The document discusses key concepts related to nuclear radiation including:
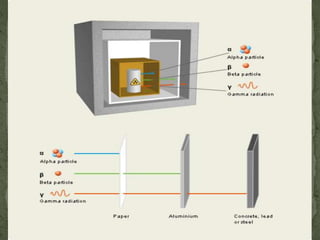
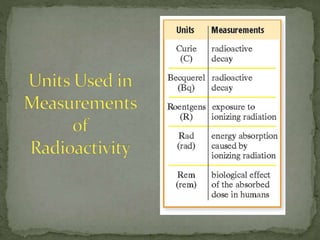
1) Defining the units roentgen and rem used to measure radiation exposure and dose, distinguishing that rem factors in human tissue effects.
2) Describing three common radiation detection devices - film badges, Geiger-Müller counters, and scintillation counters.
3) Outlining applications of radioactive nuclides including radioactive dating, medical uses like cancer treatment, tracing movement in the body, and extending food shelf life.