1. The document defines discrete random variables as random variables that can take on a finite or countable number of values. It provides an example of a discrete random variable being the number of heads from 4 coin tosses.
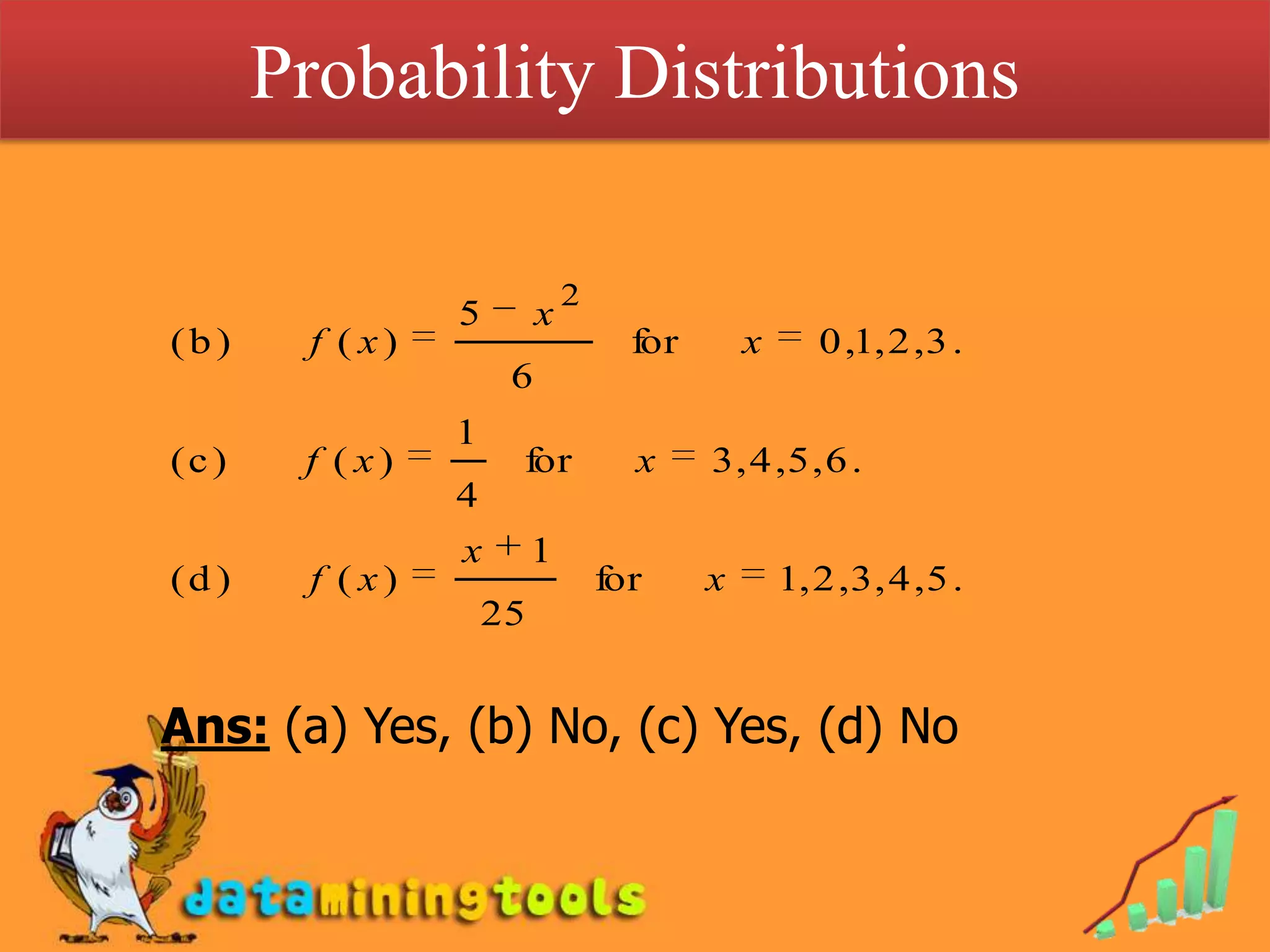
2. It introduces the probability mass function (pmf) as a function that gives the probability of a discrete random variable taking on a particular value. The pmf must be greater than or equal to 0 and sum to 1.
