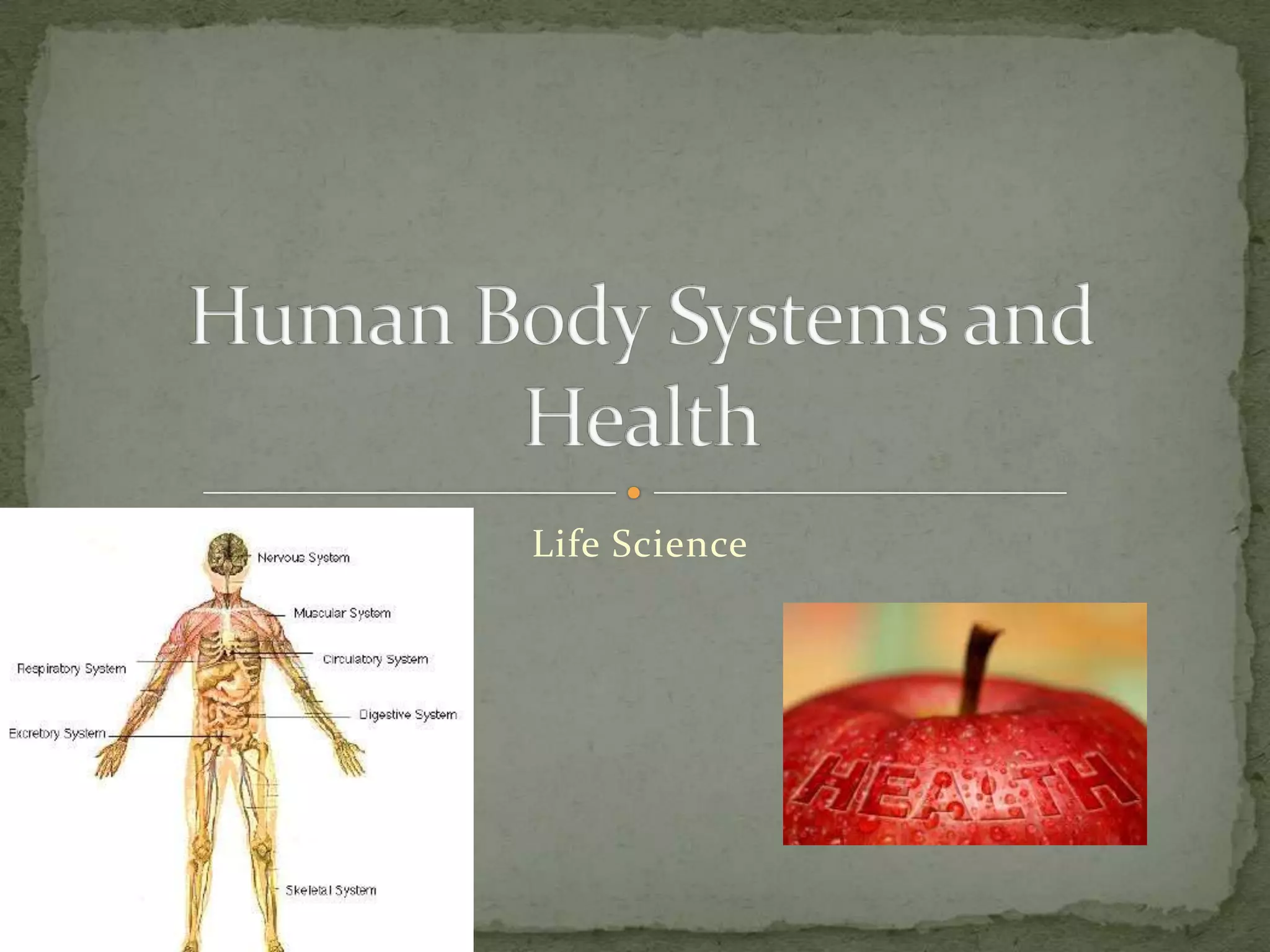
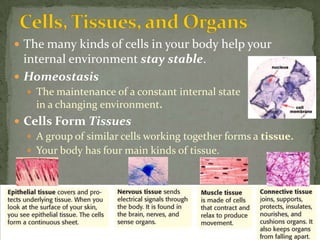
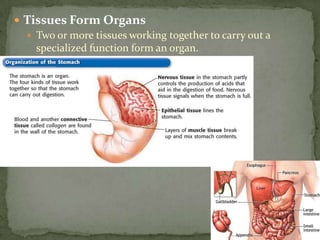
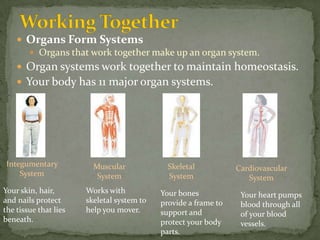
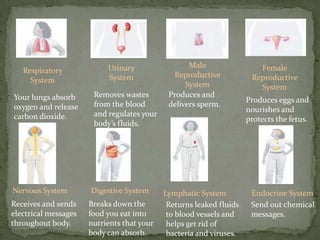
The document discusses the organization and structure of the human body. It explains that cells form tissues, tissues form organs, and organs work together in organ systems to maintain homeostasis. It lists the 11 major organ systems - integumentary, skeletal, muscular, cardiovascular, respiratory, nervous, digestive, urinary, lymphatic, reproductive, and endocrine - and briefly describes the basic function of each system. Working together, the organ systems help regulate body functions and keep the internal environment stable.