This document provides an overview of one-dimensional random variables including definitions, types (discrete vs continuous), and probability distributions. It defines a random variable as a function that assigns a numerical value to each outcome of a random experiment. Random variables can be either discrete, taking on countable values, or continuous, assuming any value in an interval. The probability distribution of a discrete random variable is defined by a probability mass function, while a continuous random variable has a probability density function. Examples are given of both types of random variables and their distributions.

![Page 2 of 11
Example 1: Consider the different possible orderings of boy (B) and girl (G) in four sequential
births. There are 2*2*2*2= 16 possibilities, so the sample space is:
BBBB GGBB BGBB GBBB
BBBG BGBG GBBG GGBG
BBGB BGGB GBGB GGGB
BBGG BGGG GBGG GGGG
If girl and boy are each equally likely [P(G) = P(B) = 1/2], and the gender of each child is
independent of that of the previous child, then the probability of each of these 16 possibilities is:
(1/2)(1/2)(1/2)(1/2) = 1/16.
Now count the number of girls in each set of four sequential births:
BBBB (0) GGBB (2) BGBB (1) GBBB (1)
BBBG (1) BGBG (2) GBBG (2) GGBG (3)
BBGB (1) BGGB (2) GBGB (2) GGGB (3)
BBGG (2) BGGG (3) GBGG (3) GGGG (4)
Notice that:
each possible outcome is assigned a single numeric value,
all outcomes are assigned numeric values, and
the value assigned varies across the outcomes.
The count of the number of girls is a random variable:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch5-211225160556/75/Ch5-2-2048.jpg)


![Page 5 of 11
Solution: The sample space of the experiment contains the following:
S = {HH, HT, TH, TT}
Let the random variable X denotes the ‘number of heads’. We then use the probability function
P(X) to assign probability to each outcome consequently; the probability distribution is given
below:
0 1 2
( ) 1/4 1/2 1/4
Notes:
a) Suppose that the discrete random variable X may assume only a finite number of values,
say , , … , . If each outcome is equally probable, then we obviously have ( ) =
( ) = ⋯ = ( ) = .
b) If X assumes a countably infinite number of values, then it is impossible to have all
outcomes equally probable. For we cannot possibly satisfy the condition ∑ P(x ) = 1
if we must have ( ) = c for all .
c) In every finite interval, there will be at most afinite number of possible values of X. if
some such interval contains none of these possible values, we assign a probability zero to
it. That is, if = { , , … , } and if no ∈ [a, b], then ( ≤ ≤ ) = 0.
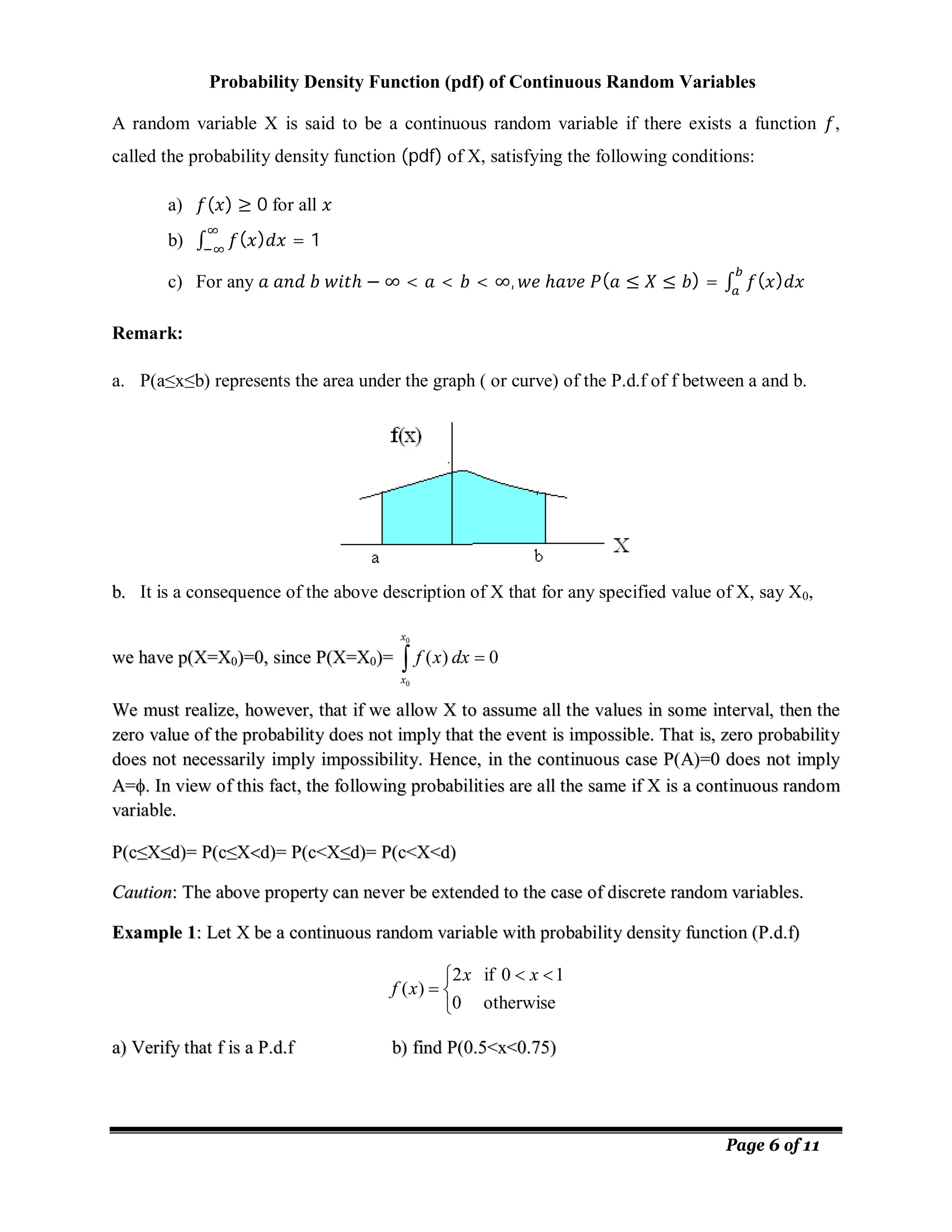
3.3. Continuous Random Variable
Definition: A random variable X is said to be a continuous random variable if it assumes all
values in some interval (c,d), where c and d are real numbers.
Examples:
• Height of students at a certain college.
• Mark of a student.
• Life time of light bulbs.
• Length of time required to complete a given training.
Probability density function ( ) of continuous random variable](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch5-211225160556/75/Ch5-5-2048.jpg)