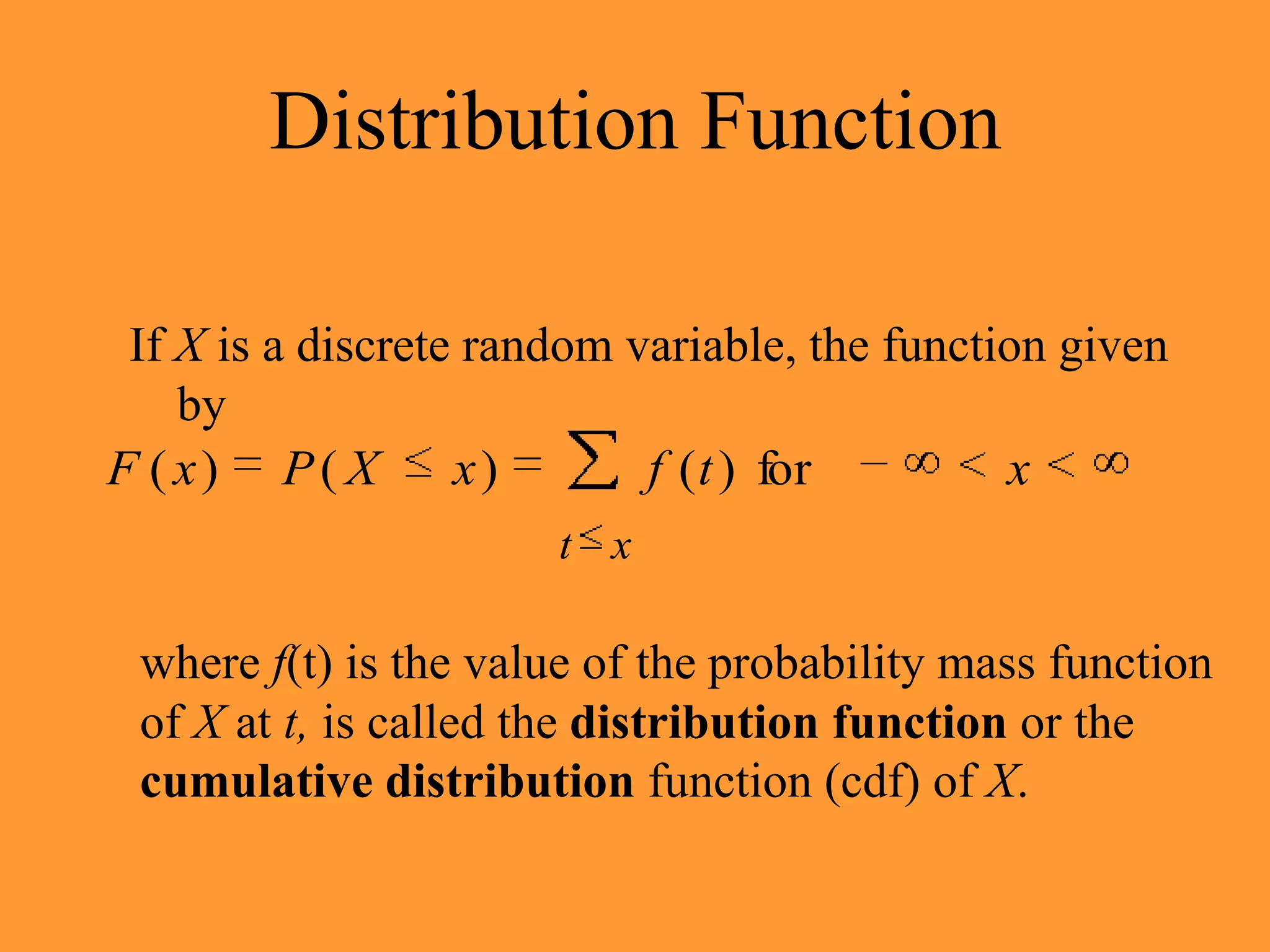
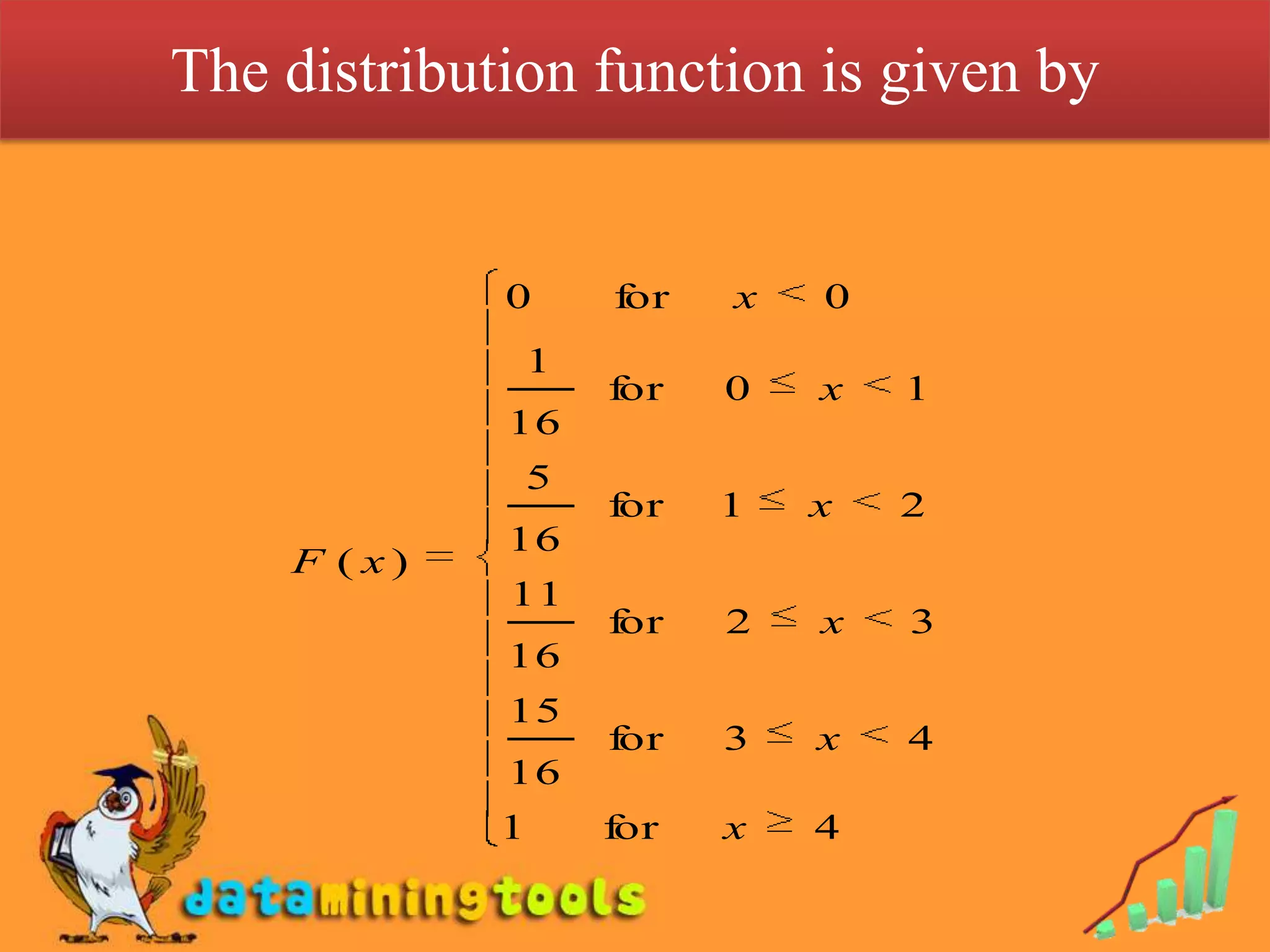
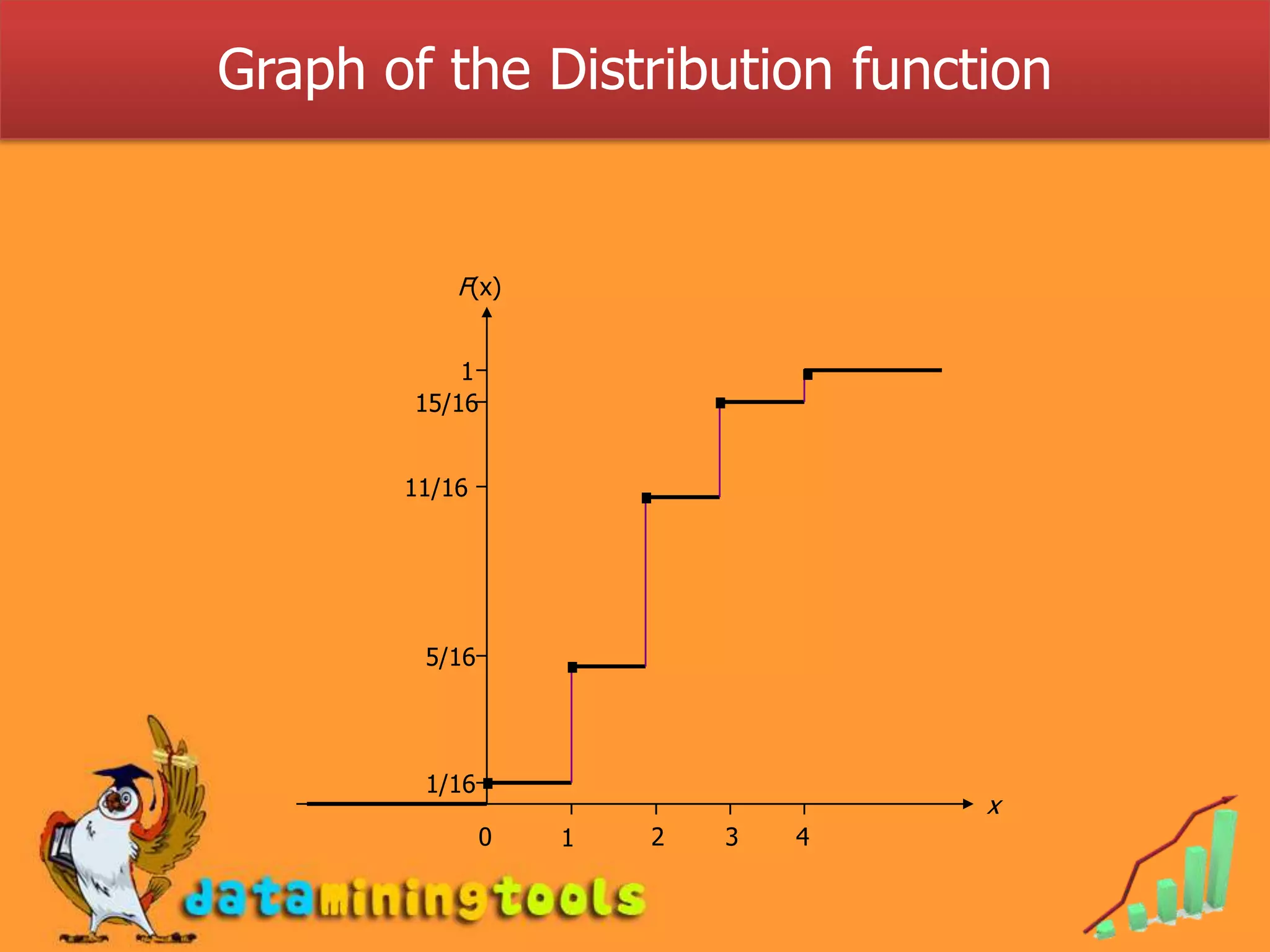
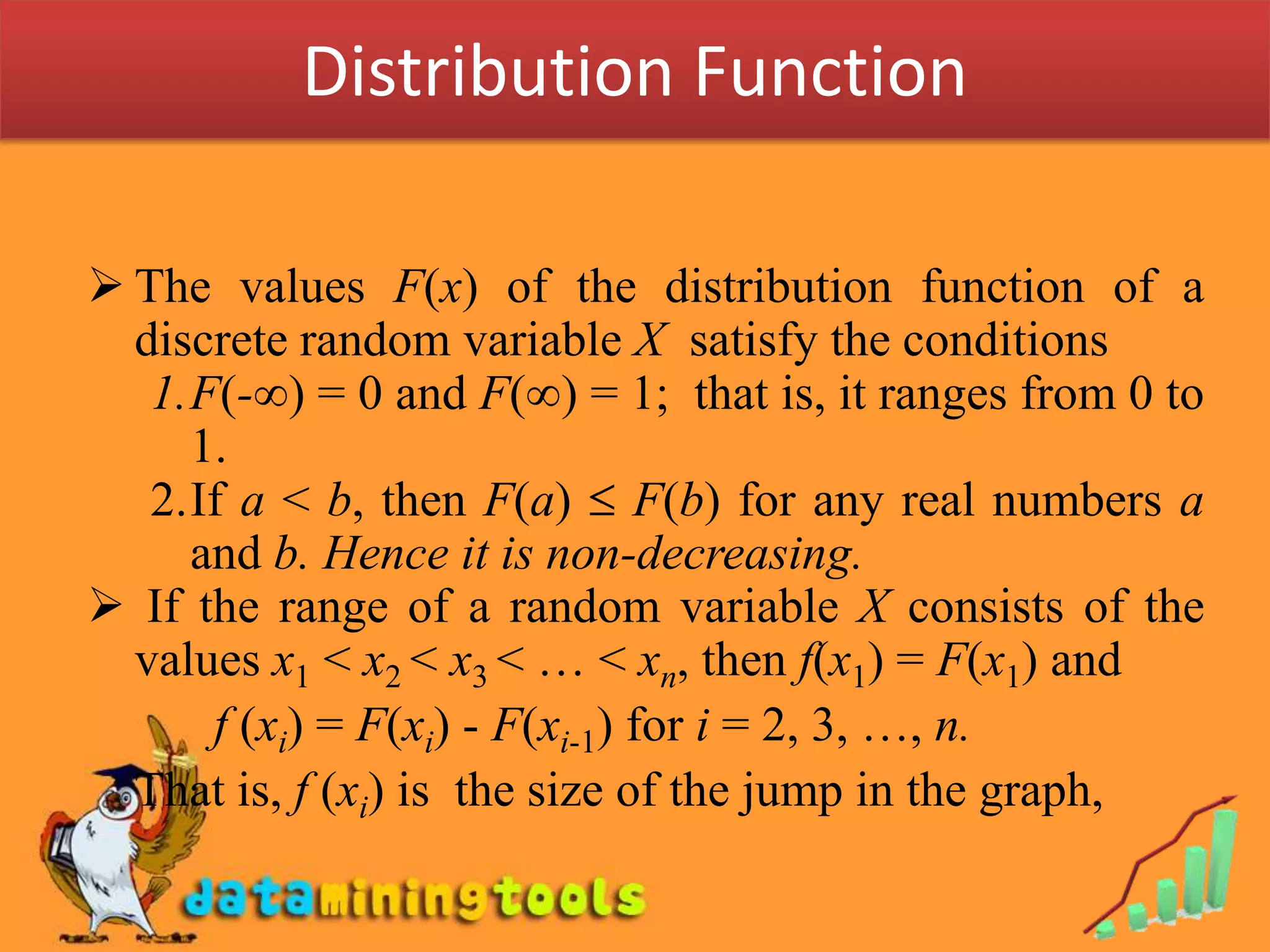
3. The cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a discrete random variable is defined as the sum of the probabilities of the random variable being less than or equal to a particular value. The CDF ranges from 0 to 1 and increases monotonically.




![Random Variables Example: A point P is chosen at random in a circle C with radius r. Let X be the distance of the point from the center of the circle. Then X is a (continuous) random variables with RX = [0, r]PCrXO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-4discreterandomvariablesandprobabilitydistributions-100217061705-phpapp01/75/Discrete-Random-Variables-And-Probability-Distributions-5-2048.jpg)
![Probability DistributionsIf X is discrete random variable, the function given by f(x) = P[X = x] for each x within the range of X is called the probability mass function (pmf) of X.To express the probability mass function, we give a table that exhibits the correspondence between the values of random variable and the associated probabilities](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-4discreterandomvariablesandprobabilitydistributions-100217061705-phpapp01/75/Discrete-Random-Variables-And-Probability-Distributions-6-2048.jpg)