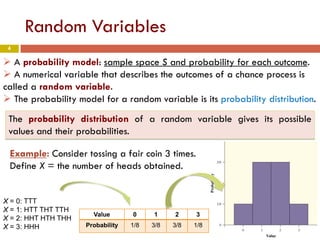
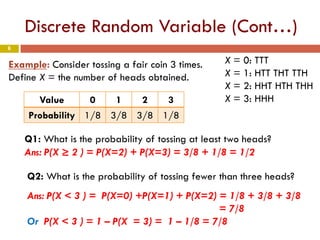
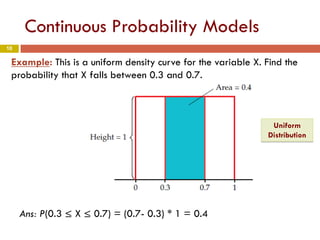
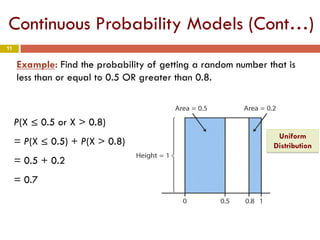
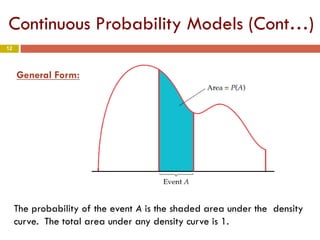
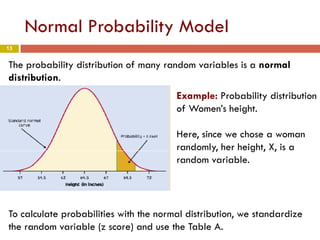
Chapter 4 of the document discusses probability, detailing the concepts of randomness, probability models, and random variables, including discrete and continuous types. It explains how probability distributions describe the possible values of random variables and provides examples of calculating probabilities for both discrete and continuous cases. The chapter also covers the normal probability model and standardization of data using z-scores.







![15
Normal Probability
Model (Cont…)
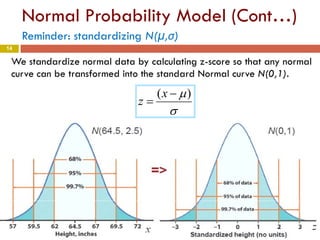
Women’s heights are normally
distributed with µ = 64.5 and σ = 2.5
in.
The z-scores for 68,
And for x = 70",
4.1
5.2
)5.6468(
=
−
=z
z =
(70−64.5)
2.5
= 2.2
The area under the curve for the interval
[68”,70”] is 0.9861-0.9192=0.0669.
Thus the probability that a randomly
chosen woman falls into this range is
6.69%. i.e.
P(68 ≤ X ≤ 70)= 6.69%.
What is the probability, if we pick one woman at random, that her height
will be between 68 and 70 inches i.e. P(68 ≤ X ≤ 70)? Here because the
woman is selected at random, X is a random variable.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter4-part2-140413141604-phpapp01/85/Chapter-4-part2-Random-Variables-15-320.jpg)