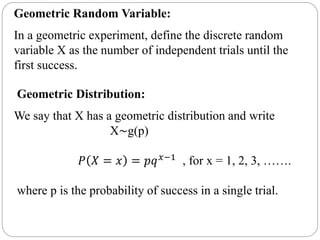
1. A geometric experiment involves independent trials with two possible outcomes (success/failure), where the probability of success (p) is constant across trials.
2. The geometric random variable (X) represents the number of trials until the first success. It has a geometric distribution where P(X=x) = p(1-p)^(x-1).
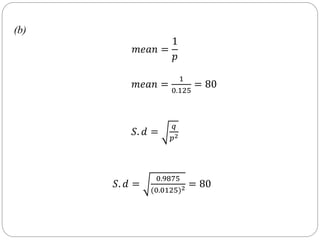
3. Examples are provided to illustrate calculating the probability of success on a given trial (x), as well as the mean and standard deviation, for geometric distributions with different probabilities of success (p).