular bracket slot on the tooth is most widely used because the entire force can be produced by single wire. Mc/Mf Ratios & Control of Root Position In above discussion, we saw that control of root position during movement requires both; force to move the tooth (moment of force) in desired direction & couple to produce the opposing momentum for control of root position. This ratio controls the position of center of rotation & describe how a tooth will respond. The heavier the moment of force, the larger the moment of couple force. Mf; moment created after applying the force to crown of tooth. Mc; moment of couple to overcome the tipping. Mc/Mf = 0 Pure Tipping (uncontrolled tipping) (tooth rotates around center of resistance), center of rotation same as center of resistance. 0< Mc/Mf <1 Controlled Tipping, CO Rotation displaced farther away from CO Resistance Mc/Mf = 1 Bodily movement/translation, CO Rotation is at Infinity Mc/Mf > 1 Root Torque/Root Uprighting/torqueing movement (root apex moves more than crown), here CO Rotation is moved incisally from center of resistance. Uncontrolled Tipping; crown moves in direction of force & root apex moves in opposite. Controlled Tipping; crown moves in the direction of force & No change in position of root. For most teeth, moment arm is 8 – 10 mm MOMENT TO FORCE RATIOS; o Moment to force ratio; 1to 7 – will produce controlled tipping. o Moment to force ratio; 8 to 10 – will produce bodily movement o Moment to force ratio; more than 10 – will produce torque Because the distance from the point of force application to the center of resistance can and does vary, moment-to-force ratios must be adjusted if following factors differs from usual condition. o root length o amount of alveolar bone support
- 5. 5Dr. Sarang Suresh Hotchandani o point of force application differs from the usual condition. When we apply the force on bracket via arch wire, the force which is felt by tooth is not same as the force which we applied, but it is less than that. Some force is lost during the friction which is present b/w bracket and arch wire. o So, the net force (after frictional resistance is subtracted) and the moment after that subtracted net force is important. o While, in the couple force, no friction is present. Matlab jeko wire san force deendas una man thoro force nikri wendo friction je kare aen baaki jeko force bachyp ooho wani tooth khe lagando aen una bachal force man jeka moment nikrandi ooha asan je kam ji aa.. jadahin ta jeka equal and opposite couple force jeko produce theendo ooho wari original force je hisab san hundo sho jo una me ka friction naahe. Means couple force wadheek hundo as compare to una force je jeko tooth te lage to friction man cut kare. Effect of NARROW v/s W I D E brackets in Fixed Appliance System Control of root position occurs in two circumstances; o Torqueing the root facially or lingually. Here moment is generated within the bracket and depends on dimension of arch wire & moment arm depend on depth of slot of bracket o Mesio distal root movement for proper paralleling of teeth during space closure. Here moment is generated across the bracket & the width of bracket determine the length of moment arm (half the width of bracket) see figure The wider the bracket, the easier will be to generate moment; because moment arm will increase & less force will be required to create moment. o Consider retracting the root of a canine tooth into a first premolar extraction site. With a retraction force of 100 gm and a 10-mm distance from the bracket to the center of resistance, a 1000 gm-mm moment will be needed. If the bracket on this tooth is 1 mm wide, 1000 gm of force will be needed at each corner of the bracket, but if the bracket is 4 mm wide, only 250 gm of force at each corner will be necessary. Advantages of W I D E brackets; o Large moment arm o Decreased force to generate the moment o Decreased Contact angle; High contact angle increases the friction b/w arch wire & bracket and decrease the amount of force transferred to tooth. NOTE; Teeth move along the arch wire as bead along string & that’s why wide brackets are advantageous for space closure by sliding. Disadvantages of W I D E brackets; o Wider the bracket, smaller the inter – bracket distance b/w adjacent teeth. This will lead to decrease in the length of wire b/w two brackets; and as we read in previous sections that;
- 6. 6Dr. Sarang Suresh Hotchandani o Decrease in length will decrease the springiness & range of wire. So, that’s why extremely wide brackets are contraindicated; o The maximum width of wide bracket should be half the width of tooth. Advantage of Narrow Brackets; o Can be used in mal – aligned teeth. o More springiness in wire. Disadvantage of Narrow Brackets; o High contact angle o Increased force THE END Written By: DR. SARANG SURESH HOTCHANDANI (BDS) Bibi Aseefa Dental College, SMBBMU. Larkana, Sindh, Pakistan hotchandaniss@hotamil.com
