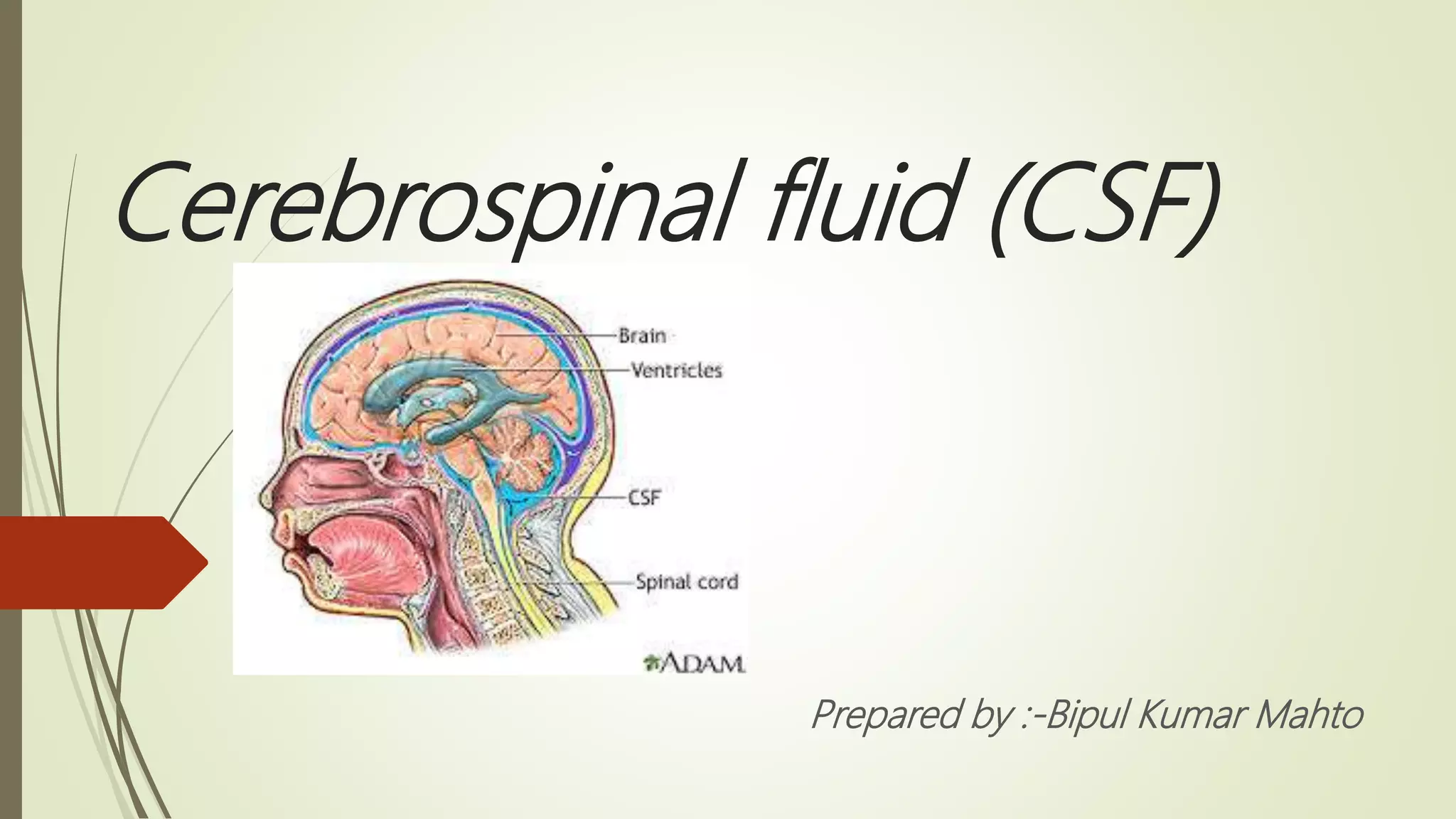
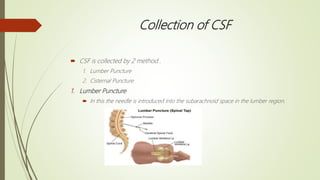
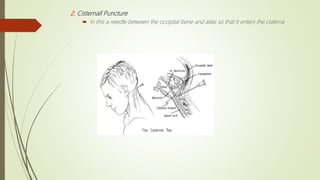
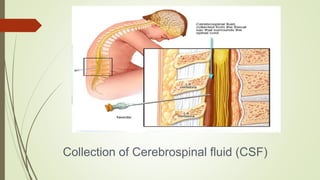
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is formed by selective dialysis of plasma by the choroid plexus in the ventricles of the brain. It circulates in the subarachnoid space around the brain and spinal cord, acting as a cushion and transporting substances. CSF is composed primarily of water, and contains proteins, glucose, and other components. It is collected through lumbar puncture between vertebrae in the lower back or through cisternal puncture in the neck, and analyzed physically, chemically, and microscopically to examine properties, cell counts, and detect any abnormalities.