![Page 8 of 11
3.4 Cumulative distribution function and its properties
D
De
ef
fi
in
ni
it
ti
io
on
n (
(C
Cu
um
mu
ul
la
at
ti
iv
ve
e D
Di
is
st
tr
ri
ib
bu
ut
ti
io
on
n F
Fu
un
nc
ct
ti
io
on
n)
) L
Le
et
t X
X b
be
e a
a r
ra
an
nd
do
om
m v
va
ar
ri
ia
ab
bl
le
e (
(d
di
is
sc
cr
re
et
te
e o
or
r
c
co
on
nt
ti
in
nu
uo
ou
us
s)
).
. T
Th
he
e f
fu
un
nc
ct
ti
io
on
n F
F t
th
ha
at
t i
is
s d
de
ef
fi
in
ne
ed
d a
as
s
F
F(
(x
x)
) =
= P
P[
[X
X
x
x]
]
i
is
s c
ca
al
ll
le
ed
d t
th
he
e c
cu
um
mu
ul
la
at
ti
iv
ve
e d
di
is
st
tr
ri
ib
bu
ut
ti
io
on
n f
fu
un
nc
ct
ti
io
on
n (
(C
Cd
df
f)
) o
of
f t
th
he
e r
ra
an
nd
do
om
m v
va
ar
ri
ia
ab
bl
le
e X
X.
.
N
No
ot
ta
at
ti
io
on
n:
: C
Cu
um
mu
ul
la
at
ti
iv
ve
e d
di
is
st
tr
ri
ib
bu
ut
ti
io
on
n f
fu
un
nc
ct
ti
io
on
n i
is
s u
us
su
ua
al
ll
ly
y d
de
en
no
ot
te
ed
d b
by
y u
up
pp
pe
er
r c
ca
as
se
e a
al
lp
ph
ha
ab
be
et
ts
s.
.
T
Th
he
eo
or
re
em
ms
s
1
1.
. I
If
f X
X i
is
s a
a d
di
is
sc
cr
re
et
te
e r
ra
an
nd
do
om
m v
va
ar
ri
ia
ab
bl
le
e,
, t
th
he
en
n
x
x
p
x
F
j
j
j
x
all
for
)
(
)
(
2
2.
. I
If
f X
X i
is
s a
a c
co
on
nt
ti
in
nu
uo
ou
us
s r
ra
an
nd
do
om
m v
va
ar
ri
ia
ab
bl
le
e,
, t
th
he
en
n
x
ds
s
f
x
F )
(
)
(
E
Ex
xa
am
mp
pl
le
e 1
1:
: L
Le
et
t S
S=
={
{H
H,
,T
T}
} a
an
nd
d X
X:
: t
th
he
e n
nu
um
mb
be
er
r o
of
f h
he
ea
ad
ds
s.
.
C
Cl
le
ea
ar
rl
ly
y,
, X
X i
is
s a
a d
di
is
sc
cr
re
et
te
e r
ra
an
nd
do
om
m v
va
ar
ri
ia
ab
bl
le
e.
. S
Si
in
nc
ce
e P
P(
(x
x=
=0
0)
)=
=1
1/
/2
2=
=P
P(
(x
x=
=1
1)
),
, w
we
e h
ha
av
ve
e
1
x
if
1
1
x
0
if
2
/
1
0
X
if
0
)
(x
F
E
Ex
xa
am
mp
pl
le
e 2
2:
: S
Su
up
pp
po
os
se
e t
th
ha
at
t a
a r
ra
an
nd
do
om
m v
va
ar
ri
ia
ab
bl
le
e X
X a
as
ss
su
um
me
es
s t
th
he
e s
si
ix
x v
va
al
lu
ue
es
s 1
1,
, 2
2,
, 3
3,
, 4
4,
, 5
5,
, 6
6 w
wi
it
th
h
p
pr
ro
ob
ba
ab
bi
il
li
it
ty
y 1
1/
/6
6.
. T
Th
he
en
n,
,
6
x
if
1
6
x
5
if
5/6
5
x
4
if
4/6
4
x
3
if
3/6
3
2
if
2/6
2
x
1
if
6
/
1
1
X
if
0
)
(
x
x
F](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch5-211225160556/75/Ch5-8-2048.jpg)


