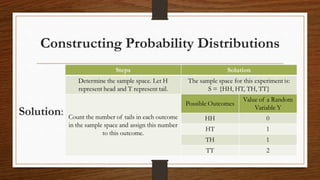
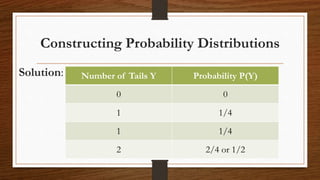
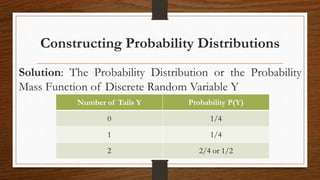
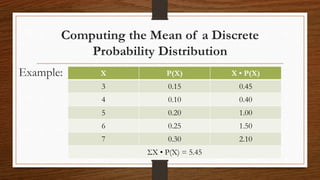
This document introduces key concepts related to random variables and probability distributions:
- A random variable is a function that assigns a numerical value to each possible outcome of an experiment. Random variables can be discrete or continuous.
- A probability distribution specifies the possible values of a random variable and their probabilities. For discrete random variables, this is called a probability mass function.
- Key properties of a probability distribution are that each probability is between 0 and 1, and the sum of all probabilities equals 1.
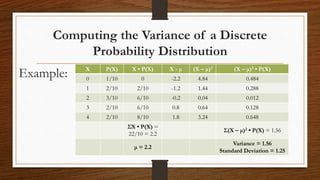
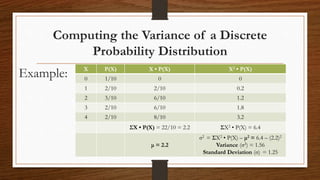
- The mean, variance, and standard deviation can be calculated from a probability distribution. The mean is the expected value, while variance and standard deviation measure dispersion around the mean.